- Congenital stromal corneal dystrophy
-
Congenital stromal corneal dystrophy Classification and external resources 
The cornea is particularly opaque in the anterior stroma by slit-lamp biomicroscopyOMIM 610048 Congenital stromal corneal dystrophy (CSCD), also called Witschel dystrophy, is an extremely rare, autosomal dominant form of human corneal dystrophy.[1] It is non-progressive and is linked to mutations in DCN gene encoding decorin protein. Only 4 families have been reported to have the disease by 2009.[2] The main features of the disease are numerous opaque flaky or feathery areas of clouding in the stroma that multiply with age and eventually preclude visibility of the endothelium. Strabismus or primary open angle glaucoma was noted in some of the patients. Thickness of the cornea stays the same, Descemet's membrane and endothelium are relatively unaffected, but the fibrills of collagen that constitute stromal lamellae are reduced in diameter and lamellae themselves are packed significantly more tightly.
Genetics
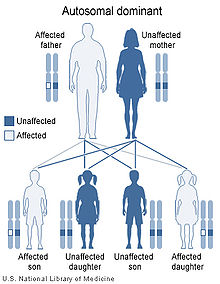
CSCD is associated with a mutation in the gene that encodes the protein decorin, located at chromosome 12q22.[1] The disorder is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner,[1] which indicates that the defective gene responsible for a disorder is located on an autosome (chromosome 12 is an autosome), and only one copy of the gene is sufficient to cause the disorder, when inherited from a parent who has the disorder.
References
- ^ a b c Bredrup, C.; Knappskog, P. M.; Majewski, J.; Rødahl, E.; Boman, H. (February 2005). "Congenital stromal dystrophy of the cornea caused by a mutation in the decorin gene" (Free full text). Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 46 (2): 420–426. doi:10.1167/iovs.04-0804. PMID 15671264. http://www.iovs.org/cgi/content/full/46/2/420.
- ^ Klintworth GK (2009). "Corneal dystrophies". Orphanet J Rare Dis 4: 7. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-4-7. PMC 2695576. PMID 19236704. http://www.ojrd.com/content/4//7.
External links
Types of human corneal dystrophy (H18.5, 371.5) Epithelial and Subepithelial Epithelial basement membrane dystrophy (OMIM 121820), called a corneal dystrophy but in reality this condition is not inherited in the majority of cases, representing a non-specific reaction to a variety of corneal insults. · Subepithelial mucinous corneal dystrophy · Meesmann juvenile epithelial corneal dystrophy (MECD, Stocker-Holt dystrophy, OMIM 122100) · Lisch epithelial dystrophy · Gelatinous drop-like corneal dystrophyBowman layer Reis-Bucklers corneal dystrophy (CDB1) aka. Granular corneal dystrophy type III · Thiel-Behnke dystrophy (CDB2)Stroma Lattice corneal dystrophy type I · Lattice corneal dystrophy type II · Granular corneal dystrophy type I · Granular corneal dystrophy type II · Also Granular corneal dystrophy type III see Reis-Bucklers corneal dystrophy above · Macular corneal dystrophy · Schnyder corneal dystrophy · Congenital stromal dystrophy (CSCD) · Fleck dystrophy · Posterior amorphous corneal dystrophyDescemet membrane and Endothelial Fuchs' dystrophy · Posterior polymorphous dystrophy type 1 · Posterior polymorphous dystrophy type 2 · Posterior polymorphous dystrophy type 3 · Congenital endothelial dystrophy type 1 (CHED1) · Congenital endothelial dystrophy type 2 (CHED2) · X-linked endothelial corneal dystrophyM: EYE
anat(g/a/p)/phys/devp/prot
noco/cong/tumr, epon
proc, drug(S1A/1E/1F/1L)
Genetic disorder, extracellular: scleroprotein disease (excluding laminin and keratin) Collagen disease COL1: Osteogenesis imperfecta · Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, types 1, 2, 7
COL2: Hypochondrogenesis · Achondrogenesis type 2 · Stickler syndrome · Marshall syndrome · Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita · Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia, Strudwick type · Kniest dysplasia (see also C2/11)
COL3: Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, types 3 & 4 (Sack–Barabas syndrome)
COL4: Alport syndrome
COL5: Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, types 1 & 2
COL6: Bethlem myopathy · Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy
COL7: Epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica · Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa · Bart syndrome · Transient bullous dermolysis of the newborn
COL8: Fuchs' dystrophy 1
COL9: Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia 2, 3, 6
COL10: Schmid metaphyseal chondrodysplasia
COL11: Weissenbacher–Zweymüller syndrome · Otospondylomegaepiphyseal dysplasia (see also C2/11)
COL17: Bullous pemphigoidLaminin Junctional epidermolysis bullosa · Laryngoonychocutaneous syndromeOther Congenital stromal corneal dystrophy · Raine syndrome · Urbach–Wiethe disease · TECTA (DFNA8/12, DFNB21)see also fibrous proteins
B structural (perx, skel, cili, mito, nucl, sclr) · DNA/RNA/protein synthesis (drep, trfc, tscr, tltn) · membrane (icha, slcr, atpa, abct, othr) · transduction (iter, csrc, itra), trfkCategories:- Diseases of the eye and adnexa
- Rare diseases
- Autosomal dominant disorders
- Genetic disorder stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.