- Carbamoyl phosphate
-
Carbamoyl phosphate 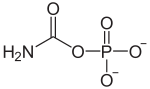
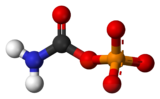 (Carbamoyloxy)phosphonic acid
(Carbamoyloxy)phosphonic acidIdentifiers CAS number 590-55-6 PubChem 278 MeSH Carbamoyl+phosphate Jmol-3D images Image 1 - C(=O)(N)OP(=O)(O)O
Properties Molecular formula CH2NO5P2- Molar mass 141.020 g/mol  phosphate (verify) (what is:
phosphate (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Carbamoyl phosphate is an anion of biochemical significance. In land-dwelling animals it is an intermediary metabolite participating in the nitrogen disposal through in the urea cycle and the synthesis of pyrimidines.
It is produced from bicarbonate, ammonia (derived from glutamate), and phosphate (from ATP). The synthesis is catalysed by the enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthetase, as follows:
- HCO3− + ATP → ADP + HO–C(O)–OPO32− (carboxyl phosphate)
- HO–C(O)–OPO32− + NH3 + OH− → HPO42− + −O–C(O)NH2 + H2O
- −O–C(O)NH2 + ATP → ADP + H2NC(O)OPO32−
See also
References
- Nelson, David L. and Michael M. Cox. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry fourth edition. W. H. Freeman and company New York.
Nucleotide metabolic intermediates Purine metabolism AnabolismCatabolismPyrimidine metabolism AnabolismCarbamoyl phosphate · Carbamoyl aspartic acid · 4,5-Dihydroorotic acid · Orotic acid · Orotidine 5'-monophosphate · Uridine monophosphateCatabolismbiochemical families: prot · nucl · carb (glpr, alco, glys) · lipd (fata/i, phld, strd, gllp, eico) · amac/i · ncbs/i · ttpy/iL-citrulline Carbamoyl
phosphateL-ornithine 
Pi 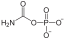
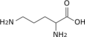

L-aspartate Urea 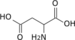
+ ATP 
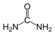
PPi + AMP H2O 
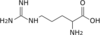

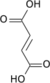
L-argininosuccinate Fumarate L-arginine Categories:- Organophosphates
- Carbamates
- Acid anhydrides
- Urea cycle
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
