- Armenian Army
-
Հայկական Բանակ
Haykakan Banak
Armenian ArmyActive January 28, 1992 – Present Country Republic of Armenia Type Army Role Ground warfare Size 43,772 (including 16,803 professional and 26,969 conscripts)[1] Engagements Nagorno-Karabakh War
Peacekeeping roles in Kosovo and AfghanistanCommanders Notable
commanders-Harut Kassabian
-Vazgen Manukyan
-Arkady Ter-TatevosyanThe Armenian Army (Armenian: Հայկական Բանակ) is the largest branch of the Armed Forces of Armenia and consists of the ground forces responsible for the country's land-based operations. It was established in conjunction with the other components of Armenia's military on January 28, 1992, several months after the republic declared its independence from the Soviet Union. The army's first head was the former deputy commander-in-chief of the Soviet Ground Forces, Norat Ter-Grigoryants.[2] In compliance with its strategic allies, Armenia has sent over 1,500 officers to be trained in Greece and Russia.[3]
Since the end of the Nagorno-Karabakh War, Armenia has committed many elements of the army to help bolster the defense and defend the unrecognized Republic of Nagorno-Karabakh from a possible renewal of hostilities with neighboring Azerbaijan. Jane's World Armies reports that both conscripts and officers from Armenia are routinely sent for duty to Karabakh, often posted to the frontline between Karabakh Armenian and Azerbaijani forces.[4]
Contents
History
The Armenian army's history is described to have gone through three different stages.[3] It entered the first stage in February 1988, from the beginning of the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict where Armenian militias were formed to combat growing hostilities in the region against similar Azeri units with the impending break of the Soviet Union. The second phase of the development of the army began in 1992, several months after Armenia had declared its independence. Ter-Grigoryants and other civilian officials in the Armenian Ministry of Defense including Vazgen Manukyan and Vazgen Sargsyan sought to establish a "small, well-balanced, combat-ready defense force."[5] The third phase began after the end of the war and continues on until today.
Most of the army's staff officers were members of the former Soviet military as an estimated 5,000 Armenians were serving as high level officers in it prior to the collapse of the Soviet Union.[6] Almost immediately after its independence, Armenia was embroiled in the Nagorno-Karabakh War with neighboring Azerbaijan. Intending to establish a force of 30,000 men, the army's standing force increased to 50,000 by early 1994. During the war, the military remained on high alert and bolstered defenses in the region of Zangezur, opposite of the Azerbaijani exclave of Nakhichevan to its west. Purported artillery bombardment in May 1992 from the region led to skirmishes between the two sides including the Armenian army's incursion into several of the villages. Since 1994, the army has taken an active role in ensuring the defense of the Nagorno Karabakh Republic in conjunction with its own Nagorno-Karabakh Defense Army.[7]
International missions
 An Armenian patrol, part of the Armenian KFOR contingent in Kosovo, carrying out an inspection at a checkpoint.
An Armenian patrol, part of the Armenian KFOR contingent in Kosovo, carrying out an inspection at a checkpoint.
The Armenian army has collaborated in several international missions with the West. On February 12, 2004, Armenia deployed a platoon-sized unit (three squads) to Kosovo as a part of the Greek peacekeeping battalion. The unit, known as the Peacekeeping Forces of Armenia, is headquartered in Camp "REGAS FEREOS" as a part of the Multi-National Task Force East and is tasked with maintaining vehicle check points, providing security for the base but also serves as a quick reaction force and crowd and riot control.[8] In 2008, the KFOR unit was expanded, adding a second platoon plus company staff (bringing Armenia's contingent to about 85 personnel).[9]
In the autumn of 2004, the Armenian government approved to dispatch a 46-man contingent from the army consisting of sappers, engineers and doctors under Polish command as part of the Multinational Force in Iraq. On November 10, 2006 Senior Lieutenant Georgy Nalbandyan was injured in a mine explosion in Iraq but survived after being transported for surgeries to a hospital in Landstuhl, Germany near Ramstein Air Base.[10] On October 6, 2008, due to improving security conditions, the contingent's tour of duty came to an end.[11]
