- Dicyclopentadiene
-
Dicyclopentadiene[1] 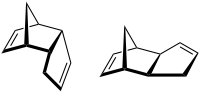
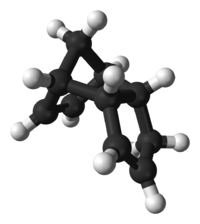 Tricyclo[5.2.1.02,6]deca-3,8-dieneOther names1,3-Dicyclopentadiene
Tricyclo[5.2.1.02,6]deca-3,8-dieneOther names1,3-DicyclopentadieneIdentifiers Abbreviations DCPD CAS number 77-73-6 
PubChem 6492  , 6428576 (6R)
, 6428576 (6R)  , 10396885 (1S,7R)
, 10396885 (1S,7R) 
ChemSpider 6247  , 24532442 (2H12)
, 24532442 (2H12)  , 4933978 (6R)
, 4933978 (6R)  , 8572323 (1S,7R)
, 8572323 (1S,7R) 
EC number 247-724-5 UN number UN 2048 KEGG C14411 
MeSH Dicyclopentadiene RTECS number PC1050000 Beilstein Reference 1904092 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - C1C=CC2C1C3CC2C=C3
Properties Molecular formula C10H12 Molar mass 132.20 g/mol Density 0.98 g/cm3 Melting point 32.5 °C
Boiling point 170 °C
Hazards NFPA 704 Flash point 32 °C  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Dicyclopentadiene, abbreviated DCPD, is a chemical compound with formula C10H12. At room temperature, it is a white crystalline solid with a camphor-like odor. Its energy density is 10,975 Wh/l. Dicyclopentadiene is coproduced in large quantities in the steam cracking of naphtha and gas oils to ethylene. The major use is in resins, particularly, unsaturated polyester resins. It is also used in inks, adhesives, and paints. It is also a kind of high-energy fuel. [2]
The top seven suppliers worldwide together had an annual capacity in 2001 of 395 million pounds (179 kilotonnes).[3]
Reactivity
When heated above 150 °C, dicyclopentadiene undergoes a retro-Diels-Alder reaction to yield cyclopentadiene, a popular ligand in inorganic chemistry. The reaction is reversible and at room temperature cyclopentadiene slowly dimerizes to reform dicyclopentadiene.
Hydrogenation of dicyclopentadiene gives endo-tetrahydrodicyclopentadiene which on reaction with aluminium chloride at elevated temperature rearranges to adamantane.[4]
Dicyclopentadiene is a monomer in polymerization reactions for example as copolymer with ethylene or styrene utilizing only the norbornene double bond.[5] Polydicyclopentadiene is the homopolymer.
References
- ^ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 2744
- ^ http://www.ec21.com/product-details/Dicyclopentadiene--3407789.html
- ^ Chemical Profiles-Dicyclopentadiene
- ^ Paul von R. Schleyer, M. M. Donaldson, R. D. Nicholas, and C. Cupas (1973), "Adamantane", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv5p0016; Coll. Vol. 5: 16
- ^ Li, Xiaofang; Hou, Zhaomin (2005). "Scandium-Catalyzed Copolymerization of Ethylene with Dicyclopentadiene and Terpolymerization of Ethylene, Dicyclopentadiene, and Styrene". Macromolecules 38: 6767. doi:10.1021/ma051323o.
External links
Categories:- Cycloalkenes
- Dienes
- Monomers
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

