- Congenital endothelial dystrophy type 2
-
Congenital endothelial dystrophy type 2 Classification and external resources
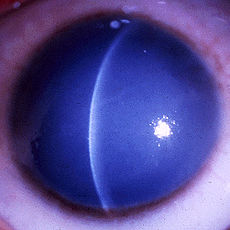
A markedly opaque cornea due to stromal edema secondary to defective endothelial cells (Courtesy of Dr. Ahmed A. Hidajat)OMIM 217700 Congenital endothelial dystrophy type 2 is a rare form of human corneal dystrophy. It is associated with mutations in SLC4A11 gene.[1]
References
- ^ Vithana EN, Morgan P, Sundaresan P, Ebenezer ND, Tan DT, Mohamed MD, Anand S, Khine KO, Venkataraman D, Yong VH, Salto-Tellez M, Venkatraman A, Guo K, Hemadevi B, Srinivasan M, Prajna V, Khine M, Casey JR, Inglehearn CF, Aung T (July 2006). "Mutations in sodium-borate cotransporter SLC4A11 cause recessive congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy (CHED2)". Nat. Genet. 38 (7): 755–7. doi:10.1038/ng1824. PMID 16767101.
See also
Types of human corneal dystrophy (H18.5, 371.5) Epithelial and Subepithelial Epithelial basement membrane dystrophy (OMIM 121820), called a corneal dystrophy but in reality this condition is not inherited in the majority of cases, representing a non-specific reaction to a variety of corneal insults. · Subepithelial mucinous corneal dystrophy · Meesmann juvenile epithelial corneal dystrophy (MECD, Stocker-Holt dystrophy, OMIM 122100) · Lisch epithelial dystrophy · Gelatinous drop-like corneal dystrophyBowman layer Reis-Bucklers corneal dystrophy (CDB1) aka. Granular corneal dystrophy type III · Thiel-Behnke dystrophy (CDB2)Stroma Lattice corneal dystrophy type I · Lattice corneal dystrophy type II · Granular corneal dystrophy type I · Granular corneal dystrophy type II · Also Granular corneal dystrophy type III see Reis-Bucklers corneal dystrophy above · Macular corneal dystrophy · Schnyder corneal dystrophy · Congenital stromal dystrophy (CSCD) · Fleck dystrophy · Posterior amorphous corneal dystrophyDescemet membrane and Endothelial Fuchs' dystrophy · Posterior polymorphous dystrophy type 1 · Posterior polymorphous dystrophy type 2 · Posterior polymorphous dystrophy type 3 · Congenital endothelial dystrophy type 1 (CHED1) · Congenital endothelial dystrophy type 2 (CHED2) · X-linked endothelial corneal dystrophyM: EYE
anat(g/a/p)/phys/devp/prot
noco/cong/tumr, epon
proc, drug(S1A/1E/1F/1L)
Genetic disorder, membrane: Solute carrier disorders 1-10 SLC1A3 (Episodic ataxia 6) · SLC2A1 (De Vivo disease) · SLC2A5 (Fructose malabsorption) · SLC2A10 (Arterial tortuosity syndrome) · SLC3A1 (Cystinuria) · SLC4A1 (Hereditary spherocytosis 4/Hereditary elliptocytosis 4) · SLC4A11 (Congenital endothelial dystrophy type 2, Fuchs' dystrophy 4) · SLC5A1 (Glucose-galactose malabsorption) · SLC5A2 (Renal glycosuria) · SLC5A5 (Thyroid dyshormonogenesis type 1) · SLC6A19 (Hartnup disease) · SLC7A7 (Lysinuric protein intolerance) · SLC7A9 (Cystinuria)11-20 SLC11A1 (Crohn's disease) · SLC12A3 (Gitelman syndrome) · SLC16A1 (HHF7) · SLC16A2 (Allan–Herndon–Dudley syndrome) · SLC17A5 (Salla disease) · SLC17A8 (DFNA25)21-40 see also solute carrier family
B structural (perx, skel, cili, mito, nucl, sclr) · DNA/RNA/protein synthesis (drep, trfc, tscr, tltn) · membrane (icha, slcr, atpa, abct, othr) · transduction (iter, csrc, itra), trfkCategories:- Diseases of the eye and adnexa
- Disease stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.