- Weather in 2006
-
The weather in 2006 meant another year of extremes. The summer was very hot and dry in the Northern Hemisphere. Several regions experienced disastrous floods, but droughts were not avoided either. Hurricanes were easier to Northern America than the previous year (see 2005 Atlantic hurricane season), but in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean, typhoons were more powerful and frequent than normally.
Contents
Important weather events
Asia
Saroma tornado
On 7 November, a powerful tornado struck the town of Saroma, Hokkaido in Japan, killing nine people and injuring 26. It was the most deadly tornado to strike Japan since the beginning of records.
Typhoon Durian (Reming)
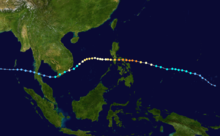
A tropical storm formed on 24 November over North Pacific Ocean, and moved west toward the Philippines. On 27 November it became a severe tropical storm. The storm continued to intensify while approaching the islands, and after 30 November the typhoon made several landfalls on different islands of the Philippines, causing over 1200 deaths. The storm then continued its path to the South China Sea, heading eventually towards southern Vietnam, where it made a landfall on 5 December. The storm weakened into a tropical depression which crossed the Gulf of Thailand and southern Thailand before finally dissipating over the Gulf of Bengal.
Southeast Asia floods
For more details on this topic, see 2006 Malaysian floods.The Typhoon Utor that crossed the Philippines on December 9, started a period of abnormally high rainfall in the southern provinces of Malaysia and in Singapore, beginning on December 18. For instance, on December 20, a 24-hour rainfall of 366mm was recorded in Singapore. The resulting floods in those areas have been described as the worst in a century by local officials. Later the same week the torrential rains moved to northern parts of Indonesia, bringing along severe floods.
As of January 2007, hundreds of thousands of people are displaced by the floods in the areas affected, and casualties number in hundreds. Food shortages and looting continue to sever the infrastructures.
Australia
2006 Australia drought
The continent of Australia experiences highly variable rainfall affected by the El Niño-Southern Oscillation. Starting 2003, a long period of drought started, described as the worst in a 1,000 years by Australian water specialists.
The situation worsened further in 2006 as the spring rains failed. In the state of South Australia, rainfall was the lowest since 1900. Average temperatures across the continent, as well, were highest since the 1950s. The situation has prompted new measures of water resources management in several Australian states.
Europe
2006 European cold wave
As a winter cold anticyclone moved from Russia (where temperatures below -40 °C were recorded) to Central Europe, many parts of Central, Eastern and Southern Europe experienced temperatures well below normal, and there was snow in the Mediterranean region where it is rare; Algiers in Algeria and Lisbon, Portugal received their first snow in decades. There were estimated 200 deaths attributed to the freezing cold in Europe.
2006 European heat wave
At the end of June 2006 a heat wave arrived in Central and Western Europe, continuing into the summer. July 2006 was the warmest month since the beginning of measurements in several European countries. In Paris, for instance, temperatures exceeded 40 °C. Mortality during the hot months was higher than normal among the elderly and others vulnerable to high temperatures. The warm, dry summer was followed in Europe by a warm, but windy and rainy autumn, caused by the warming of Northern Atlantic Ocean during the summer.
North America
The Mid-Atlantic Flood
Starting in the end of June, a persisting tropical low off the coast of North Carolina circulated moist, hot air over the Mid-Atlantic states, which, combined with a stalled jet stream, started pouring rains over the Mid-Atlantic States, resulting in rivers and other bodies of water overflowing. According to officials, the event was of a magnitude normally expected once in 200 years.
The floods claimed at least 16 fatalities and caused approximately $1 billion in damages.
2006 North American heat wave
Beginning 15 July, a heat wave spread through United States and Canada. It lasted until 27 August in different parts of the countries. In California, in particular, many records were broken, the state experiencing higher temperatures for longer periods of time than ever before. On July 22, a temperature of 119 °F / 49 °C was recorded in Woodland Hills in Los Angeles County. At least 225 deaths have been attributed to the heat wave. Also, it is considered to have played a part in many incidents that increased in frequency or severity during the heat wave, such as forest fires, ruptured water lines, buckled roads, thunderstorms and blackouts in the power grid.
Tropical cyclone seasons in 2006
Following the record-breaking 2005 Atlantic hurricane season, the 2006 season was relatively quiet in the Northern Atlantic Ocean. There were 10 storms, of which two major ones (category 3 or more on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale), compared to 28 storms with 7 major ones in 2005. No hurricanes made landfall in the United States.
In the Northwestern Pacific Ocean, however, the season was busy. 23 tropical storms formed officially, of which 15 attained the status of a typhoon. 7 of them, moreover, reached an intensity that allowed them to be called super typhoons (intensity equal to or higher than 4 on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale). The high-speed winds, torrential rains and resulting floods caused thousands of fatalities and damage to infrastructure and economy.
See also
- 2006 Atlantic hurricane season
- 2006 North Indian Ocean cyclone season
- 2006 Pacific hurricane season
- 2006 Pacific typhoon season
- 2005-06 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone season
- 2006-07 Southern Hemisphere tropical cyclone season
- Tornadoes of 2006
- Global warming
Global weather by year Preceded by
2005Weather in
2006Succeeded by
2007Categories:- 2006 meteorology
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.