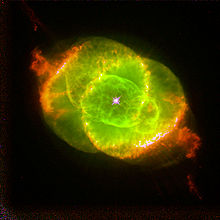
- Cat's Eye Nebula
-
Cat's Eye Nebula 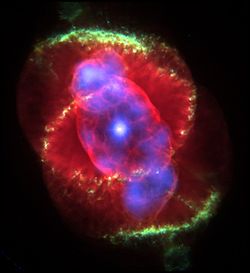
Composite image using optical images from the HST and X-ray data from the Chandra X-ray ObservatoryObservation data
(Epoch J2000)Right ascension 17h 58m 33.423s[1] Declination +66° 37′ 59.52″[1] Distance 3.3 ± 0.9 kly (1.0 ± 0.3 kpc)[2] Apparent magnitude (V) 9.8B[1] Apparent dimensions (V) Core: 20″[2] Constellation Draco Physical characteristics Radius Core: 0.2 ly[note 1] Absolute magnitude (V) −0.2+0.8
−0.6B[note 2]Notable features complex structure Other designations NGC 6543,[1] Snail Nebula,[1] Sunflower Nebula,[1] (includes IC 4677),[1] Caldwell 6 See also: Planetary nebula, Lists of nebulae Coordinates:
 17h 58m 33.423s, +66° 37′ 59.52″
17h 58m 33.423s, +66° 37′ 59.52″The Cat's Eye Nebula (NGC 6543, Caldwell 6) is a planetary nebula in the constellation of Draco. Structurally, it is one of the most complex nebulae known, with high-resolution Hubble Space Telescope observations revealing remarkable structures such as knots, jets, bubbles and sinewy arc-like features. In the center of the Cat's Eye there is a bright and hot star; around 1000 years ago this star lost its outer envelope, producing the nebula.
It was discovered by William Herschel on February 15, 1786, and was the first planetary nebula whose spectrum was investigated by the English amateur astronomer William Huggins in 1864. The results of the latter investigation demonstrated for the first time that planetary nebulae consist of hot gases, but not stars. Currently the nebula has been observed across the full electromagnetic spectrum, from far-infrared to X-rays.
Modern studies reveal several mysteries. The intricacy of the structure may be caused in part by material ejected from a binary central star, but as yet, there is no direct evidence that the central star has a companion. Also, measurements of chemical abundances reveal a large discrepancy between measurements done by two different methods, the cause of which is uncertain. Hubble Telescope observations revealed a number of faint rings around the Eye, which are spherical shells ejected by the central star in the distant past. The exact mechanism of those ejections, however, is unclear.
Contents
General information
NGC 6543 is a well-studied planetary nebula. It is relatively bright at magnitude 8.1, and also has a high surface brightness.[3] It is situated at right ascension 17h 58 m 33.4 s and declination +66°37'59″.[4] Its high declination means it is easily observable from the northern hemisphere, where historically most large telescopes have been situated.[3] NGC 6543 is situated almost exactly in the direction of the North Ecliptic Pole.
While the bright inner nebula is rather small—the major axis of the inner ellipse is 16.1 arcseconds, while the distance between the condensations is 24.7 arcseconds[5]—it has an extended halo of matter that the progenitor star ejected during its red giant phase. This halo extends over a diameter of about 300 arcseconds (5 arcminutes).[4] Cat's Eye nebula lies three thousand light-years from Earth.[6]
Observations show that the main body of the nebula has a density of about 5,000 particles/cm³ and a temperature of about 7,000–9,000 K.[7] The outer halo has a higher temperature of about 15,000 K and a much lower density.[8]
The central star of NGC 6543 is an O7 + [WR]–type star, with a temperature of approximately 80,000 K.[7] It is approximately 10,000 times as luminous as the sun, and its radius is about 0.65 times the solar value. Spectroscopic analysis shows that the star is currently losing mass in a fast stellar wind at a rate of about 3.2×10−7 solar masses per year—about 20 trillion tons per second.[7] The velocity of this wind is about 1900 km/s. Calculations indicate that the central star currently weighs just over one solar mass, but theoretical evolutionary calculations imply that it had an initial mass of about 5 solar masses.[9]
In 1994, Hubble first revealed NGC 6543's surprisingly intricate structures, including concentric gas shells, jets of high-speed gas, and unusual shock-induced knots of gas.
