- Dimer (chemistry)
-
For other uses, see Dimer (disambiguation).
A dimer is a chemical entity consisting of two structurally similar subunits called monomers joined by bonds that can be either strong or weak.
Organic chemistry
Molecular dimers are often formed by the reaction of two identical compounds e.g.: 2A → A-A. In this example, monomer "A" is said to dimerise to give the dimer "A-A". An example is Diaminocarbenes, which dimerise to give tetraaminoethylenes:
- 2 C(NR2)2 → (R2N)2C=C(NR2)2
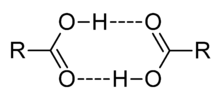
Acetic acid forms a dimer in the gas phase, the monomer units are held together by hydrogen bonds. Under special conditions, most OH-containing molecules form dimers, e.g. the water dimer.
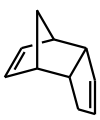
Dicyclopentadiene is an unsymmetrical dimer of two cyclopentadiene molecules that have reacted in a Diels-Alder reaction to give the product. Upon heating, it "cracks" (undergoes a retro-Diels-Alder reaction) to give identical monomers:
- C10H12 → 2 C5H6
The term homodimer is used when the two molecules are identical (e.g. A-A) and heterodimer when they are not (e.g. A-B). The reverse of dimerisation is often called dissociation.
See also
References
- "IUPAC "Gold Book" definition". http://goldbook.iupac.org/D01744.html. Retrieved 2009-04-30.
Categories:- Chemical compounds
- Oligomers
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.