- Oium
-
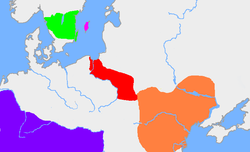
The orange area is the Chernyakhov culture, and the red area is the extent of the Wielbark Culture in the 3rd century. The dark pink area is Gotland and the green area is the traditional extent of Götaland. The dark blue area is the Roman Empire

Oium or Aujum was a name for an area in Scythia, where the Goths under their king Filimer settled after leaving Gothiscandza, according to the Getica by Jordanes, written around 551.[1][2][3][4] Jordanes does not give the etymology, but many scholars interpret this word as a dative plural to the widespread Germanic words *aujō- or *auwō- and means "well-watered meadow" or "island".[2][3]
According to some historians, Jordanes' account of the Goths' history in Oium was constructed from his reading of earlier classical accounts and from oral tradition.[5][6] According to other historians, Jordanes' narrative has little relation to Cassiodorus,'[7] no relation to oral traditions,[8] and little relation to actual history.[9]
Archaeologically, the Chernyakhov culture of parts of Ukraine, Moldova, and Romania corresponds with Gothic Scythia.[10]
Contents
Jordanes
Settlement
Jordanes states that king Filimer led the Goths in a search for suitable lands and when they arrived in Oium, they were delighted with the richness of the land. They crossed a bridge to get there, but when half the army[11] had made it across, the bridge fell into ruin, and so no one else could pass into the area anymore. According to Jordanes, the Goths claimed the land for themselves and defeated the previous inhabitants, the Spali.[12]
The Goths left Oium in a second migration to Moesia, Dacia and Thrace, but eventually returned, settling north of the Black Sea. Upon their return, they were divided under two ruling dynasties. The Visigoths were ruled by the Balþi and the Ostrogoths by the Amali. This account fits the patterns of the Wielbark culture and the Chernyakhov culture, which show a Germanic migration from the Vistula Basin to Ukraine.[13]
Merger with Scythian, Dacian and Thracian history from classic sources
Jordanes wrote that “Getae (Dacians) are the same with Goths, on the testimony of Orosius Paulus” [14]
Jordanes wrote that the Goths were descendents of Scythians and Thracians and thus had the same history. According to Jordanes, their royal line had originated near the sea of Azov, then moved northward toward Scandzia where they established a separate priest-king line on the island of Gotland.[citation needed]
According to him, this royal line of Goths fought Vesosis, the king of Egypt under their king Tanausis. After a battle at the river of Phasis, in Georgia, they pursued the Egyptians all the way back to Egypt.[15]
After Tanausis death, the Goths were said to have embarked on another expedition, and a neighbouring tribe tried to kidnap the Gothic women. However, the women defended themselves and defeated the attackers under the leaders Lampeto and Marpesia. The two leaders cast lots, and Marpesia pursued the enemy into Asia where she conquered many tribes and apparently formed the Amazons.[16]
The story continues with the Gothic king Antyrus being approached by Darius, the king of Persia, who wanted to marry his daughter. When Antyrus refused the marriage, he was attacked by Darius, and after Darius by his son Xerxes. None of the attacks are described as being successful.[17]
At another point in the narrative, Philip II allied with the Goths by marrying Medopa who was the daughter of king Gudila. However, Philip needed gold and wanted to pillage the town of Odessos, a town belonging to the Goths. The Goths sent out their Godis who were dressed in white and played harps, chanting to their gods to help them. This stunned the Macedonians so much that they returned.[18]
According to Jordanes, a king named Sitalces wanted revenge much later, and gathered 150 000 men to attack the Athenians. He fought Perdiccas II, whom Alexander I had left as a ruler, and the Goths laid Greece waste.[19]
When Burebista was king, he received a priestly reformer named Decaeneus, and this Decaeuneus advised the Goths to pillage Germania. He also gave the Goths laws, named bi-lageineis, taught them logic, philosophy and astrology. Then he selected a priestly elite who was taught theology and named them the Pilleati. The remainder of the Goths were called the Capillati.[20]
Julius Caesar tried to subdue the Goths without success, and the Goths also remained free during the reign of Tiberius.[20]
When Decaeneus was dead, Comosicus took his place, and after Comosicus, Scoryllus ruled the Goths in Dacia.[20]
A long time passed and the Romans were ruled by Emperor Domitian (A.D. 81-96). As the Goths (historically, the Dacians) feared his avarice, they broke the truce with the Romans and pillaged the banks of the Danube and killed the soldiers and the generals. At this time Diurpaneus (king Duras-Diurpaneus of Dacia 69–86 or Decebalus who ruled 87-106) was king of the Goths and Oppius Sabinus was the governor of Moesia (having succeeded Fontejus Agrippa (69–70). In 85, the Goths (Dacians) beheaded Oppius Sabinus and plundered many Roman cities and fortifications. Domitian arrived with the legions to Illyria and sent Fuscus with a selected force. Fuscus used boats to build a pontoon bridge and crossed the Danube upstream from the Goths. The Gothic army defeated the Romans, killed Fuscus and pillaged the Roman camp (86 AD).