In July 2009, the Defense Minister of Armenia, Seyran Ohanyan, announced that Armenia would send a force to participate with the International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) in the War in Afghanistan by the end of the year. He did not mention how large the force would be but did note that it probably would include munitions experts and communications officers. A MOD spokesmen also stated that the force would include medical specialists and translators as well. Ohanyan added that Armenian officers who served in the Soviet military during the Soviet War in Afghanistan also expressed the desire to return there as members of the new force.[12] In November 2009, a NATO official affirmed that an Armenian contingent numbering 30 troops will join the ISAF sometime in early 2010.[13] That number was revised to 40 in early December, when the Armenian parliament overwhelmingly voted in approval of the contingent's deployment. The servicemen arrived in Afghanistan in February 2010, where, under German command, they are tasked to defend the regional airport in Kunduz.[14]
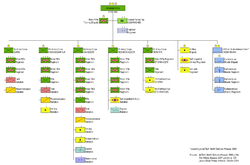
Organization
Armenian soldiers at the old building of the Vazgen Sargsyan Military Institute
General Staff
- Colonel-General Seyran Ohanyan - Defense Minister
- Colonel-General Mikael Harutyunyan - Chief Military Inspector and Presidential Advisor
- Colonel-General Gurgen Daribaltayan — Deputy head of Chief of Staff and special military adviser to current president, Serzh Sargsyan
- Colonel-General Harut Kassabyan - Commader of Capital Guard
- Lieutenant-General Aghik Myurzabekyan
- Lieutenant-General Arthur Aghabekyan
- Lieutenant-General Yuri Khachaturov
- Lieutenant-General Gurgen Melkonyan
- Lieutenant-General Roland Kereshyan
Academies
- Monte Melkonian Military Academy
- Vazgen Sargsyan Military Academy
Field Forces
- 1st Army Corps (HQ Goris)[4]: one independent tank battalion, one independent reconnaissance battalion, two motor rifle regiments.[15]
- 2nd Army Corps (HQ Khachaghbyur): one independent tank battalion, one independent reconnaissance battalion, one independent rifle regiment, two independent motor rifle regiments, one independent artillery battalion.
- 3rd Army Corps (HQ Vanadzor): one independent rifle regiment, one independent artillery battalion, one independent tank battalion, one independent reconnaissance battalion, one independent rocket artillery battalion, four independent motor rifle regiments, one maintenance battalion, one signals battalion.
- 4th Army Corps (HQ Yeghegnadzor): four independent motor rifle regiments, an independent self-propelled artillery battalion, one signals battalion.
- 5th Army Corps (HQ Nubarashen in Yerevan): two fortified areas, one independent motor rifle regiment, one independent rifle regiment.
- Army-level Troops:[15] one air and air defence joint command (Jane's World Armies mentions an Army Air and Air Defence at Chobankara under Colonel Ararat Hambarian), one training motor rifle brigade, one special forces regiment (Jane's World Armies mentions a regiment at Nubarashen under Colonel Artur Simonian), one artillery brigade, one self-propelled artillery regiment, one anti-tank regiment, one engineer regiment with demining centre, one surface-to-air missile brigade, two surface-to-air missile regiments, one radiotechnical (radar) regiment.
Brinkster.net reported in 2004 that according to media reports, the Army included the 555th Motor Rifle Regiment,[16] the 83rd Motor Rifle Brigade (Dasheksan), the 1st Motor Rifle Brigade, the 7th Fortified Region (Gyumri), the 9th Fortified Region (Etchmiadzin), a Motor Rifle Regiment (Etchmiadzin), the 538th Motor Rifle Regiment (Ağdaban), a Motor Rifle Regiment (Shushi), and the 545th Motor Rifle Regiment.
Equipment
Small arms in service with the army reportedly include the SPG-9, AKM, AK-74, AKS-74U, PK machine guns, Makarov PM, NSV (machine gun), Dragunov Sniper Rifles, Zastava M93 Black Arrow, and RPG-7 rocket propelled grenades.
Jane's reported in 2008 that the Armenian Army had 20 T-80s, 160 T-72s and 80 T-54s and T-22 in service.[17] According to the International Institute for Strategic Studies's report of 2007, also in service were 80 BMP-1s, 20 BMP-1Ks, 57 BMP-2s, and 22 BRM-1K infantry fighting vehicles. Wheeled APCs reported included 25 BTR-60s, 100 BTR-60 "look-a-likes" (a CFE equipment category), 21 BTR-70s, 50 BTR-80s, 145 MT-LBs, and 120 BRDM-2 scout vehicles.[15]
Anti-aircraft defense equipment included S-300, SA-4 Ganef, 2K12 Kub S-75, and S-125 weapon systems. Self-propelled air defense artillery systems include the ZSU-23-4 radar guided anti-aircraft weapon system, and the ZU-23-2 original Soviet variant.
