- Otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia
-
Otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia Classification and external resources OMIM 215150 DiseasesDB 32024 Otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia (OSMED) is an autosomal recessive disorder of bone growth that results in skeletal abnormalities, severe hearing loss, and distinctive facial features. The name of the condition indicates that it affects hearing (oto-) and the bones of the spine (spondylo-), and enlarges the ends of bones (megaepiphyses).
The features of OSMED are similar to those of another skeletal disorder, Weissenbacher-Zweymüller syndrome. Otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia is a subtype of collagenopathy, types II and XI.
Contents
Diagnosis
The distinctive characteristics of OSMED include severe bone and joint problems and very severe hearing loss. This disorder affects the epiphyses, the parts of the bone where growth occurs. People with the condition are often shorter than average because the bones in their arms and legs are unusually short. Other skeletal signs include enlarged joints, short hands and fingers, and flat bones of the spine (vertebrae). People with the disorder often experience back and joint pain, limited joint movement, and arthritis that begins early in life. Severe high-tone hearing loss is common. Typical facial features include protruding eyes; a sunken nasal bridge; an upturned nose with a large, rounded tip; and a small lower jaw. Some affected infants are born with an opening in the roof of the mouth, which is called a cleft palate.
Pathophysiology
Mutations in the COL11A2 gene cause otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia. The protein made by the COL11A2 gene is involved in the production of type XI collagen. This type of collagen is important for the normal development of bone and other connective tissues. Mutations in the COL11A2 gene lead to a loss of function of this type of collagen, resulting in the signs and symptoms of OSMED.
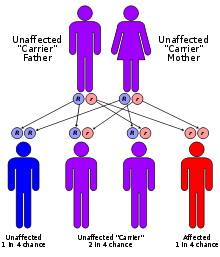
OSMED is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, which means the defective gene is located on an autosome, and two copies of the defective gene - one from each parent - must be inherited for a person to be affected by the disorder. The parents of a child with an autosomal recessive disorder are usually not affected but are carriers of one copy of the altered gene. A recessive pattern of inheritance makes OSMED unique among the type II and type XI collagenopathies.
Epidemiology
The frequency of this disorder is unknown, but it is very rare. Only a few families with the condition have been reported.
References
- Melkoniemi M, Brunner HG, Manouvrier S, Hennekam R, Superti-Furga A, Kaariainen H, Pauli RM, van Essen T, Warman ML, Bonaventure J, Miny P, Ala-Kokko L (2000). "Autosomal recessive disorder otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia is associated with loss-of-function mutations in the COL11A2 gene". Am J Hum Genet 66 (2): 368–77. doi:10.1086/302750. PMC 1288089. PMID 10677296. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1288089.
- van Steensel MA, Buma P, de Waal Malefijt MC, van den Hoogen FH, Brunner HG (1997). "Oto- spondylo-megaepiphyseal dysplasia (OSMED): clinical description of three patients homozygous for a missense mutation in the COL11A2 gene". Am J Med Genet 70 (3): 315–23. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19970613)70:3<315::AID-AJMG19>3.0.CO;2-O. PMID 9188673.
External links
This article incorporates public domain text from The U.S. National Library of Medicine
Osteochondrodysplasia (Q77–Q78, 756.4–756.5) Osteodysplasia/
osteodystrophySpondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita · Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia · Otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasiaOther/ungroupedFLNB (Boomerang dysplasia) · Opsismodysplasia · Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia (McCune-Albright syndrome)Chondrodysplasia/
chondrodystrophy
(including dwarfism)enchondromatosis (Ollier disease, Maffucci syndrome)Other dwarfismFibrochondrogenesis · Short rib-polydactyly syndrome (Majewski's polydactyly syndrome) · Léri-Weill dyschondrosteosisGenetic disorder, extracellular: scleroprotein disease (excluding laminin and keratin) Collagen disease COL1: Osteogenesis imperfecta · Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, types 1, 2, 7
COL2: Hypochondrogenesis · Achondrogenesis type 2 · Stickler syndrome · Marshall syndrome · Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita · Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia, Strudwick type · Kniest dysplasia (see also C2/11)
COL3: Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, types 3 & 4 (Sack–Barabas syndrome)
COL4: Alport syndrome
COL5: Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, types 1 & 2
COL6: Bethlem myopathy · Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy
COL7: Epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica · Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa · Bart syndrome · Transient bullous dermolysis of the newborn
COL8: Fuchs' dystrophy 1
COL9: Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia 2, 3, 6
COL10: Schmid metaphyseal chondrodysplasia
COL11: Weissenbacher–Zweymüller syndrome · Otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia (see also C2/11)
COL17: Bullous pemphigoidLaminin Junctional epidermolysis bullosa · Laryngoonychocutaneous syndromeOther Congenital stromal corneal dystrophy · Raine syndrome · Urbach–Wiethe disease · TECTA (DFNA8/12, DFNB21)Categories:- Autosomal recessive disorders
- Collagen disease
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.