- DARPA Grand Challenge (2007)
-
The third driverless car competition of the DARPA Grand Challenge[1], was commonly known as the DARPA Urban Challenge. It took place on November 3, 2007 at the site of the now-closed George Air Force Base (currently used as Southern California Logistics Airport), in Victorville, California (Google map), in the West of the United States[2]. Discovery's Science channel followed a few of the teams and covered the Urban Challenge in its Robocars series [3].
Contents
Overview
The $2 million winner was Tartan Racing, a collaborative effort by Carnegie Mellon University and General Motors Corporation, with their vehicle "Boss", a heavily-modified Chevrolet Tahoe. The second place finisher earning the $1 million prize was the Stanford Racing Team with their entry "Junior", a 2006 Volkswagen Passat. Coming in third place was team Victor Tango from Virginia Tech winning the $500,000 prize with their 2005 Ford Escape hybrid, "Odin"[2].
The course involved a 96 kilometres (60 mi) urban area course, to be completed in less than 6 hours. Rules included obeying all traffic regulations while negotiating with other traffic and obstacles and merging into traffic. While the 2004 and 2005 events were more physically challenging for the vehicles, the robots operated in isolation and did not encounter other vehicles on the course. The Urban Challenge required designers to build vehicles able to obey all traffic laws while they detect and avoid other robots on the course. This is a particular challenge for vehicle software, as vehicles must make "intelligent" decisions in real time based on the actions of other vehicles. Other than previous autonomous vehicle efforts that focused on structured situations such as highway driving with little interaction between the vehicles, this competition operated in a more cluttered urban environment and required the cars to perform sophisticated interactions with each other, such as maintaining precedence at a 4-way stop intersection. [4]
The advantages of this technology are potentially enormous. Well-coordinated fully automatic driving will be much more efficient, with reduction in traffic jams and road accidents, which cost trillions per year in the US alone. Efficiency will also reduce energy consumption and thus pollution and climate change.
Unlike the past two challenges, DARPA announced that some teams were to receive development funding, based on proposals submitted to DARPA. Eleven teams could receive up to US$1 million a piece under this special program track (Track A) [5]. These 11 teams largely represent major universities and large corporate interests such as CMU teaming with GM, Stanford teaming with Volkswagen, Virginia Tech teaming with TORC Technologies, Oshkosh Truck, Honeywell, Raytheon, Caltech, Autonomous Solutions, Cornell, and MIT. One of the few independent entries in Track A was the Golem Group.
Basic Rules for 2007
- Vehicle must be stock or have a documented safety record.
- Vehicle must obey the California state driving laws.
- Vehicle must be entirely autonomous, using only the information it detects with its sensors and public signals such as GPS.
- DARPA will provide the route network 24 hours before the race starts.
- Vehicles will complete the route by driving between specified checkpoints.
- DARPA will provide a file detailing the order the checkpoints must be driven to 5 minutes before the race start.
- Vehicles may “stop and stare” for at most 10 seconds.
- Vehicles must operate in rain and fog, with GPS blocked.
- Vehicles must avoid collision with vehicles and other objects such as carts, bicycles, traffic barrels, and objects in the environment such as utility poles.
- Vehicles must be able to operate in parking areas and perform U-turns as required by the situation.
Initial site visits
In June/July 2007, 53 teams (see list below) were notified that they qualified for DARPA Site visits. Those teams that were successful in these evaluations moved on to a national qualifying event that took place in October 2007.
Semi-finalists
On August 9, 2007, after completing the site visits, DARPA announced[6] the 36 semi-finalists selected to participate in the Urban Challenge National Qualification Event (NQE) that took place October 26–31, 2007. Originally, the top 20 teams from that event were scheduled to proceed to the final competition on November 3, however only 11 teams were selected. The 36 semifinalists were:
National Qualification Event
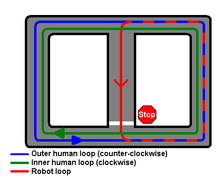
The National Qualification Event for the 2007 challenge occurred between October 26 and 31, 2007. 35 teams were selected to participate in this semifinal round. The qualifying rounds included 3 areas: A, B, and C. Area A was a test of the robots' ability to merge. A 2-way loop of human traffic (provided by professional stunt drivers) surrounded a one-way road running from one side of the loop to the other. Robots had to go from the one-way road, make a left turn into traffic, follow the loop 180 degrees, and make another left turn onto the one-way road again. Robots were free to make as many laps as they could in the allotted time. Area B was mostly closed to spectators except for the start and finish, and involved the robots navigating a long suburban route demonstrating parking, navigation, and avoiding stalled cars along the way. Area B was part of the final event course. In Area C, robots performed several loops into two 4-way intersections in order to test their implementation of 4-way stops. Each loop, human drivers would provide a progressively more difficult intersection situation. At some points in Area C, roads would be blocked to test robots' ability to re-plan routes.
On November 1, 2007 it was announced that there would be only 11 teams competing in the Urban Challenge[2][7]. The 11 teams selected to compete were the following:
- AnnieWay
- Ben Franklin
- Team CarOLO
- Cornell
- Intelligent Vehicle Systems
- MIT
- Stanford Racing
- Tartan Racing
- Team Oshkosh
- Team UCF
- Victor Tango
DARPA's reasoning for only qualifying 11 teams was primarily safety-related. DARPA felt that since there would be real humans near the robots in the traffic cars as well as DARPA officials scoring robot performance, safety was paramount.[8].
