- History of Danish
-
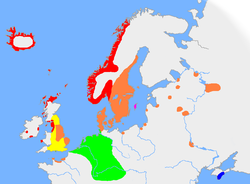
The approximate extent of Old Norse and related languages in the early 10th century:
 Old West Norse dialectOld East Norse dialectOld Gutnish dialectOther Germanic languages with which Old Norse still retained some mutual intelligibility
Old West Norse dialectOld East Norse dialectOld Gutnish dialectOther Germanic languages with which Old Norse still retained some mutual intelligibility
This article is part of the series on:
Danish languageUse:
Alphabet
Phonology
GrammarOther topics:
History
Literature
This article is part of a series on:
Old NorseDialects- Old West Norse
- (Old Icelandic · Old Norwegian · Greenlandic Norse)
- Old East Norse
- (Old Danish · Old Swedish)
- Old Gutnish
Use- Orthography
- Runic alphabet
- (Younger Futhark · Medieval)
- Latin alphabet
- Grammar
- Phonology
- Morphology
LiteratureAncestorsThe Danish language originates from a common Germanic language. In the 8th century the language of Scandinavia, Proto-Norse, had undergone some changes and evolved into Old Norse. This language began to undergo new changes that did not spread to all of Scandinavia, which resulted in the appearance of two similar dialects, Old West Norse (Norway and Iceland) and Old East Norse (Denmark and Sweden).
Old East Norse is in Sweden called Runic Swedish and in Denmark Runic Danish, but until the 12th century, the dialect was the same in the two countries. The dialects are called runic because the main body of text appears in the runic alphabet. Unlike Proto-Norse, which was written with the Elder Futhark alphabet, Old Norse was written with the Younger Futhark alphabet, which only had 16 letters. Due to the limited number of runes, some runes were used for a range of phonemes, such as the rune for the vowel u which was also used for the vowels o, ø and y, and the rune for i which was also used for e.
A change that separated Old East Norse (Runic Swedish/Danish) from Old West Norse was the change of the diphthong æi (Old West Norse ei) to the monophthong e, as in stæin to sten. This is reflected in runic inscriptions where the older read stain and the later stin. There was also a change of au as in dauðr into ø as in døðr. This change is shown in runic inscriptions as a change from tauþr into tuþr. Moreover, the øy (Old West Norse ey) diphthong changed into ø as well, as in the Old Norse word for "island".
From 1100 and onwards, the dialect of Denmark began to diverge from that of Sweden. The innovations spread unevenly from Denmark which created a series of minor dialectal boundaries, isoglosses, ranging from Zealand to Svealand.
Some notable authors of works in Danish are existential philosopher Søren Kierkegaard, prolific fairy tale author Hans Christian Andersen, and playwright Ludvig Holberg. Three 20th century Danish authors have become Nobel Prize laureates in Literature: Karl Adolph Gjellerup and Henrik Pontoppidan (joint recipients in 1917) and Johannes Vilhelm Jensen (awarded 1944).
The first translation of the Bible in Danish was published in 1550.
References
- "Language" (PDF). Royal Danish ministry of foreign affairs. http://www.um.dk/Publikationer/UM/English/FactsheetDenmark/Language/pdf/sprog_uk_03.pdf.
Histories of the world's languages Bulgarian · Catalan · Chinese (Mandarin) · Czech · Danish · Dutch · English · Esperanto · French (Quebec) · German · Greek · Hungarian · Hindustani · Icelandic · Interlingua · Irish · Korean · Latin · Macedonian · Moldovan · Norwegian · Persian · Portuguese · Romanian · Russian · Scots · Slovak · Spanish · Swedish · Welsh
Germanic languages · Germanic philology Language subgroups Reconstructed Proto-Germanic · Proto-Germanic grammarHistorical languages NorthEastWestModern languages Afrikaans · Alemannic · Danish · Dutch · English · Faroese · German · Gutnish · Icelandic · Limburgish · Low German · Luxembourgish · North Frisian · Norwegian · Saterland Frisian · Scots · Swedish · Vilamovian · West Frisian · YiddishDiachronic features Synchronic features Language histories Categories:- Language histories
- Danish language
- Old Norse language
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.