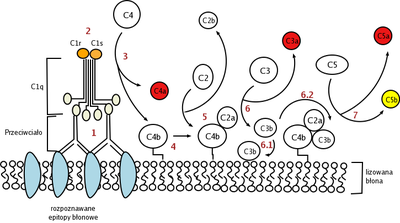
- Complement component 4
-
complement component 4A (Rodgers blood group) Identifiers Symbol C4A Entrez 720 HUGO 1323 OMIM 120810 RefSeq NM_007293 UniProt P0C0L4 Other data Locus Chr. 6 p21.3 complement component 4B (Childo blood group) Identifiers Symbol C4B Entrez 721 HUGO 1324 OMIM 120820 RefSeq NM_000592 UniProt P0C0L5 Other data Locus Chr. 6 p21.3 Complement component 4 is a protein involved in the complement system.
It is cleaved into proteins 4a and 4b.
- C4a is an anaphylatoxin.
- C4b forms part of C3-convertase, in conjunction with 2a:
- C4b can bind CR1.
- C4d is the final proteolytic remnant of deposited C4b on endothelium, remains covalently attached to endothelium for little more than a week and easily detectable by antibody staining.
C4d is the most clinically used marker for humoral rejection. It is a degradation product of the activated complement factor C4b. C4d is typically initiated by binding of antibodies to specific target molecules. Following activation and degradation of the C4 molecule, thio-ester groups are exposed, which allow transient, covalent binding of the degradation product C4d to endothelial cell surfaces and extracellular matrix components of vascular basement membranes near the sites of C4 activation. C4d is also found in intracytoplasmic vacuoles of endothelial cells. Covalent binding renders C4d a stable molecule that can easily be detected by immunohistochemistry.
Detection of C4d is regarded as an indirect sign, a ‘footprint’ of an antibody response. This observation marks a ‘revolution’: For the first time, a general and robust immunohistochemical marker for humoral rejection is identified. Since C4d is practically never detected along peritubular capillaries in the native diseased and inflamed kidney, such as active lupus nephritis, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) disease, or anti-glomerular basement membrane (GBM) disease, its detection seems ‘transplant-specific’[citation needed]. However, it should be kept in mind that, apart from the classical antibody-mediated route of complement activation, C4 can also be activated via an alternative, antibody-independent mechanism, the ‘mannan-binding lectin’ pathway. Thus, C4d may also be potentially deposited without prior antibody binding. At the current time, it is unknown whether this lectin pathway plays any pathophysiological role in the activation of C4 in renal transplants. Therefore, based on our current understanding, C4d accumulation is considered to be a marker for an ‘antibody-mediated allo-response’. The detection of C4d in a graft biopsy, in ideal circumstances, should be amended by clinical information on circulating donor-specific antibodies against major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I or class II.
Clinical significance
Complement tests C4 (C) FB (A) C3 CH50 Conditions · ↓ ↓ ↓ PSG, C3 NeF AA ↓ · ↓ · HA, C4D · · · ↓ TCPD ↓ · /↓ ↓ ↓ SLE ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ inflammation It is responsible for the Chido Rodgers blood group system.[1]
C4d has been identified as a biomarker for systemic lupus erythematosus.[2]
References
- ^ Chido Rodgers blood group system at BGMUT Blood Group Antigen Gene Mutation Database at NCBI, NIH
- ^ Liu CC, Manzi S, Kao AH, Navratil JS, Ruffing MJ, Ahearn JM (2005). "Reticulocytes bearing C4d as biomarkers of disease activity for systemic lupus erythematosus". Arthritis Rheum. 52 (10): 3087–99. doi:10.1002/art.21305. PMID 16200588.
Proteins: complement system (C, L, A) Activators/enzymes EarlyMiddleLateInhibitors Complement receptors Categories:- Genes on chromosome 6
- Transfusion medicine
- Blood antigen systems
- Complement system
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.