The Goths' history
After this use of Dacian, Thracian and Scythian history, Jordanes returns to Gothic tradition by reciting the line of descent of the Gothic royal family from Gapt (Gaut or Odin).
This digression is followed by a statement that the Goths entered Moesia and Thrace in the late 2nd century where they stayed for some time. Based on Quintus Aurelius Symmachus, he writes that Emperor Maximinus Thrax (235 AD - 238 AD) was the son of a Goth who arrived at this time and an Alan woman.
Norse mythology
In the Hervarar saga, there is an account of Gothic legendary history and of battles with the Huns, and it may have been composed by Geats in southern Sweden, who have a prominent place in the poetry.[21] The saga conveys names of historical places in Ukraine during the period c. 150-450,[22] and they comprise for instance a form of the name for the Carpathians which most scholars agree is "a relic of extremely ancient tradition".[23] The Goths' capital is called Árheimar and is located on the Danpar (Dniepr). The place name Árheimar has been connected to the name Oium by both Heinzel and Schütte.[24]
In this legend, the Scandinavian Heidrek usurps the Gothic throne in Reidgotaland. Heidrek appears to establish a first contact with the Huns by kidnapping the Hun Princess Sifka, raping her and sending her back to the Huns pregnant with Hlod. When Heidrek dies in the Carpathians, his son Angantyr succeeds him. However, his second son Hlod, who had grown up with the Huns, claims his inheritance and attacks with a Hunnish horde comprising 187 200 mounted warriors.
The Goths are aided by the old Geatish king Gizur, and the war ends in an epic battle on the plains of the Danube, when Angantyr slays his brother Hlod.
See also
Germanic peoples Languages Prehistory Roman Iron Age Migration Period Germanic Iron Age · Alamanni · Anglo-Saxons (Angles · Jutes · Saxons) · Burgundians · Dani · Franks · Frisii · Geats · Goths (Visigoths · Ostrogoths · Valagoths · Gothic Wars) · Gotlanders · Lombards · Suebi · Suiones · Vandals · Varangians · Christianization of the Germanic peoples · RomanizationSociety and culture Mead hall · Poetry · Migration Period art · Runes (Runic calendar) · Sippe · Law (Lawspeaker · Thing) · Calendar · King · Names · Numbers · Romano-Germanic cultureReligion Wodanaz · Veleda · Tuisto · Mannus · Paganism (Anglo-Saxon · Continental Germanic mythology · Frankish · Norse) · Christianity (Arianism · Gothic)Dress Warfare Burial practices List of Germanic peoples · Portal:Ancient Germanic culture References
- ^ Jordanes, Getica, chapter IV (25) (link to translation by Mierow, 1915)
- ^ a b LISTSERV 14.4
- ^ a b Green, Dennis Howard (1998). Language and History in the Early Germanic World. Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0521794234, p.167.
- ^ Merrills, Andrew H. (2005). History and Geography in Late Antiquity. Cambridge University, ISBN 0521846013, p.120: "The term may, of course, have been a simple invention of Jordanes or Cassiodorus, intended to lend a witty verisimilitude to a knowingly derivative origin myth."
