- Drawing
-
Drawing is a form of visual art that makes use of any number of drawing instruments to mark a two-dimensional medium. Common instruments include graphite pencils, pen and ink, inked brushes, wax color pencils, crayons, charcoal, chalk, pastels, markers, styluses, and various metals (such as silverpoint). An artist who practices or works in drawing may be called a draughtsman or draftsman.[1]
A small amount of material is released onto the two dimensional medium, leaving a visible mark. The most common support for drawing is paper, although other materials, such as cardboard, plastic, leather, canvas, and board, may be used. Temporary drawings may be made on a blackboard or whiteboard or indeed almost anything. The medium has been a popular and fundamental means of public expression throughout human history. The relatively easy availability of basic drawing instruments makes drawing more universal than most other media.
Contents
Overview
Drawing is a form of visual expression and is one of the major forms within the visual arts. There are several categories of drawing, including cartooning. Certain drawing methods or approaches, such as "doodling," other informal kinds of drawing, and the surrealist method of "entopic graphomania", in which dots are made at the sites of impurities in a blank sheet of paper, and lines are then made between the dots, may or may not be considered part of "drawing" as a "fine art". Likewise, tracing—drawing on a thin piece of paper, sometimes designed for that purpose (tracing paper), around the outline of preexisting shapes that show through the paper—is also not considered fine art, although it may be part of the draughtsman's preparation.
The word drawing is both (1) a noun and (2) the present-participle and gerund forms of the verb draw. To draw is to produce a drawing. A quick, unrefined drawing may be called a sketch.
Drawing is generally concerned with the marking of lines and areas of tone onto paper. Traditional drawings were monochrome, or at least had little colour,[2] while modern colored-pencil drawings may approach or cross a boundary between drawing and painting. In Western terminology, however, drawing is distinct from painting, even though similar media often are employed in both tasks. Dry media, normally associated with drawing, such as chalk, may be used in pastel paintings. Drawing may be done with a liquid medium, applied with brushes or pens. Similar supports likewise can serve both: painting generally involves the application of liquid paint onto prepared canvas or panels, but sometimes an underdrawing is drawn first on that same support. Drawing is often exploratory, with considerable emphasis on observation, problem-solving, and composition. Drawing is also regularly used in preparation for a painting, further obfuscating their distinction.
History
It is not known when art or drawing was established. Sketches and paintings have been produced since prehistoric times, as demonstrated by cave and rock paintings. By the 12th to 13th centuries A.D., monks were preparing illuminated manuscripts on vellum and parchment in monasteries throughout Europe and were using lead styli to draw lines for their writings and for the outlines for their illuminations. Soon artists generally were using silver to make drawings and underdrawings. Initially they used and re-used wooden tablets with prepared ground for these drawings. When paper became generally available, from the 14th century onwards, artists' drawings, both preparatory studies and finished works, became increasingly common.
Notable Draftsmen
Since the 14th century, each century has produced artists who have created great drawings.
- Notable draftsmen of the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries include Leonardo da Vinci, Albrecht Dürer, Michelangelo, Raphael, and Donatello.
- Notable draftsmen of the 17th century include Claude, Nicolas Poussin, Rembrandt, Guercino, and Peter Paul Rubens.
- Notable draftsmen of the 18th century include Jean-Honoré Fragonard, Giovanni Battista Tiepolo, and Antoine Watteau.
- Notable draftsmen of the 19th century include Paul Cézanne, Aubrey Beardsley, Jacques Louis David, Pierre-Paul Prud'hon, Edgar Degas, Théodore Géricault, Francisco Goya, Jean Ingres, Odilon Redon, Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec, Honoré Daumier, and Vincent van Gogh.
- Notable draftsmen of the 20th century include Käthe Kollwitz, Max Beckmann, Jean Dubuffet, Egon Schiele, Arshile Gorky, Paul Klee, Oscar Kokoschka, Alphonse Mucha, M. C. Escher, André Masson, Jules Pascin, and Pablo Picasso.
Media
The medium is the means by which ink, pigment or color are delivered onto the drawing surface. Most drawing media are either dry (e.g. graphite, charcoal, pastels, Conté, silverpoint), or use a fluid solvent or carrier (marker, pen and ink). Watercolor pencils can be used dry like ordinary pencils, then moistened with a wet brush to get various painterly effects. Very rarely, artists have drawn with (usually decoded) invisible ink. Metalpoint drawing usually employs either of two metals: silver or lead.[3] More rarely used are gold, platinum, copper, brass, bronze and tinpoint.
Applying media
Almost all draughtsmen use their hands and fingers to apply the media, with the exception of some handicapped individuals who draw with their mouth or feet.[citation needed]
Prior to working on an image, the artist will likely want to gain an understanding of how the various media will work. The different drawing implements can be tried on practice sheets in order to determine value and texture, and how to apply the implement in order to produce various effects.
The stroke of the drawing implement can be used to control the appearance of the image. Ink drawings typically use hatching, which consists of groups of parallel lines.[4] Cross-hatching uses hatching in two or more different directions to create a darker tone. Broken hatching, or lines with intermittent breaks, is used to form lighter tones, and by controlling the density of the breaks a graduation of tone can be achieved. Stippling, uses dots to produce tone, texture or shade.
