- NCOA7
-
Nuclear receptor coactivator 7 Identifiers Symbols NCOA7; ERAP140; ESNA1; FLJ45605; MGC88425; Nbla00052; Nbla10993; dJ187J11.3 External IDs OMIM: 609752 MGI: 2444847 HomoloGene: 65245 GeneCards: NCOA7 Gene Gene Ontology Molecular function • protein binding Cellular component • intracellular
• nucleusBiological process • regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent
• cell wall macromolecule catabolic processSources: Amigo / QuickGO RNA expression pattern 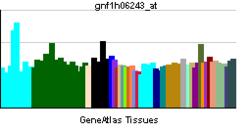
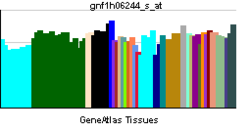
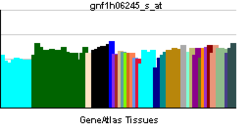
More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 135112 211329 Ensembl ENSG00000111912 ENSMUSG00000039697 UniProt Q8NI08 Q3TM55 RefSeq (mRNA) NM_001122842.2 NM_172495 RefSeq (protein) NP_001116314.1 NP_766083 Location (UCSC) Chr 6:
126.1 – 126.25 MbChr 10:
30.36 – 30.52 MbPubMed search [1] [2] Nuclear receptor coactivator 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NCOA7 gene.[1][2]
Contents
See also
References
- ^ Shao W, Halachmi S, Brown M (Apr 2002). "ERAP140, a Conserved Tissue-Specific Nuclear Receptor Coactivator". Mol Cell Biol 22 (10): 3358–72. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.10.3358-3372.2002. PMC 133794. PMID 11971969. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=133794.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: NCOA7 nuclear receptor coactivator 7". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=135112.
External links
Further reading
- Ohira M, Morohashi A, Nakamura Y et al. (2003). "Neuroblastoma oligo-capping cDNA project: toward the understanding of the genesis and biology of neuroblastoma". Cancer Lett. 197 (1–2): 63–8. doi:10.1016/S0304-3835(03)00085-5. PMID 12880961.
- Halachmi S, Marden E, Martin G et al. (1994). "Estrogen receptor-associated proteins: possible mediators of hormone-induced transcription". Science 264 (5164): 1455–8. doi:10.1126/science.8197458. PMID 8197458.
- Nguyen TA, Hoivik D, Lee JE, Safe S (1999). "Interactions of nuclear receptor coactivator/corepressor proteins with the aryl hydrocarbon receptor complex". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 367 (2): 250–7. doi:10.1006/abbi.1999.1282. PMID 10395741.
- Hartley JL, Temple GF, Brasch MA (2001). "DNA Cloning Using In Vitro Site-Specific Recombination". Genome Res. 10 (11): 1788–95. doi:10.1101/gr.143000. PMC 310948. PMID 11076863. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=310948.
- Wiemann S, Weil B, Wellenreuther R et al. (2001). "Toward a Catalog of Human Genes and Proteins: Sequencing and Analysis of 500 Novel Complete Protein Coding Human cDNAs". Genome Res. 11 (3): 422–35. doi:10.1101/gr.GR1547R. PMC 311072. PMID 11230166. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=311072.
- Simpson JC, Wellenreuther R, Poustka A et al. (2001). "Systematic subcellular localization of novel proteins identified by large-scale cDNA sequencing". EMBO Rep. 1 (3): 287–92. doi:10.1093/embo-reports/kvd058. PMC 1083732. PMID 11256614. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1083732.
- Rushing SR, Denison MS (2002). "The silencing mediator of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptors can interact with the aryl hydrocarbon (Ah) receptor but fails to repress Ah receptor-dependent gene expression". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 403 (2): 189–201. doi:10.1016/S0003-9861(02)00233-3. PMID 12139968.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139241.
- Mungall AJ, Palmer SA, Sims SK et al. (2003). "The DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 6". Nature 425 (6960): 805–11. doi:10.1038/nature02055. PMID 14574404.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=528928.
- Wiemann S, Arlt D, Huber W et al. (2004). "From ORFeome to Biology: A Functional Genomics Pipeline". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2136–44. doi:10.1101/gr.2576704. PMC 528930. PMID 15489336. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=528930.
- Mehrle A, Rosenfelder H, Schupp I et al. (2006). "The LIFEdb database in 2006". Nucleic Acids Res. 34 (Database issue): D415–8. doi:10.1093/nar/gkj139. PMC 1347501. PMID 16381901. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1347501.
- Durand M, Kolpak A, Farrell T et al. (2007). "The OXR domain defines a conserved family of eukaryotic oxidation resistance proteins". BMC Cell Biol. 8: 13. doi:10.1186/1471-2121-8-13. PMC 1847813. PMID 17391516. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1847813.
External links
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
Transcription coregulators Coactivators Corepressors ATP-dependent remodeling factors see also transcription factor/coregulator deficiencies
B bsyn: dna (repl, cycl, reco, repr) · tscr (fact, tcrg, nucl, rnat, rept, ptts) · tltn (risu, pttl, nexn) · dnab, rnab/runp · stru (domn, 1°, 2°, 3°, 4°)Categories:- Human proteins
- Gene expression
- Transcription coregulators
- Chromosome 6 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