Observations
The Nebula was discovered by William Herschel on February 15, 1786, who likened its appearance to a planetary disk. Cat's Eye was the first planetary nebula to be observed with a spectroscope. It was done by the pioneer spectroscopist William Huggins on August 29, 1864.[10] Huggins' observations, which revealed that nebula's spectrum was non-continuous and made of a few bright lines, were the first indication that planetary nebulae consist of extremely rarefied gases.[3] Since those early observations, NGC 6543 has been observed right across the electromagnetic spectrum.
Infrared observations
Observations of NGC 6543 at far-infrared wavelengths (about 60 μm) reveal the presence of stellar dust at low temperatures. The dust is believed to have formed during the last phases of the progenitor star's life. It absorbs light from the central star and re-radiates it at infrared wavelengths. The spectrum of the infrared dust emission implies that the dust temperature is about 85 K, while the mass of the dust is estimated at 6.4 × 10−4 solar masses.[11]
Infrared emission also reveals the presence of un-ionised material such as molecular hydrogen (H2) and argon. In many planetary nebulae, molecular emission is greatest at larger distances from the star, where more material is un-ionised, but molecular hydrogen emission in NGC 6543 seems to be bright at the inner edge of its outer halo. This may be due to shock waves exciting the H2 as ejecta moving at different speeds collide. The overall appearance of Cat's Eye Nebula in infrared (wavelengths 2–8 μm) is similar in visible light.[12]
Optical and ultraviolet observations
NGC 6543 has been extensively observed at ultraviolet and optical wavelengths. Spectroscopic observations at these wavelengths are used in abundance determinations,[13] while images at these wavelengths have been used to reveal the intricate structure of the nebula.[14]
The Hubble Space Telescope image produced here is in false colour, designed to highlight regions of high and low ionisation. Three images were taken, in filters isolating the light emitted by singly ionised hydrogen at 656.3 nm, singly ionised nitrogen at 658.4 nm and doubly ionised oxygen at 500.7 nm. The images were combined as red, green and blue channels respectively, although their true colours are red, red and green. The image reveals two 'caps' of less ionised material at the edge of the nebula.[15]
X-ray observations
Recent observations at X-ray wavelengths by the Chandra X-ray Observatory have revealed the presence of extremely hot gas within NGC 6543 with the temperature of 1.7 × 106 K.[16] The image at the top of this article is a combination of optical images from the Hubble Space Telescope with the Chandra X-ray images. It is thought that the very hot gas results from the violent interaction of a fast stellar wind with material previously ejected. This interaction has hollowed out the inner bubble of the nebula.[14]
Chandra observations have also revealed a point source at the position of the central star. The spectrum of this source extends to the hard part of the X-ray spectrum, to 0.5–1.0 keV. The star with the photospheric temperature of about 100,000 K would not be expected to emit strongly in hard X-rays, and so their presence is something of a mystery. It may suggest the presence of a high temperature accretion disk within a binary star system.[17]
Distance
A long-standing problem in the study of planetary nebulae is that their distances are generally not well known. Many methods for estimating distances to planetary nebulae rely on making general assumptions, which may be very inaccurate for the object concerned.[18]
In recent years, however, observations made using the Hubble Space Telescope have allowed a new method of determining distances. All planetary nebulae are expanding, and observations several years apart and with high enough angular resolution will reveal the growth of the nebula in the plane of the sky. This is typically very small—only a few milliarcseconds a year or less. Spectroscopic observations can reveal the velocity of expansion of the nebula along the line of sight using the Doppler effect. Then, comparing the angular expansion with the known expansion velocity, the distance to the nebula can be calculated.[18]
Hubble Space Telescope observations of NGC 6543 several years apart have been used to calculate its distance. Its angular expansion rate is approximately 10 milliarcseconds per year, while its expansion velocity along the line of sight has been found to be 16.4 km/s. Combining these two results implies that NGC 6543 is 1001 ± 269 parsecs (3×1019 m), or about 3300 light-years away from Earth.[19]
Age
The angular expansion of the nebula can also be used to estimate its age. If it has been expanding at a constant rate of 10 milliarcseconds a year, then it would take 1000 ± 260 years to reach a diameter of 20 arcseconds. This may be an upper limit to the age, as ejected material will be slowed as it encounters material ejected from the star at earlier stages of its evolution, as well as the interstellar medium.[19]
Composition
Like most astronomical objects, NGC 6543 consists mostly of hydrogen and helium, with heavier elements present in small quantities. The exact composition may be determined by spectroscopic studies. Abundances are generally expressed relative to hydrogen, the most abundant element.[8]
Different studies generally find varying values for elemental abundances. This is often because spectrographs attached to telescopes do not collect all the light from objects being observed, instead gathering light from a slit or small aperture. Therefore, different observations may sample different parts of the nebula.
