- Cystine
-
Cystine 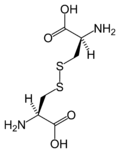

Identifiers CAS number 56-89-3 
ChemSpider 575 
UNII 48TCX9A1VT 
KEGG C01420 
ChEBI CHEBI:35492 
ChEMBL CHEMBL366563 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - C(C(C(=O)O)N)SSCC(C(=O)O)N
Properties Molecular formula C6H12N2O4S2 Molar mass 240.3 g mol−1 Hazards MSDS External MSDS  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Cystine is a dimeric amino acid formed by the oxidation of two cysteine residues that covalently link to make a disulfide bond. This organosulfur compound has the formula (SCH2CH(NH2)CO2H)2. It is a white solid, and melts at 247-249 °C. It was discovered in 1810 by William Hyde Wollaston but was not recognized as being derived of proteins until it was isolated from the horn of a cow in 1899.[1] Through formation of disulfide bonds within and between protein molecules, cystine is a significant determinant of the tertiary structure of most proteins. Disulfide bonding, along with hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions is partially responsible for the formation of the gluten matrix in bread. Human hair contains approximately 5% cystine by mass.[2]
Properties and nutritional aspects
The disulfide link is readily reduced to give the corresponding thiol cysteine. This reaction is typically effected with thiols such as mercaptoethanol or dithiothreitol.
- (SCH2CH(NH2)CO2H)2 + 2 RSH → 2 HSCH2CH(NH2)CO2H + RSSR
For this reason, the nutritional benefits and sources of cystine are identical to those for the more-common cysteine. Disulfide bonds cleave more rapidly at higher temperatures.[3]
See also
- Cystinuria
- Cystinosis
- Cysteine
- Lanthionine, similar with mono-sulphide link
References
- ^ "cystine." Encyclopædia Britannica. 2007. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. 27 July 2007 www.britannica.com/eb/article-9028437/cystine
- ^ Gortner, R. A.; W. F. Hoffman, W. F. (1941), "l-Cystine", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=CV1P0194; Coll. Vol. 1: 194
- ^ M.A. Aslaksena, O.H. Romarheima, T. Storebakkena and A. Skrede (28 June 2006). "Evaluation of content and digestibility of disulfide bonds and free thiols in unextruded and extruded diets containing fish meal and soybean protein sources". Animal Feed Science and Technology 128 (3–4): 320–330. doi:10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2005.11.008.
E numbers Colours (E100–199) • Preservatives (E200–299) • Antioxidants & acidity regulators (E300–399) • Thickeners, stabilisers & emulsifiers (E400–499) • pH regulators & anticaking agents (E500–599) • Flavour enhancers (E600–699) • Miscellaneous (E900–999) • Additional chemicals (E1100–1599)
Waxes (E900–909) • Synthetic glazes (E910–919) • Improving agents (E920–929) • Packaging gases (E930–949) • Sweeteners (E950–969) • Foaming agents (E990–999)
L-cysteine (E920) • L-cystine (E921) • Potassium persulfate (E922) • Ammonium persulfate (E923) • Potassium bromate (E924) • Chlorine (E925) • Chlorine dioxide (E926) • Azodicarbonamide (E927) • Carbamide (E927b) • Benzoyl peroxide (E928)
Categories:- Organic disulfides
- Sulfur amino acids
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
