- Columba (constellation)
-
Columba Constellation 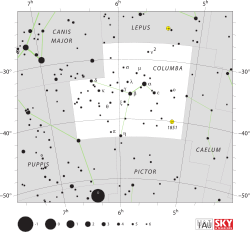
List of stars in ColumbaAbbreviation Col Genitive Columbae Pronunciation /kəˈlʌmbə/, genitive /kəˈlʌmbiː/ Symbolism the dove Right ascension 6 h Declination −35° Quadrant SQ1 Area 270 sq. deg. (54th) Main stars 5 Bayer/Flamsteed
stars18 Stars with planets 0 Stars brighter than 3.00m 1 Stars within 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) 0 Brightest star α Col (Phact) (2.65m) Nearest star Gliese 218
(48.89 ly, 14.99 pc)Messier objects 0 Meteor showers None Bordering
constellationsLepus
Caelum
Pictor
Puppis
Canis MajorVisible at latitudes between +45° and −90°.
Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of February.Columba is a small, faint constellation created in the late sixteenth century. Its name is Latin for dove. It is located just south of Canis Major and Lepus.
Contents
History
Columba was created by Dutch astronomer Petrus Plancius in 1592 in order to differentiate the 'unformed stars' of the large constellation Canis Major. Plancius first depicted Columba on the small celestial planispheres of his large wall map of 1592. It is also shown on his smaller world map of 1594 and on early Dutch celestial globes.
Plancius originally named the constellation Columba Noachi ("Noah's Dove"), referring to the dove that gave Noah the information that the Great Flood was receding. This name is found on early 17th-century celestial globes and star atlases (such as Bayer's Uranometria of 1603[1]).
Notable features
Columba is rather inconspicuous, the brightest star α Columbae having the magnitude of 2.65m. α Columbae is called Phact, which comes from Arabic Al-Fakhita (the dove). The only other named star is Beta, β, Columbae, which has the name Wazn or Wezn, from the Arabic for a weight.
Columba is the constellation that is at the solar antapex - the Earth (and Sun) is moving away from its direction as the solar system moves through space.
The constellation contains the runaway star μ Columbae, which was probably expelled from the ι Orionis system.
See also
Citations
References
- Ian Ridpath and Wil Tirion (2007). Stars and Planets Guide, Collins, London. ISBN 978-0007251209. Princeton University Press, Princeton. ISBN 978-0691135564.
External links
Andromeda · Antlia · Apus · Aquarius · Aquila · Ara · Aries · Auriga · Boötes · Caelum · Camelopardalis · Cancer · Canes Venatici · Canis Major · Canis Minor · Capricornus · Carina · Cassiopeia · Centaurus · Cepheus · Cetus · Chamaeleon · Circinus · Columba · Coma Berenices · Corona Australis · Corona Borealis · Corvus · Crater · Crux · Cygnus · Delphinus · Dorado · Draco · Equuleus · Eridanus · Fornax · Gemini · Grus · Hercules · Horologium · Hydra · Hydrus · Indus · Lacerta · Leo · Leo Minor · Lepus · Libra · Lupus · Lynx · Lyra · Mensa · Microscopium · Monoceros · Musca · Norma · Octans · Ophiuchus · Orion · Pavo · Pegasus · Perseus · Phoenix · Pictor · Pisces · Piscis Austrinus · Puppis · Pyxis · Reticulum · Sagitta · Sagittarius · Scorpius · Sculptor · Scutum · Serpens · Sextans · Taurus · Telescopium · Triangulum · Triangulum Australe · Tucana · Ursa Major · Ursa Minor · Vela · Virgo · Volans · VulpeculaNearby APList Categories:- Columba constellation
- Constellations
- Southern constellations
- Eastern constellations
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