However, results for NGC 6543 broadly agree that, relative to hydrogen, the helium abundance is about 0.12, carbon and nitrogen abundances are both about 3×10−4, and the oxygen abundance is about 7×10−4.[13] These are fairly typical abundances for planetary nebulae, with the carbon, nitrogen and oxygen abundances all larger than the values found for the sun, due to the effects of nucleosynthesis enriching the star's atmosphere in heavy elements before it is ejected as a planetary nebula.[20]
Deep spectroscopic analysis of NGC 6543 may indicate that the nebula contains a small amount of material which is highly enriched in heavy elements; this is discussed below.[13]
Kinematics and morphology
The Cat's Eye Nebula is structurally a very complex nebula, and the mechanism or mechanisms, which have given rise to its complicated morphology, are not well understood.[14] The central bright part of the nebular consists of the inner elongated bubble (inner ellipse) filled with hot gas. It in turn is nested into a pair of larger spherical bubbles conjoined together along their waist. The waist is observed as the second larger ellipse lying perpendicular to the bubble with hot gas.[5]
The structure of the bright portion of the nebula is primarily caused by the interaction of a fast stellar wind being emitted by the central star with material ejected during the formation of the nebula. This interaction causes the emission of X-rays discussed above. The stellar wind, blowing with the velocity as high as 1900 km/s, has 'hollowed out' the inner bubble of the nebula, and appears to have burst the bubble at both ends.[14]
It is also suspected that the central star of the nebula may be a binary star. The existence of an accretion disk caused by mass transfer between the two components of the system may give rise to polar jets, which would interact with previously ejected material. Over time, the direction of the polar jets would vary due to precession.[21]
Outside the bright inner portion of the nebula, there are a series of concentric rings, thought to have been ejected before the formation of the planetary nebula, while the star was on the asymptotic giant branch of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. These rings are very evenly spaced, suggesting that the mechanism responsible for their formation ejected them at very regular intervals and at very similar speeds.[4] The total mass of the rings is about 0.1 solar masses.[22] The pulsations that formed the rings probably started 15,000 years ago and ceased about 1,000 years ago, when the formation of the bright central part began (see above).[23]
Further out, a large faint halo extends to large distances from the star. The halo again predates the formation of the main nebula. The mass of the halo is estimated as 0.26–0.92 solar masses.[22]
Open questions
Despite intensive study, the Cat's Eye Nebula still holds many mysteries. The concentric rings surrounding the inner nebula seem to have been ejected at intervals of from a few hundred to a few thousand years, a timescale which is rather difficult to explain. Thermal pulsations, which cause formation of planetary nebulae, are believed to take place at intervals of tens of thousands of years, while smaller surface pulsations are thought to occur at intervals of years to decades. A mechanism which would eject material over the timescales required to form the concentric rings in the Cat's Eye Nebula is not known yet.[23]
The spectra of planetary nebulae consist of emission lines superimposed on a continuum. The emission lines may be formed either by collisional excitation of ions in the nebula, or by recombination of electrons with ions. Collisionally excited lines are generally much stronger than recombination lines, and so have historically been used to determine abundances. However, recent studies have found that abundances derived from recombination lines seen in the spectrum of NGC 6543 are some three times higher than those derived from collisionally excited lines. The cause of this discrepancy is probably related to spatial temperature fluctuations inside the nebula.[13]
Notes
References
- ^ a b c d e f g (SIMBAD 2006)
- ^ a b (Reed et al. 1999)
- ^ a b c (Moore 2007)
- ^ a b c (Balick, Wilson & Hajian 2001, p. 354)
- ^ a b (Reed et al. 1999, p. 2433)
- ^ Nemiroff, Robert. "The Cat's Eye Nebula From Hubble". NASA. http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap070513.html. Retrieved october 26, 2011.