Sketch drawings use similar techniques, although with pencils and drawing sticks continuous variations in tone can be achieved. For best results the lines in a sketch are typically drawn to follow the contour curves of the surface, thus producing a depth effect. When drawing hair, the lines of the sketch follow the direction of the hair growth.
Typically a drawing will be filled in based on which hand the artist favors. A right-handed artist will want to draw from left to right in order to avoid smearing the image. Sometimes the artist will want to leave a section of the image blank while filling in the remainder of the picture. A frisket can be used for this purpose. The shape of the area to be preserved is cut out of the frisket, and the resulting shape is then applied to the drawing surface. This will protect the surface from receiving any stray marks before it is ready to be filled in.
Another method to preserve a section of the image is to apply a spray-on fixative to the surface. This will hold loose material more firmly to the sheet and prevent it from smearing. However the fixative spray typically uses chemicals that can negatively affect the respiratory system, so it should be employed in a well-ventilated area such as outdoors.
Materials
Paper comes in a variety of different sizes and qualities, ranging from newspaper grade up to high quality and relatively expensive paper sold as individual sheets.[5] Papers can vary in texture, hue, acidity, and strength when wet. Smooth paper is good for rendering fine detail, but a more "toothy" paper will hold the drawing material better. Thus a coarser material is useful for producing deeper contrast.
Newsprint and typing paper may be useful for practice and rough sketches. Tracing paper is used to experiment over a half-finished drawing, and to transfer a design from one sheet to another. Cartridge paper is the basic type of drawing paper sold in pads. Bristol board and even heavier acid-free boards, frequently with smooth finishes, are used for drawing fine detail and do not distort when wet media (ink, washes) are applied. Vellum is extremely smooth and suitable for very fine detail. Coldpressed watercolor paper may be favored for ink drawing due to its texture.
Acid-free, archival quality paper keeps its color and texture far longer than wood pulp based paper such as newsprint, which will turn yellow and become brittle much sooner.
The basic tools are a drawing board or table, pencil sharpener and eraser, and for ink drawing, blotting paper. Other tools used are circle compass, ruler, and set square. Fixative is used to prevent pencil and crayon marks from smudging. Drafting tape is used to secure paper to drawing surface, and also to mask an area to keep it free of accidental marks sprayed or spattered materials and washes. An easel or slanted table is used to keep the drawing surface in a suitable position, which is generally more horizontal than the position used in painting.
Tone
Shading is the technique of varying the tonal values on the paper to represent the shade of the material as well as the placement of the shadows. Careful attention to reflected light, shadows, and highlights can result in a very realistic rendition of the image.
Blending uses an implement to soften or spread the original drawing strokes. Blending is most easily done with a medium that does not immediately fix itself, such as graphite, chalk, or charcoal, although freshly applied ink can be smudged, wet or dry, for some effects. For shading and blending, the artist can use a blending stump, tissue, a kneaded eraser, a fingertip, or any combination of them. A piece of chamois is useful for creating smooth textures, and for removing material to lighten the tone. Continuous tone can be achieved with graphite on a smooth surface without blending, but the technique is laborious, involving small circular or oval strokes with a somewhat blunt point.
Shading techniques that also introduce texture to the drawing include hatching and stippling. There are a number of other methods for producing texture in the picture: in addition to choosing a suitable paper, the type of drawing material and the drawing technique will result in different textures. Texture can be made to appear more realistic when it is drawn next to a contrasting texture; a coarse texture will be more obvious when placed next to a smoothly blended area. A similar effect can be achieved by drawing different tones close together; a light edge next to a dark background will stand out to the eye, and almost appear to float above the surface.
Layout
Measuring the dimensions of a subject while blocking in the drawing is an important step in producing a realistic rendition of the subject. Tools such as a compass can be used to measure the angles of different sides. These angles can be reproduced on the drawing surface and then rechecked to make sure they are accurate. Another form of measurement is to compare the relative sizes of different parts of the subject with each other. A finger placed at a point along the drawing implement can be used to compare that dimension with other parts of the image. A ruler can be used both as a straightedge and a device to compute proportions.
When attempting to draw a complicated shape such as a human figure, it is helpful at first to represent the form with a set of primitive shapes. Almost any form can be represented by some combination of the cube, sphere, cylinder, and cone. Once these basic shapes have been assembled into a likeness, then the drawing can be refined into a more accurate and polished form. The lines of the primitive shapes are removed and replaced by the final likeness. Drawing the underlying construction is a fundamental skill for representational art and is taught in many books and schools, as its correct application will resolve most uncertainties about smaller details and make the final image look self-consistent.
A more refined art of figure drawing relies upon the artist possessing a deep understanding of anatomy and the human proportions. A trained artist is familiar with the skeleton structure, joint location, muscle placement, tendon movement, and how the different parts work together during movement. This allows the artist to render more natural poses that do not appear artificially stiff. The artist is also familiar with how the proportions vary depending on the age of the subject, particularly when drawing a portrait.
