- Draco (constellation)
-
Draco Constellation 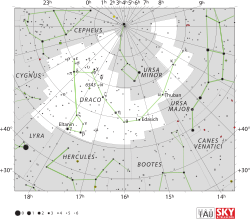
List of stars in DracoAbbreviation Dra Genitive Draconis Pronunciation /ˈdreɪkoʊ/, genitive /drəˈkoʊnɨs/ Symbolism the Dragon Right ascension 17 h Declination +65° Quadrant NQ3 Area 1083 sq. deg. (8th) Main stars 14 Bayer/Flamsteed
stars76 Stars with planets 9 Stars brighter than 3.00m 3 Stars within 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) 7 Brightest star γ Dra (Eltanin) (2.24m) Nearest star Struve 2398
(11.52 ly, 3.53 pc)Messier objects 1 Meteor showers Draconids Bordering
constellationsBoötes
Hercules
Lyra
Cygnus
Cepheus
Ursa Minor
Camelopardalis
Ursa MajorVisible at latitudes between +90° and −15°.
Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of July.Draco is a constellation in the far northern sky. Its name is Latin for dragon. Draco is circumpolar (that is, never setting) for many observers in the northern hemisphere. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations today.
In Chinese astronomy, constellation Draco were divided in two areas. The areas are:
- Purple Forbidden enclosure (紫微垣, Zǐ Wēi Yuán)
- The Black Tortoise of the North (北方玄武, Běi Fāng Xuán Wǔ)
Contents
Notable features
Eltanin (Gamma Draconis) is the brightest star in Draco, with an apparent magnitude of 2.24.
The constellation contains the star recently named Kepler-10 which has been confirmed to be orbited by Kepler-10b, the smallest ever rocky Earth-sized planet detected outside of our solar system.
The star Thuban (α Draconis) was the northern pole star around 2700 BC, during the time of the ancient Egyptians. Due to the effects of precession, it will once again be the pole star around the year 21000 AD.
One of the deep-sky objects in Draco is the Cat's Eye Nebula (NGC 6543), a planetary nebula that is said to look like a blue disc. There are several faint galaxies in Draco, one of which is the lenticular galaxy NGC 5866, sometimes considered to be Messier Object 102. Another is the Draco Dwarf Galaxy, one of the least luminous galaxies with an absolute magnitude of -8.6 and a diameter of only about 3,500 light years, discovered by Albert G. Wilson of Lowell Observatory in 1954.
The Draco nebula (a soft X-ray shadow) is outlined by contours in the image at right and is blue-black. This image was produced by ROSAT of a portion of the constellation Draco.
Mythology
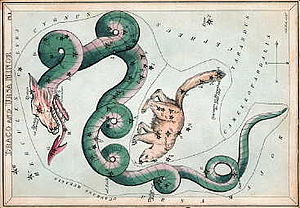 Draco coils around the north celestial pole, as depicted in Urania's Mirror, a set of constellation cards published in London c.1825
Draco coils around the north celestial pole, as depicted in Urania's Mirror, a set of constellation cards published in London c.1825
Draco, the dragon is an element in several of the more famous Ancient Greek myths. Draco represents Ladon, the dragon sometimes depicted with one hundred heads who guarded the golden apples of the Hesperides. The eleventh of the Twelve Labours of Hercules was to steal the golden apples. He killed Ladon with one of the arrows he dipped in the poison blood of the hydra. Hercules had no way of getting the apples even so because of the nymphs that watch over the apple tree. Atlas, the bearer of the sky, offered to get him an apple if Hercules could take his place until he returned. Hercules knew that Atlas was allowed passage because the nymphs who watched over the tree were his daughters, and agreed. Atlas came back with the apples, but he had no intention of letting Hercules walk away while he had to bear the weight of the sky on his shoulders. He was going to leave, but Hercules asked Atlas if he could hold the sky while Hercules put on his lion skin that he got from killing the Nemean Lion. Atlas stupidly agreed. Quickly, Hercules grabbed the apple from Atlas's hand, leaving Atlas holding the sky once more while Hercules completed his labor. According to the legend, Hera later placed the dragon in the sky as the constellation Draco. Due to its position and nearby constellations in the zodiac sign of Libra (i.e. Ursa Major, Ursa Minor, and Boötes), the group of constellations can be seen to tell the tale of the eleventh labor.[original research?]
