- Dibutyl phthalate
-
Dibutyl phthalate 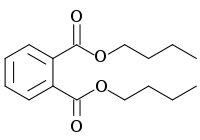
 Dibutyl phthalateOther namesDi-n-butyl phthalate, Butyl phthalate, n-Butyl phthalate, 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid dibutyl ester, o-Benzenedicarboxylic acid dibutyl ester, DBP, Palatinol C, Elaol
Dibutyl phthalateOther namesDi-n-butyl phthalate, Butyl phthalate, n-Butyl phthalate, 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid dibutyl ester, o-Benzenedicarboxylic acid dibutyl ester, DBP, Palatinol C, ElaolIdentifiers CAS number 84-74-2 
PubChem 3026 ChemSpider 2918 
UNII 2286E5R2KE 
EC number 201-557-4 KEGG C14214 
RTECS number TI0875000 Properties Molecular formula C16H22O4 Molar mass 278.34 g mol−1 Appearance Colorless oily liquid Density 1.05 g/cm3 at 20 °C Melting point -35 °C, 238 K, -31 °F
Boiling point 340 °C, 613 K, 644 °F
Solubility in water 0.013 g/L log P 4.72 Hazards R-phrases R50 R61 R62 S-phrases S45 S53 S61 Main hazards Dangerous for the environment (N), Harmful (Xi) NFPA 704 Flash point 157 °C (closed cup) Autoignition
temperature402 °C Explosive limits 0.5 - 3.5%  phthalate (verify) (what is:
phthalate (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Dibutyl phthalate (DBP) is a commonly used plasticizer. It is also used as an additive to adhesives or printing inks. It is soluble in various organic solvents, e.g. in alcohol, ether and benzene. DBP is also used as an ectoparasiticide.
Contents
Legislative Control
European Union
The use of this substance in cosmetics, including nail polishes, is banned in the European Union under Directive 76/768/EEC 1976.[1][2]
The use of DBP has been restricted in the European Union for use in children's toys since 1999.[3]
United States
DBP was added to the California Proposition 65 (1986) list of suspected teratogens in November 2006. It is a suspected endocrine disruptor. It was used in some nail polishes; all major producers began eliminating this chemical from nail polishes in the Fall of 2006.
DBP was permanently banned in children's toys and childcare articles, in concentrations of 1000 ppm or greater, under section 108 of the Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act of 2008 (CPSIA).
Production
DBP is produced by the reaction of n-butanol with phthalic anhydride. It is produced domestically by Eastman Chemical Company, but they have announced that they will end production and exit the DBP and DEP (diethyl phthalate) market in December 2011.[4]
The Czech manufacturer DEZA continues to produce DBP under REACh registration
Exposure
Based on urine samples from people of different ages, the European Commission Scientific Committee on Health and Environmental Risks (SCHER) concluded that total exposures to individual phthalates in the general population are below tolerable daily intakes (TDI), except in the case of DBP for which efforts to further reduce exposures are needed.[5]
Food Contamination
DHP and DEHP have been found in food as a substitute for palm oil during a scandal in Taiwan. Among the kinds of foods were yoghurt powder, energy drinks, fruit jam, powder and syrup.[6]
Obesity
A study on CDC data published in Environmental Health Perspectives, revealed that American men with abdominal obesity or insulin resistance (a precursor to diabetes) were more likely to have high levels of DEHP and DBP metabolites in their urine than men without those problems.[7][dead link]
See also
- Phthalic acid
- Phthalates
- Diisobutyl phthalate (DIBP)
References
- ^ [1] EU Council Directive 76/768/EEC of 27 July 1976 on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to cosmetic products]
- ^ Example of a nail polish recall in Ireland of nail polish containing dibutyl phthalate
- ^ Ban of phthalates in childcare articles and toys, press release IP/99/829, 10 November 1999
- ^ "Eastman Announces Discontinuation of Manufacture of DEP and DBP Plasticizers". Eastman. March 16, 2011. http://www.eastman.com/Company/News_Center/2011/Pages/Eastman_Announces_Discontinuation_of_Manufacture_of_DEP_and_DBP_Plasticizers.aspx.
- ^ "Phthalates in school supplies". GreenFacts Website. http://copublications.greenfacts.org/en/phthalates-school-supplies/. Retrieved 2009-06-10.
- ^ http://www.abs-cbnnews.com/lifestyle/05/31/11/taiwanese-products-dehp-named
- ^ Fat's Hidden Trigger
External links
- International Chemical Safety Card 0036
- MSDS sheet
- Dibutyl Phthalate and Cosmetics
- Hazardous substance fact sheet
- Occupational safety and health guideline for dibutyl phthalate
Health issues of plastics and Polyhalogenated compounds (PHCs) Plasticizers: Phthalates Miscellaneous plasticizers Monomers Bisphenol A (BPA, in Polycarbonates) · Vinyl chloride (in PVC)Miscellaneous additives incl. PHCs Health issues Miscellanea PVC · Plastic recycling · Plastic bottle · Vinyl chloride · Dioxins · Polystyrene · Styrofoam · PTFE (Teflon) · California Proposition 65 · List of environmental health hazards · Persistent organic pollutant · European REACH regulation · Japan Toxic Substances Law · Toxic Substances Control ActCategories:- Plasticizers
- Phthalates
- Endocrine disruptors
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