- ^ a b c (Wesson & Liu 2004, pp. 1026, 1028)
- ^ a b (Wesson & Liu 2004, p. 1029)
- ^ (Bianchi, Cerrato & Grewing 1986)
- ^ (kwok 2000, p. 1)
- ^ (Klaas et al. 2006, p. 523)
- ^ (Hora et al. 2004, p. 299)
- ^ a b c d (Wesson & Liu 2004, pp. 1026–1027, 1040–1041)
- ^ a b c d (Balick & Preston 1987, pp. 958, 961–963)
- ^ (Wesson & Liu 2004, pp. 1027–1031)
- ^ (Chu et al. 2001)
- ^ (Guerrero et al. 2001)
- ^ a b (Reed et al. 1999, p. 2430)
- ^ a b (Reed et al. 1999, pp. 2433–2438)
- ^ (Hyung et al. 2000)
- ^ (Miranda & Solf 1992)
- ^ a b (Balick, Wilson & Hajian 2001, p. 358)
- ^ a b (Balick, Wilson & Hajian 2001, pp. 359–360)
Cited sources
- Balick, Bruce; Preston, Heather L. (October 1987), "A wind-blown bubble model for NGC 6543", Astronomical Journal 94: 958–963, Bibcode 1987AJ.....94..958B, doi:10.1086/114528
- Balick, Bruce; Wilson, Jeanine; Hajian, Arsen R. (2001), "NGC 6543: The Rings Around the Cat's Eye", Astronomical Journal 121 (1): 354, Bibcode 2001AJ....121..354B, doi:10.1086/318052
- Bianchi, L.; Cerrato, S.; Grewing, M. (November 1986), "Mass loss from central stars of planetary nebulae—the nucleus of NGC 6543", Astronomy and Astrophysics 169 (1–2): 227–236, Bibcode 1986A&A...169..227B
- Chu, You-Hua; Guerrero, Martı´n A.; Gruendl, Robert A.; Williams, Rosa M.; Kaler, James B. (2001), "Chandra reveals the X-ray glint in the cat's eye", Astrophysical Journal 553 (1): L69–L72, arXiv:astro-ph/0101444, Bibcode 2001ApJ...553L..69C, doi:10.1086/320495
- Guerrero, Martín A.; Chu, You-Hua; Gruendl, Robert A.; Williams, Rosa M.; Kaler, James B. (2001), "The Enigmatic X-Ray Point Sources at the Central Stars of NGC 6543 and NGC 7293", Astrophysical Journal 553 (1): L55–L58, arXiv:astro-ph/0104270, Bibcode 2001ApJ...553L..55G, doi:10.1086/320509
- Hora, Joseph L.; Latter, William B.; Allen, Lori E.; Marengo, Massimo; Deutsch, Lynne K.; Pipher, Judith L. (2004), "Infrared Array Camera (IRAC) Observations of Planetary Nebulae", Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series 154 (1): 296–301, Bibcode 2004ApJS..154..296H, doi:10.1086/422820
- Hyung, S.; Aller, L. H.; Feibelman, W. A.; Lee, W. B.; de Koter, A. (2000), "The optical spectrum of the planetary nebula NGC 6543", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 318 (1): 77–91, Bibcode 2000MNRAS.318...77H, doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2000.03642.x
- Klaas, U.; Walker, S. J.; Müller, T. G.; Richards, P. J.; Schreiber, J. (2006), "Multi-aperture photometry of extended IR sources with ISOPHOT. I. The nature of extended IR emission of planetary Nebulae", Astronomy and Astrophysics 452 (2): 523–535, Bibcode 2006A&A...452..523K, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20053245
- Kwok, Sun (2000), "Chapter1: History and overview", The origin and evolution of planetary nebulae, Cambridge University Press, pp. 1–7, ISBN 0-521-62313-8, http://books.google.com/?id=7NfqpZxO_o0C