- ^ Merrills, Andrew H. (2005). History and Geography in Late Antiquity. Cambridge University, ISBN 0521846013, p.120: "The influence of oral tradition in this passage [the passage introducing Oium] is palpable. Classical and scriptural parallels for the over-population motif, the Arcadian description of the Scythian Canaan and the broken bridge image do suggest that Gothic migration stories had not survived uncontaminated by contact with the Mediterranean world, but they remain recognizably the tropes of oral tradition", and p. 121: "Jerome and Orosius had identified the relatively unfamiliar Goths with the Scythian Getae of ancient historiography. [...] In the wake of this authority, the identification of Oium could be made with little comment".
- ^ Wolfram, Herwig (2006). "Gothic history as historical ethnography" and Origo et religio: ethnic traditions and literature in early medieval texts". In From Roman Provinces to Medieval Kingdoms. Ed. Thomas F. X. Noble, Routledge, ISBN 0415327415, pp. 43-90.
- ^ Amory, Patrick: People and Identity in Ostrogothic Italy 489-554, pp. 36 & 292.
Kulikowski, Michael: Rome's Gothic Wars, pp. 50-51. - ^ Amory, Patrick: People and Identity in Ostrogothic Italy 489-554, p. 295: "It is a mistake to think that any of the material in the Getica comes from oral tradition."
- ^ Kulikowski, Michael: Rome's Gothic Wars, p. 66.
- ^ On the identification of Oium with the Sintana de Mures/Chernyakhov culture-area:
Green, D.H.: Language and history in the early Germanic world, pp. 167-168.
On the extent of the Sintana de Mures/Chernyakhov culture and its identification with the Goths:
Heather, Peter and Matthews, John: Goths in the Fourth Century, pp. 50-52 & 88-92
Kulikowski, Michael: Rome's Gothic Wars, pp. 62-63.
Note that Kulikowski has criticized the use of the Getica as a source for the period; Kulikowski, Michael: Rome's Gothic Wars, p. 66. - ^ Translation per Merrills, p. 120: "he decided that the army of the Goths with their families should move from that region [...] and it is said that when half the army had been brought over, the bridge whereby they had crossed the river fell into utter ruin."
- ^ Jordanes, Mierow, ed., Getica IV (27), http://www.ucalgary.ca/~vandersp/Courses/texts/jordgeti.html#IV
- ^ Heather, Peter J. (1999). The Visigoths from the Migration Period to the Seventh Century. Boydell & Brewer, ISBN 0851157629, p. 16.
- ^ THE ORIGIN AND DEEDS OF THE GOTHS by JORDANES - translated by Charles C. Mierow
- ^ Jordanes, Getica, chapter VI (47) (link to translation by Mierow, 1915)
- ^ Jordanes, Getica, chapter VII (49) (link to translation by Mierow, 1915)
- ^ Jordanes, Getica, chapter X (link to translation by Mierow, 1915)
- ^ Jordanes, Getica, chapter X (65) (link to translation by Mierow, 1915)
- ^ Jordanes, Getica, chapter X (66) (link to translation by Mierow, 1915)
- ^ a b c Jordanes, Getica, chapter XI (67) (link to translation by Mierow, 1915)
- ^ Pritsak, Omeljan. (1981). The origin of Rus'. Cambridge, Mass.: Distributed by Harvard University Press for the Harvard Ukrainian Research Institute. ISBN 0-674-64465-4 p. 198
- ^ Pritsak, Omeljan. (1981). The origin of Rus'. Cambridge, Mass.: Distributed by Harvard University Press for the Harvard Ukrainian Research Institute. ISBN 0-674-64465-4 p. 214
- ^ Pritsak, Omeljan. (1981). The origin of Rus'. Cambridge, Mass.: Distributed by Harvard University Press for the Harvard Ukrainian Research Institute. ISBN 0-674-64465-4 p. 199
- ^ Pritsak, Omeljan. (1981). The origin of Rus'. Cambridge, Mass.: Distributed by Harvard University Press for the Harvard Ukrainian Research Institute. ISBN 0-674-64465-4 p. 209
External links
Categories:- Goths
- Gothic cities and towns
- Historical regions in Ukraine
- History of the Germanic peoples
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.