In another Greek legend, Draco represents the dragon killed by Cadmus before founding the city of Thebes, Greece. In a third legend, it represents the dragon that guarded the Golden Fleece (occasionally revealed as the sleeping or nearly dead figure of Ladon) and was killed by Jason. The fact that the stars of this circumpolar constellation never set plays an important part in its mythologies.[citation needed]
In Roman legend, Draco was a dragon killed by the goddess Minerva and tossed into the sky upon his defeat.[citation needed]
Early Christians originally of the Roman or Greek faith then depicted Draco as the serpent who tempted Adam and Eve in the Garden of Eden.
The Arabs did not interpret the constellation as a dragon, seeing instead an asterism called the Mother Camels.[citation needed]
In Chinese Astronomy, Draco is part of the Purple Forbidden enclosure, in which Draco represent one of the three great gods, and the abode of the Celestial Emperor. The Forbidden City, literally "purple forbidden city", is considered as a terrestrial mirror to the celestial palace and thus named after the constellation. A region at the curve of the Dragon's tail is called "Tien Choo" or "Heaven's Kitchen".
Namesakes
USS Draco (AK-79) was a United States Navy Crater class cargo ship named after the constellation.
References
- Ian Ridpath and Wil Tirion (2007). Stars and Planets Guide, Collins, London. ISBN 978-0007251209. Princeton University Press, Princeton. ISBN 978-0691135564.
- موسوعة اسماء النجوم عند العرب في الفلك القديم والحديث - د. عبد الرحيم بدر - 1998
External links
Andromeda · Antlia · Apus · Aquarius · Aquila · Ara · Aries · Auriga · Boötes · Caelum · Camelopardalis · Cancer · Canes Venatici · Canis Major · Canis Minor · Capricornus · Carina · Cassiopeia · Centaurus · Cepheus · Cetus · Chamaeleon · Circinus · Columba · Coma Berenices · Corona Australis · Corona Borealis · Corvus · Crater · Crux · Cygnus · Delphinus · Dorado · Draco · Equuleus · Eridanus · Fornax · Gemini · Grus · Hercules · Horologium · Hydra · Hydrus · Indus · Lacerta · Leo · Leo Minor · Lepus · Libra · Lupus · Lynx · Lyra · Mensa · Microscopium · Monoceros · Musca · Norma · Octans · Ophiuchus · Orion · Pavo · Pegasus · Perseus · Phoenix · Pictor · Pisces · Piscis Austrinus · Puppis · Pyxis · Reticulum · Sagitta · Sagittarius · Scorpius · Sculptor · Scutum · Serpens · Sextans · Taurus · Telescopium · Triangulum · Triangulum Australe · Tucana · Ursa Major · Ursa Minor · Vela · Virgo · Volans · VulpeculaStars of Draco Bayer α (Thuban) • β (Rastaban) • γ (Eltanin) • δ (Altais) • ε (Tyl) • ζ (Aldhibah) • η (Aldhibain) • θ • ι (Edasich) • κ • λ (Gianfar) • μ (Arrakis) • ν (Kuma) • ξ (Grumium) • ο • π • ρ • σ (Alsafi) • τ • υ • φ • χ • ψ (Dziban) • ω • b • c • d • e • f • g • h • i • AFlamsteed 1 (λ, Gianfar) • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 (κ) • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 (i) • 11 (α, Thuban) • 12 (ι, Edasich) • 13 (θ) • 14 (η, Aldhibain) • 15 (A) • 16 • 17 • 18 (g) • 19 (h) • 20 • 21 (μ, Arrakis) • 22 (ζ, Aldhibah) • 23 (β, Rastaban) • 24 (ν¹, Kuma) • 25 (ν², Kuma) • 26 • 27 (f) • 28 (ω) • 29 • 30 • 31 (ψ, Dziban) • 32 (ξ, Grumium) • 33 (γ, Eltanin) • 34 • 35 • 36 • 37 • 38 • 39 (b) • 40 • 41 • 42 • 43 (φ) • 44 (χ) • 45 (d) • 46 (c) • 47 (ο) • 48 • 49 • 50 • 51 • 52 (υ) • 53 • 54 • 55 • 56 • 57 (δ, Altais) • 58 (π) • 59 • 60 (τ) • 61 (σ, Alsafi) • 62 • 63 (ε, Tyl) • 64 (e) • 65 • 66 • 67 (ρ) • 68 • 69 • 70 • 71 • 72 • 73 • 74 • 75 • 76Nearby Struve 2398 • Gliese 687 • σ (Alsafi) • GJ 1221 • Gliese 625 • GJ 4053 • Gliese 793 • SSSPM J1138-7722 • GJ 1227 • χ (Batentaban Borealis) • WISE 1647+5632Categories:- Draco constellation
- Constellations
- Dragons
- Northern constellations
- Constellations listed by Ptolemy
- Western constellations
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