- Miranda, L. F.; Solf, J. (1992), "Long-slit spectroscopy of the planetary nebula NGC 6543—Collimated bipolar ejections from a precessing central source?", Astronomy and Astrophysics 260 (1–2): 397–410, Bibcode 1992A&A...260..397M
- Moore, S. L. (2007), "Observing the Cat's Eye Nebula", Journal of the British Astronomical Association 117 (5): 279–280, Bibcode 2007JBAA..117R.279M
- Reed, Darren S.; Balick, Bruce; Hajian, Arsen R.; Klayton, Tracy L.; Giovanardi, Stefano; Casertano, Stefano; Panagia, Nino; Terzian, Yervant (1999), "Hubble Space Telescope Measurements of the Expansion of NGC 6543: Parallax Distance and Nebular Evolution", Astronomical Journal 118 (5): 2430–2441, arXiv:astro-ph/9907313, Bibcode 1999AJ....118.2430R, doi:10.1086/301091
- SIMBAD (December 22, 2006), Results for Cat's Eye Nebula, SIMBAD, Centre de Données Astronomiques de Strasbourg, http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-id?protocol=html&Ident=Cat's+Eye+Nebula
- Wesson, R.; Liu, X.-W. (2004), "Physical conditions in the planetary nebula NGC 6543", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 351 (3): 1026–1042, Bibcode 2004MNRAS.351.1026W, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2004.07856.x
External links
- Cat's Eye Nebula Release at ESA/Hubble
- Cat's Eye Nebula images at ESA/Hubble
- Chandra X-Ray Observatory Photo Album: NGC 6543
- Astronomy Picture of the Day
- The Cat's Eye Nebula October 31, 1999
- Halo of the Cat's Eye 2010 May 9
- Hubble Probes the Complex History of a Dying Star—HubbleSite article about the Cat's Eye Nebula.
- NGC6543 The Cats Eye Nebula
- Hubble's Color Toolbox: Cat's Eye Nebula—article showing image composite process used to produce an image of the nebula
- Cat's Eye Nebula on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images
The Caldwell catalogue List C1 · C2 · C3 · C4 · C5 · C6 · C7 · C8 · C9 · C10 · C11 · C12 · C13 · C14 · C15 · C16 · C17 · C18 · C19 · C20 · C21 · C22 · C23 · C24 · C25 · C26 · C27 · C28 · C29 · C30 · C31 · C32 · C33 · C34 · C35 · C36 · C37 · C38 · C39 · C40 · C41 · C42 · C43 · C44 · C45 · C46 · C47 · C48 · C49 · C50 · C51 · C52 · C53 · C54 · C55 · C56 · C57 · C58 · C59 · C60 · C61 · C62 · C63 · C64 · C65 · C66 · C67 · C68 · C69 · C70 · C71 · C72 · C73 · C74 · C75 · C76 · C77 · C78 · C79 · C80 · C81 · C82 · C83 · C84 · C85 · C86 · C87 · C88 · C89 · C90 · C91 · C92 · C93 · C94 · C95 · C96 · C97 · C98 · C99 · C100 · C101 · C102 · C103 · C104 · C105 · C106 · C107 · C108 · C109See also  Book:Caldwell catalogue ·
Book:Caldwell catalogue ·  Category:Caldwell objects
Category:Caldwell objects  Portal:Astronomy ·
Portal:Astronomy ·  Commons:Caldwell objectsCategories:
Commons:Caldwell objectsCategories:- Caldwell objects
- Draco constellation
- NGC objects
- Planetary nebulae
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.