Artillery reported in service includes the BM-30 Smerch multiple rocket launcher,[18] BM-21 "Grad" and 9А51 "Prima": 50-round launcher on a Ural-4320 5t chassis, 2S3 Akatsiya, 2S1 Gvozdika, D-30 - (90), 6WM-80, 34 152 mm towed gun-howitzer M1955 (D-20), and 26 152 mm gun 2A36. Reports of 29 T-12 antitank guns are not confirmed by the IISS, which only lists 9P149 tank destroyers (9K114 Shturm missiles mounted on MT-LB chassis) and AT-5 Spandrel antitank guided missiles. Smaller AD systems reported in service include the 9K33 Osa, Strela 2, 9K35 Strela-10, 57 mm AZP S-60. Radars in service reportedly include the P-40 radar, P-15 radar, and P-12 radar.
See also
Notes
- ^ The Military Balance 2010. London: Routledge for the IISS. 2010. p. 174. ISBN 1857435575.
- ^ Petrosyan, David. "Formation and Development of Armenian Armed Forces." Moscow Defence Brief. Centre for Analysis of Strategies and Technologies, Moscow, 6-2002, accessed November 2009. Ter-Grigoryants had previously served with the 40th Army (Soviet Union) in Afghanistan as chief of staff, supervising operations in May 1982 [1].
- ^ a b Ministry of Defence of the Republic of Armenia. General History of the Armenian Army. Retrieved January 31, 2006.
- ^ a b Jane's World Armies Armenia, October 2004.
- ^ Curtis, Glenn E. and Ronald G. Suny. "Armenia" in Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia Country Studies. Ed. Glenn E. Curtis. Washington D.C.: Federal Research Division Library of Congress, 1995, p. 72.
- ^ Mirsky, Georgiy I. On Ruins of Empire: Ethnicity and Nationalism in the Former Soviet Union. Westport, CT: Greenwood Press, 1997, p. 63. ISBN 0-313-30044-5.
- ^ See Richard Giragosian, "Armenia and Karabakh: One Nation, Two States." AGBU Magazine. № 1, Vol. 19, May 2009, pp. 12-13.
- ^ Kosovo Force. KFOR Contingent: Armenia. KFOR. Last updated January 24, 2006. Accessed February 9, 2007.
- ^ NATO’s relations with Armenia. NATO. Retrieved November 29, 2009.
- ^ "Armenian peacekeeper to undergo two more surgeries." Public Radio of Armenia. November 20, 2006. Retrieved February 1, 2007.
- ^ Glassey, Eric. "Armenians Complete Successful Mission." Multinational Force in Iraq. October 7, 2008. Accessed September 6, 2009.
- ^ "Armenia to send forces to Afghanistan this year." Armenian Reporter. July 24, 2009. Retrieved September 6, 2009.
- ^ "Armenia To Send Troops To Afghanistan." RFE/RL. November 09, 2009. Retrieved November 29, 2009.
- ^ "Armenian Parliament Endorses Troop Deployment To Afghanistan." RFE/RL. December 8, 2009. Retrieved January 3, 2010.
- ^ a b c IISS (2007). The Military Balance 2007. London: Routledge for the IISS. p. 155. ISBN 978-1-85743-437-8.
- ^ See Human Rights Watch/Helsinki, Azerbaijan: Seven years of conflict in Nagorno-Karabakh, p. 69
- ^ Jane's World Armies Armenia, 2008.
- ^ An unspecified number are in service in the army, according to Armenian Defense Ministry officials, with plans to acquire more: "Armenian Military 'Interested' In Acquiring Russian Rocket Artillery." RFE/RL. June 9, 2011. Retrieved June 11, 2011.
External links
Armies (land forces) in Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- Vatican City
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Kosovo
- Nagorno-Karabakh Republic
- Northern Cyprus
- South Ossetia
- Transnistria
 Armenia topics
Armenia topicsHistory (timeline) EarlyOrigins · Name · Kura-Araxes culture · Hayk · Hayasa-Azzi · Mitanni · Nairi · Kingdom of Urartu · Orontid dynasty · Kingdom of Armenia · Roman Armenia · Byzantine Armenia · Bagratuni Armenia · Armenian Kingdom of CiliciaMiddleModernBy topicGovernment and
politicsConstitution · President · Prime Minister · National Assembly · Political parties · Elections · Foreign relations · Corruption · Human rights · LGBT rights · Relations with the European Union · more on government / politicsEconomy Armenian dram · Central Bank · List of companies · Armex · Agriculture · Industry · Communications · Transport · Energy · Mining · Waste management · International rankingsAdministrative
divisionsArmed Forces Geography Demographics Religion Culture Symbols Categories:- Armies by country
- Military of Armenia
- Military units and formations established in 1992
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.