- Citrulline
-
Citrulline 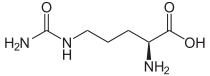
 2-Amino-5-(carbamoylamino)pentanoic acid
2-Amino-5-(carbamoylamino)pentanoic acidIdentifiers CAS number 372-75-8 
PubChem 9750 ChemSpider 9367 
UNII 29VT07BGDA 
DrugBank DB00155 KEGG D07706 
ChEBI CHEBI:16349 
ChEMBL CHEMBL444814 
IUPHAR ligand 722 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - O=C(O)[C@@H](N)CCCNC(=O)N
Properties Molecular formula C6H13N3O3 Molar mass 175.19 g mol−1  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references The organic compound citrulline is an α-amino acid. Its name is derived from citrullus, the Latin word for watermelon, from which it was first isolated in 1930.[1] It has the idealized formula H2NC(O)NH(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. It is a key intermediate in the urea cycle, the pathway by which mammals excrete ammonia.
Contents
Biosynthesis
Citrulline is made from ornithine and carbamoyl phosphate in one of the central reactions in the urea cycle. It is also produced from arginine as a by-product of the reaction catalyzed by NOS family (NOS; EC 1.14.13.39).[2] Arginine is first oxidized into N-hydroxyl-arginine, which is then further oxidized to citrulline concomitant with release of nitric oxide.
Function
Although citrulline is not coded for by DNA directly, several proteins are known to contain citrulline as a result of a posttranslational modification. These citrulline residues are generated by a family of enzymes called peptidylarginine deiminases (PADs), which convert arginine into citrulline in a process called citrullination or deimination. Proteins that normally contain citrulline residues include myelin basic protein (MBP), filaggrin, and several histone proteins, whereas other proteins, such as fibrin and vimentin are susceptible to citrullination during cell death and tissue inflammation.
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis often have detectable antibodies against proteins containing citrulline. Although the origin of this immune response is not known, detection of antibodies reactive with citrulline (anti-citrullinated protein antibodies) containing proteins or peptides is now becoming an important help in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis.[3]
In recent studies, citrulline has been found to relax blood vessels.[4]
Sources
Citrulline in the form of citrulline malate is sold as a performance-enhancing athletic dietary supplement, which was shown to reduce muscle fatigue in a preliminary clinical trial.[5]
The rind of watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) is a good natural source of citrulline.[6]
See also
References
- ^ Wada, M (1930). "Über Citrullin, eine neue Aminosäure im Presssaft der Wassermelone, Citrullus vulgaris Schrad.". Biochem. Zeit. 224: 420.
- ^ Cox M, Lehninger AL, Nelson DR (2000). Lehninger principles of biochemistry (3rd ed.). New York: Worth Publishers. ISBN 1-57259-153-6.
- ^ Coenen D, Verschueren P, Westhovens R, Bossuyt X (March 2007). "Technical and diagnostic performance of 6 assays for the measurement of citrullinated protein/peptide antibodies in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis". Clin. Chem. 53 (3): 498–504. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2006.078063. PMID 17259232. http://www.clinchem.org/cgi/content/full/53/3/498.
- ^ Viagra-Like Effects From Watermelon
- ^ Bendahan D, Mattei JP, Ghattas B, Confort-Gouny S, Le Guern ME, Cozzone PJ (Aug 2002). "Citrulline/malate promotes aerobic energy production in human exercising muscle". Br J Sports Med 36 (4): 282–9. doi:10.1136/bjsm.36.4.282. PMC 1724533. PMID 12145119. http://bjsm.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=12145119.
- ^ Watermelon May Have Viagra-effect
Categories:- Amino acids
- Ureas
- Urea cycle
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
