- Diastrophic dysplasia
-
Diastrophic dysplasia Classification and external resources OMIM 222600 DiseasesDB 30759 eMedicine orthoped/632 Diastrophic dysplasia (DTD) is an autosomal recessive[1] dysplasia which affects cartilage and bone development. ("Diastrophism" is a general word referring to a twisting.)[2]
Affected individuals have short stature with very short arms and legs and joint problems that restrict mobility.
Contents
Symptoms
This condition is also characterized by an unusual clubfoot) with twisting of the metatarsals, inward- and downward-turning foot, tarsus valgus, and inversion adducted appearances. Furthermore they classically present with scoliosis (progressive curvature of the spine, and unusually positioned thumbs (hitchhiker thumbs). About half of infants with diastrophic dysplasia are born with an opening in the roof of the mouth called a cleft palate. Swelling of the external ears is also common in newborns and can lead to thickened, deformed ears.
The signs and symptoms of diastrophic dysplasia are similar to those of another skeletal disorder called atelosteogenesis, type 2. Diastrophic dysplasia tends to be less severe, however.
Genetic prevalence
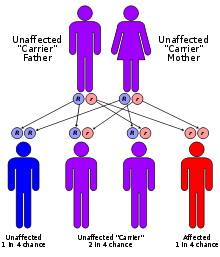 Diastrophic dysplasia has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance.
Diastrophic dysplasia has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance.
Diastrophic dysplasia affects about 1 in 100,000 births. Mutations in the SLC26A2 gene cause diastrophic dysplasia, and it is one of a spectrum of skeletal disorders caused by mutations in the SLC26A2 gene. The protein made by this gene is essential for the normal development of cartilage and for its conversion to bone. Cartilage is a tough, flexible tissue that makes up much of the skeleton during early development. Most cartilage is later converted to bone, but in adulthood this tissue continues to cover and protect the ends of bones and is present in the nose and external ears. Mutations in the SLC26A2 gene alter the structure of developing cartilage, preventing bones from forming properly and resulting in the skeletal problems characteristic of diastrophic dysplasia.
This condition is an autosomal recessive disorder, which means the defective gene is located on an autosome, and both parents must carry one copy of the defective gene in order to have a child born with the disorder. The parents of a child with an autosomal recessive disorder are usually not affected by the disorder.
See also
Matt Roloff, a businessman and motivational speaker, has diastrophic dysplasia dwarfism. He is a vocal proponent of research and understanding of the disorder, as well as the assimilation of fellow sufferers into everyday life
The Little People of America is an organization of people with all kinds of short-stature syndromes, family members and caregivers, dedicated to improving the quality of life of affected persons, and improving their integration into society.
See also
- Achondrogenesis type 1B
External links
This article incorporates some public domain text from The U.S. National Library of Medicine
References
- ^ Hästbacka J, Sistonen P, Kaitila I, Weiffenbach B, Kidd KK, De La Chapelle A (December 1991). "A linkage map spanning the locus for diastrophic dysplasia (DTD)". Genomics 11 (4): 968–973. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(91)90021-6. PMID 1783404.
- ^ "diastrophic - Definition from the Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary". http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/diastrophic. Retrieved 2009-03-12.
Osteochondrodysplasia (Q77–Q78, 756.4–756.5) Osteodysplasia/
osteodystrophyOther/ungroupedFLNB (Boomerang dysplasia) · Opsismodysplasia · Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia (McCune-Albright syndrome)Chondrodysplasia/
chondrodystrophy
(including dwarfism)enchondromatosis (Ollier disease, Maffucci syndrome)Achondrogenesis (type 1B) · Recessive multiple epiphyseal dysplasia · Atelosteogenesis, type II · Diastrophic dysplasiaOther dwarfismFibrochondrogenesis · Short rib-polydactyly syndrome (Majewski's polydactyly syndrome) · Léri-Weill dyschondrosteosisCategories:- Autosomal recessive disorders
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