Teams were given sparsely defined waypoints charting the course for the robocars to follow. However, other teams generated a detailed map of the qualifications tracks. A debriefing published by one of the teams illustrates graphically the course it was given by DARPA contrasted against the course used by the winning team [9].
Finals
Starting Area: 34°35′05″N 117°22′08″W / 34.5846°N 117.369°W[10]
The final event for the Darpa Urban Challenge took place on November 3, 2007, and included all 11 teams which made it past the semi-final National Qualification Event. The event was broadcast on a live webcast via the DARPA Urban Challenge website, narrated by Marty Reid (racing sportscaster) and Grant Imahara (of MythBusters acclaim), with "sideline reporting" by Jamie Hyneman (also of Mythbusters).[2]
The final event consisted of three missions, approximately 55 miles (89 km) in total, given to each team. A team's score for each mission was computed by taking the total time taken to complete the mission, and adding and subtracting penalties and bonuses. Penalties were assessed for excessive delay, violating traffic rules, exhibiting dangerous behavior, etc. Vehicles were frequently manually paused for safety reasons; if a vehicle was not the root cause of such a pause then the duration of the pause was not counted in its final score. In order to officially complete the race, a vehicle's adjusted time for the three missions must be under six hours[11].
Six autonomous vehicle teams finished the event; Carnegie Mellon, Stanford, Virginia Tech, Ben Franklin Racing, MIT, and Cornell. On November 4, CMU's Boss was named the winner, followed by Stanford's Junior, then Virginia Tech's Odin, and MIT's Talos[12]. Final adjusted scores for the six vehicles were not announced.
Race Participants & Results
Team Name ID# Vehicle Type Team Location Time Taken
(h:m:s)Result Tartan Racing 19 Boss 2007 Chevy Tahoe Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 4:10:20 1st Place; averaged approximately 14 miles per hour throughout the course [13][14] Stanford Racing 03 Junior 2006 Volkswagen Passat Wagon Stanford University, Palo Alto, California 4:29:28 2nd Place; averaged about 13.7 miles per hour (22.0 km/h) throughout the course[13][15] VictorTango 32[16] Odin 2005 Ford Hybrid Escape Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, Virginia 4:36:38 3rd Place; averaged slightly less than 13 miles per hour (21 km/h) throughout the course[13] MIT 79 Talos Land Rover LR3 MIT, Cambridge, Massachusetts Approx. 6 hours 4th Place.[17] The Ben Franklin Racing Team 74 Little Ben 2006 Toyota Prius University of Pennsylvania, Lehigh University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania Over 6 hour limit One of 6 teams to finish course Cornell 26 Skynet 2007 Chevy Tahoe Cornell University, Ithaca, New York Over 6 hour limit One of 6 teams to finish course Team CarOLO 62 Caroline 2006 Volkswagen Passat Braunschweig, Germany DNF Eliminated fifth during mission one of the finals. Pulled after two near collisions head on in traffic circles. Team UCF 13 Knight Rider 1996 Subaru Outback Legacy 4WD University of Central Florida, Orlando, Florida DNF Eliminated fourth during mission one. Vehicle vs building incident[18] Team Oshkosh 21 TerraMax Marine Medium Tactical Vehicle Replacement (MTVR) Oshkosh, Wisconsin DNF Eliminated third during mission one. Vehicle vs building incident[18] Honeywell/Intelligent Vehicle Systems 15 XAV-250 Ford F-250 Troy, MI – Dearborn, MI – Minneapolis, MN DNF Eliminated first or second during mission one. Froze at intersection[18] AnnieWay 54 AnnieWAY Passat Variant 2.0 FSI Karlsruhe, Germany DNF Eliminated first or second during mission one. Froze at entrance to traffic circle[18] References
- ^ "The contest, called the Grand Challenge and sponsored by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, or Darpa, featured both robot collisions and robot traffic jams." John Markoff (2007-11-05). "Crashes and Traffic Jams in Military Test of Robotic Vehicles". New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2007/11/05/technology/05robot.htm.
- ^ a b c d Welcome
- ^ [1]
- ^ http://www.darpa.mil/grandchallenge/docs/urb_challenge_announce.pdf
- ^ [2]
- ^ http://www.darpa.mil/grandchallenge/docs/PR_UC_Semifinalist_Announcement.pdf
- ^ TG Daily - DARPA only allows 11 teams into the Urban Challenge
- ^ TG Daily - Video: “We really don’t know what they’re going to do” – DARPA Urban Challenge head
- ^ Team Jefferson Debriefing [3].
- ^ "DARPA Grand Challenge Site Resources page". http://www.darpa.mil/grandchallenge/resources.asp. Retrieved October 2007.
- ^ http://www.darpa.mil/grandchallenge/docs/Urban_Challenge_Rules_102707.pdf
- ^ MIT finishes fourth in DARPA challenge for robotic vehicles - MIT News Office
- ^ a b c Carnegie Takes First in DARPA's Urban Challenge | Danger Room from Wired.com
- ^ First-Place Finish - Carnegie Mellon University
- ^ Stanford Racing Team
- ^ The Virginia Tech robot carried number 32 to commemorate the thirty-two people killed in the campus massacre on April 16, 2007 [4].
- ^ Contact
- ^ a b c d 3 Teams Out of the Running at Auto-Bot Race | Danger Room from Wired.com
External links
 Media related to DARPA Grand Challenge at Wikimedia CommonsCategories:
Media related to DARPA Grand Challenge at Wikimedia CommonsCategories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.