- Diazoxide
-
Diazoxide 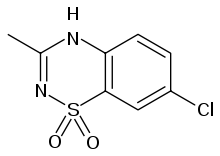
Systematic (IUPAC) name 7-chloro-3-methyl-4H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine 1,1-dioxide Clinical data Trade names Proglycem AHFS/Drugs.com monograph Pregnancy cat. C(AU) C(US) Legal status POM (UK) ℞-only (US) Routes Oral, intravenous Pharmacokinetic data Protein binding 90% Metabolism Hepatic oxidation and sulfate conjugation Half-life 21-45 hours Excretion Renal Identifiers CAS number 364-98-7 
ATC code C02DA01 V03AH01 PubChem CID 3019 IUPHAR ligand 2409 DrugBank APRD00914 ChemSpider 2911 
UNII O5CB12L4FN 
KEGG D00294 
ChEBI CHEBI:4495 
ChEMBL CHEMBL181 
Chemical data Formula C8H7ClN2O2S Mol. mass 230.672 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Diazoxide (INN; brand name Proglycem[1]) is a potassium channel activator, which causes local relaxation in smooth muscle by increasing membrane permeability to potassium ions. This switches off voltage-gated calcium ion channels which inhibits the generation of an action potential.
Uses
Diazoxide is used as a vasodilator in the treatment of acute hypertension or malignant hypertension.[2]
Diazoxide also inhibits the secretion of insulin from the pancreas, thus it is used to counter hypoglycemia in disease states such as insulinoma (a tumor producing insulin)[3] or congenital hyperinsulinism.
Chemistry
Diazoxide can be prepared from dichloronitrobenzene:[4]
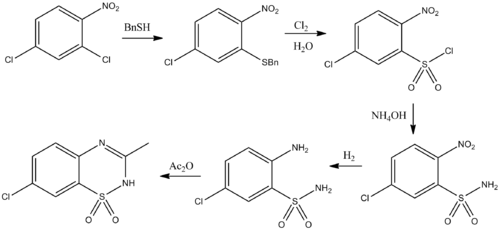
References
- ^ Diazoxide, drugs.com
- ^ van Hamersvelt HW, Kloke HJ, de Jong DJ, Koene RA, Huysmans FT (August 1996). "Oedema formation with the vasodilators nifedipine and diazoxide: direct local effect or sodium retention?". J. Hypertens. 14 (8): 1041–5. PMID 8884561.
- ^ Huang Q, Bu S, Yu Y, et al. (January 2007). "Diazoxide prevents diabetes through inhibiting pancreatic beta-cells from apoptosis via Bcl-2/Bax rate and p38-beta mitogen-activated protein kinase". Endocrinology 148 (1): 81–91. doi:10.1210/en.2006-0738. PMID 17053028. http://endo.endojournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=17053028.
- ^ Rubin, A. A.; Roth, F. E.; Winbury, M. M.; Topliss, J. G.; Sherlock, M. H.; Sperber, N.; Black, J. (1961). "New Class of Antihypertensive Agents". Science 133 (3470): 2067. doi:10.1126/science.133.3470.2067.
Nonsympatholytic vasodilatory antihypertensives (C02) Nitrovasodilator NO (arterioles and venules)N (arteriolar)(arteriolar) Potassium channel opener Minoxidil • Diazoxide(arteriolar) Calcium channel blocker see listOther therapeutic products (V03AG–V03AZ) Treatment of hypercalcemia Sodium cellulose phosphateTreatment of hypoglycaemia DiazoxideMedical gases Nerve depressants Categories:- Sulfonamides
- Vasodilators
- Potassium channel openers
- Benzothiadiazines
- Organochlorides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