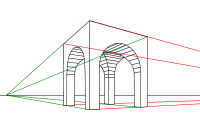
Perspective
Linear perspective is a method of portraying objects on a flat surface so that the dimensions shrink with distance. The parallel, straight edges of any object, whether a building or a table, will follow lines that eventually converge at infinity. Typically this point of convergence will be along the horizon, as buildings are built level with the flat surface. When multiple structures are aligned with each other, such as buildings along a street, the horizontal tops and bottoms of the structures will all typically converge at a vanishing point.
When both the fronts and sides of a building are drawn, then the parallel lines forming a side converge at a second point along the horizon (which may be off the drawing paper.) This is a "two-point perspective". Converging the vertical lines to a point in the sky then produces a "three-point perspective".
Depth can also be portrayed by several techniques in addition to the perspective approach above. Objects of similar size should appear ever smaller the further they are from the viewer. Thus the back wheel of a cart will appear slightly smaller than the front wheel. Depth can be portrayed through the use of texture. As the texture of an object gets further away it becomes more compressed and busy, taking on an entirely different character than if it was close. Depth can also be portrayed by reducing the amount of contrast of more distant objects, and also by making the colors more pale. This will reproduce the effect of atmospheric haze, and cause the eye to focus primarily on objects drawn in the foreground.
Artistry
The composition of the image is an important element in producing an interesting work of artistic merit. The artist plans the placement of elements in the art in order to communicate ideas and feelings with the viewer. The composition can determine the focus of the art, and result in a harmonious whole that is aesthetically appealing and stimulating.
The illumination of the subject is also a key element in creating an artistic piece, and the interplay of light and shadow is a valuable method in the artist's toolbox. The placement of the light sources can make a considerable difference in the type of message that is being presented. Multiple light sources can wash out any wrinkles in a person's face, for instance, and give a more youthful appearance. In contrast, a single light source, such as harsh daylight, can serve to highlight any texture or interesting features.
When drawing an object or figure, the skilled artist pays attention to both the area within the silhouette and what lies outside. The exterior is termed the negative space, and can be as important in the representation as the figure. Objects placed in the background of the figure should appear properly placed wherever they can be viewed.
A study is a draft drawing that is made in preparation for a planned final image. Studies can be used to determine the appearances of specific parts of the completed image, or for experimenting with the best approach for accomplishing the end goal. However a well-crafted study can be a piece of art in its own right, and many hours of careful work can go into completing a study.
Digital illustration
Computer art is the use of digital tools to produce images under the direct manipulation of the artist, usually through a pointing device such as a tablet or a mouse. It is distinguished from computer-generated art, which is produced by a computer using mathematical models created by the artist.
Computer art is also distinct from digital manipulation of photographs, in that it is an original construction "from scratch". Photographic elements may be incorporated into such works, but they are not the primary basis or source for them.
See also
- Architectural drawing
- Color theory
- Composition
- Diagram
- Digital illustration
- Engineering drawing
- Figure drawing
- GPS drawing
- Illustration
- Multi-Sketch
- Pen
- Sketch (drawing)
- Technical drawing
- Traditional animation
References
- ^ http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/draughtsman
- ^ See grisaille and chiaroscuro
- ^ Cennino Cennini, The Craftsman's Handbook (Il Libra dell'Arte), trans. David V. Thompson, Jr. New Haven, Connecticut: Yale University Press, 1933
- ^ This use of hatching is to be distinguished from the use of a hatching system in heraldry to indicate tincture (i.e. what "color", in layman's language, the arms are) in a monochromatic context.)
- ^ Mayer, Ralph. The Artist's Handbook of Materials and Techniques. Viking. ISBN 0-670-83701-6.
Further reading
- Betty Edwards, The New Drawing on the Right Side of the Brain, HarperCollins Publishers Ltd; 3Rev Ed edition, 2001, ISBN 978-0007116454
- Brommer, Gerald F. Exploring Drawing. Worcester, Massachusetts: Davis Publications. 1988.
- Bodley Gallery, New York, N.Y., Modern master drawings, 1971, OCLC 37498294.
- Frank Lohan, Pen & Ink Techniques, Contemporary Books, 1978, ISBN 0-8092-7438-8.
- J. D. Hillberry, Drawing Realistic Textures in Pencil, North Light Books, 1999, ISBN 0-89134-868-9.
- Landa, Robin. Take a line for a walk: A Creativity Journal. Boston: Wadsworth, 2011. ISBN: 978-1111839222
- Spears, Heather. The Creative Eye. London: Arcturus. 2007. ISBN 978-0-572-03315-6.
- World Book, Inc. The World Book Encyclopedia Volume 5, 1988, ISBN 0-7166-0089-7.
- Drawing/Thinking: Confronting an Electronic Age, edited by Marc Treib, 2008, ISBN, 0-415-77560-4.
External links
- Timeline of Drawing Development in Children
- On Drawing, an essay about the craft of drawing, by artist Norman Nason
Visual arts Computer art · Decorative arts · Drawing · Filmmaking · New media · Painting · Photography · Printmaking · SculptureCategories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.