- Delphinus
-
Delphinus Constellation 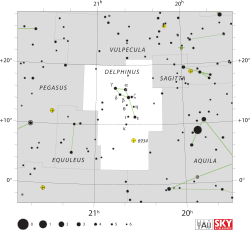
List of stars in DelphinusAbbreviation Del Genitive Delphini Pronunciation /dɛlˈfaɪnəs/ Delfínus, genitive /dɛlˈfaɪnaɪ/ Symbolism Dolphin Right ascension 21 h Declination +10° Quadrant NQ4 Area 189 sq. deg. (69th) Main stars 5 Bayer/Flamsteed
stars19 Stars with planets 5 Stars brighter than 3.00m 0 Stars within 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) 2 Brightest star Rotanev (β Del) (3.63m) Nearest star HU Del
(29.01 ly, 8.89 pc)Messier objects 0 Meteor showers None Bordering
constellationsVulpecula
Sagitta
Aquila
Aquarius
Equuleus
PegasusVisible at latitudes between +90° and −70°.
Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of October.Delphinus is a constellation in the northern sky, close to the celestial equator. Its name is Latin for dolphin. Delphinus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains among the 88 modern constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. It is one of the smaller constellations, ranked 69th in size.
Delphinus's brightest stars form a distinctive asterism that can easily be recognized. It is bordered (clockwise from north) by Vulpecula the fox, Sagitta the arrow, Aquila the eagle, Aquarius the water-carrier, Equuleus the foal and Pegasus the flying horse.
Contents
Notable features
Stars
The two brightest stars of this constellation, Svalocin (Alpha Delphini) and Rotanev (Beta Delphini), are not, as one might expect, names dating from antiquity, but instead date from a star catalogue of 1814 that was published at the Palermo Observatory in Italy. When read backwards they form the name Nicolaus Venator which is the Latinized version of the name of the assistant director of that observatory at that time, Niccolò Cacciatore (both Cacciatore and Venator mean hunter).
- α Del (Sualocin): B9 IV, 3.77m (multiple star association, with 7 components, of which only the A & G components are the primary, the others only optical)
- β Del (Rotanev): F5 IV, 4m - 4.9 m (5-star association, of which A & B components are primary, the rest optical)
- γ Del: one of the finest double stars in the sky.
- γ1 Del: F7 V, 5.14m
- γ² Del: K1 IV, 4.27m
- δ Del: A7 IIIp, 4.43m
- The above mentioned stars form an asterism called Job's Coffin.
- ε Del (Deneb Dulfim, or the tail of the Dolphin) is a star of spectral class B6 III with a magnitude of 4
- R Delphini|R Del: Mira-type variable star with a period of 285.5 days; magnitude range between 7.6 and 13.8
- ρ Aquilae moved across the border into Delphinus in 1992
Deep Space Objects
- NGC 6891: Planetary nebula; 10.5m
- NGC 6934: This globular cluster is of magnitude 9.75
- NGC 7006: at a distance of about 185,000 light-years this globular cluster is extremely remote; 11.5m
Mythology
Delphinus is associated with two stories from Greek mythology.
According to the first one, the Greek god Poseidon wanted to marry Amphitrite, a beautiful nereid. She, however, wanting to protect her virginity, fled to the Atlas mountains. Her suitor then sent out several searchers, among them a certain Delphinus. Delphinus accidentally stumbled upon her and was able to persuade Amphitrite to accept Poseidon's wooing. Out of gratitude the god placed the image of a dolphin among the stars.[citation needed]
The second story tells of the Greek poet Arion of Lesbos (7th century BC), a court musician at the palace of Periander, ruler of Corinth. Arion had amassed a fortune during his travels to Sicily and Italy. On his way home from Tarentum his wealth caused the crew of his ship to conspire against him. Threatened with death, Arion asked to be granted a last wish which the crew granted: he wanted to sing a dirge. This he did, and while doing so, flung himself into the sea. There, he was rescued by a dolphin which had been charmed by Arion's music. The dolphin carried Arion to the coast of Greece and left.[1]
Equivalents
In Chinese astronomy, the stars of Delphinus are located within the Black Tortoise of the North (北方玄武, Běi Fāng Xuán Wǔ).[2]
Namesakes
USS Delphinus (AF-24) and USS Delphinus (PHM-1), two United States Navy ships, are named after the constellation.
See also
Notes
- ^ Herodotus, Histories I.23-24;
also Aulus Gellius, Noctes Atticae XVI.19; Plutarch, Conv. sept. sap. 160-62; Shakespeare, Twelfth Night (Act I, Sc 2, line 16) - ^ (Chinese) AEEA (Activities of Exhibition and Education in Astronomy) 天文教育資訊網 2006 年 7 月 4 日
References
- Ian Ridpath and Wil Tirion (2007). Stars and Planets Guide, Collins, London. ISBN 978-0007251209. Princeton University Press, Princeton. ISBN 978-0691135564.
- Unniversity of Wisconsin http://www.astro.wisc.edu/~dolan/constellations/constellations/Delphinus.html
External links
Andromeda · Antlia · Apus · Aquarius · Aquila · Ara · Aries · Auriga · Boötes · Caelum · Camelopardalis · Cancer · Canes Venatici · Canis Major · Canis Minor · Capricornus · Carina · Cassiopeia · Centaurus · Cepheus · Cetus · Chamaeleon · Circinus · Columba · Coma Berenices · Corona Australis · Corona Borealis · Corvus · Crater · Crux · Cygnus · Delphinus · Dorado · Draco · Equuleus · Eridanus · Fornax · Gemini · Grus · Hercules · Horologium · Hydra · Hydrus · Indus · Lacerta · Leo · Leo Minor · Lepus · Libra · Lupus · Lynx · Lyra · Mensa · Microscopium · Monoceros · Musca · Norma · Octans · Ophiuchus · Orion · Pavo · Pegasus · Perseus · Phoenix · Pictor · Pisces · Piscis Austrinus · Puppis · Pyxis · Reticulum · Sagitta · Sagittarius · Scorpius · Sculptor · Scutum · Serpens · Sextans · Taurus · Telescopium · Triangulum · Triangulum Australe · Tucana · Ursa Major · Ursa Minor · Vela · Virgo · Volans · VulpeculaFlamsteed 1 • 2 (ε, Deneb Dulfim) • 3 (η) • 4 (ζ) • 5 (ι) • 6 (β, Rotanev) • 7 (κ) • 8 (θ) • 9 (α, Sualocin) • 10 • 11 (δ) • 12 (γ) • 13 • 14 • 15 • 16 • 17 • 18 • 67 (ρ) Aql (Tso Ke)Nearby WISE 2056+1459 • Gliese 791.2Categories:- Delphinus constellation
- Constellations
- Northern constellations
- Constellations listed by Ptolemy
- Western constellations
- Legendary mammals
- Fictional toothed whales
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
