- Bis(2-ethylhexyl) adipate
-
Bis(2-ethylhexyl) adipate 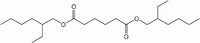 Hexanedioic acid bis(2-ethylhexyl) esterOther namesDiisooctyl adipate; Di(2-ethylhexyl) adipate
Hexanedioic acid bis(2-ethylhexyl) esterOther namesDiisooctyl adipate; Di(2-ethylhexyl) adipateIdentifiers Abbreviations DEHA CAS number 103-23-1 
PubChem 7641 ChemSpider 7358 
UNII MBY1SL921L 
KEGG C14240 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C(OCC(CC)CCCC)CCCCC(=O)OCC(CCCC)CC
Properties Molecular formula C22H42O4 Molar mass 370.57 g mol−1 Appearance colourless oily liquid Density 0.93 g/cm3 Melting point -67.8 °C, 205 K, -90 °F
Boiling point 417 °C, 690 K, 783 °F
Solubility in water negligible Vapor pressure 2.6 mm Hg at 200 °C Hazards MSDS Oxford University EU classification  Xi
XiFlash point 196 °C Autoignition
temperature377 °C  adipate (verify) (what is:
adipate (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Bis(2-ethylhexyl) adipate or DEHA is a plasticizer. DEHA is an ester of 2-ethylhexanol and adipic acid. Its chemical formula is C22H42O4.
DEHA is sometimes called "dioctyl adipate", incorrectly. Other names include diisooctyl adipate and di(2-ethylhexyl) adipate.
Use
DEHA is used as a functional hydraulic fluid, and a component of aircraft lubricants. It is sometimes also used as an ingredient in PVC-based plastic wrap.
Toxicity
DEHA has been demonstrated to induce liver adenomas and carcinomas in mice but not in rats. According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), it is "not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans (Group 3),"[1] suggesting inadequate evidence of human carcinogenicity.[2] While once on a U.S. Environmental Protection Agency list of toxic chemicals under the Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act, it has been removed because it "cannot be reasonably anticipated to cause [...] irreversible chronic health effects."[3]
References
- ^ IARC - Summaries & Evaluations: DI(2-ETHYLHEXYL) ADIPATE, 77, 2000, p. 149, http://www.inchem.org/documents/iarc/vol77/77-02.html, retrieved 2008-12-20
- ^ Inchem Preamble Evaluation, 1-5-1999, http://www.inchem.org/documents/iarc/monoeval/eval.html, retrieved 2008-12-20
- ^ Bottle Royale, http://www.snopes.com/medical/toxins/petbottles.asp, retrieved 2008-12-20
Health issues of plastics and Polyhalogenated compounds (PHCs) Plasticizers: Phthalates Miscellaneous plasticizers Monomers Bisphenol A (BPA, in Polycarbonates) · Vinyl chloride (in PVC)Miscellaneous additives incl. PHCs Health issues Miscellanea PVC · Plastic recycling · Plastic bottle · Vinyl chloride · Dioxins · Polystyrene · Styrofoam · PTFE (Teflon) · California Proposition 65 · List of environmental health hazards · Persistent organic pollutant · European REACH regulation · Japan Toxic Substances Law · Toxic Substances Control ActCategories:- Adipates
- Plasticizers
- Ester solvents
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
