- Omega Centauri
-
Omega Centauri 
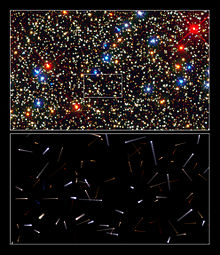
The globular cluster Omega Centauri. Credit ESOObservation data (J2000 epoch) Class Globular cluster Constellation Centaurus Right ascension 13h 26m 45.89s[1] Declination -47° 28′ 36.7″[1] Distance 15.8 ± 1.1 kly[2] (4.85 ± 0.35 kpc) Apparent magnitude (V) 3.7[3] Apparent dimensions (V) 36′.3[citation needed] Physical characteristics Mass ~5 000 000[4] M☉ (~1•1037 kg) Radius 86 ± 6 ly[5] Estimated age ~12 Gyr[6] Other designations NGC 5139,[1] GCl 24,[1] ω Centauri[2] See also: Globular cluster, List of globular clusters Coordinates:
 13h 26m 45.89s, −47° 28′ 36.7″
13h 26m 45.89s, −47° 28′ 36.7″Omega Centauri (ω Cen) or NGC 5139 is a globular cluster[7] in the constellation of Centaurus, discovered by Edmond Halley in 1677 who listed it as a nebula. Omega Centauri had been listed in Ptolemy's catalog 2000 years ago as a star. Lacaille included it in his catalog as number I.5. It was first recognized as a globular cluster by the English astronomer John William Herschel in the 1830s.[8] ("Omega Centauri" is a Bayer designation, even though the object is a cluster.)
Orbiting the Milky Way, it is both the brightest and the largest known globular cluster associated with our galaxy (1.6 Em). Of all the globular clusters in the Local Group of galaxies, only Mayall II in the Andromeda Galaxy is brighter and more massive.[9] ω Centauri is so different from other galactic globular clusters that it is thought to be of different origin.[10]
It is located about 15,800 light-years (4,850 pc) from Earth and contains several million Population II stars. The stars in its center are so crowded that they are estimated to average only 0.1 light years away from each other. It is about 12 billion years old.[citation needed]
Omega Centauri is one of the few globular clusters visible to the naked eye and appears about as large as the full Moon.[11] Kapteyn's star, which is currently only 13 light years away, is thought to originate from Omega Centauri.[12]
Contents
Dynamics
The internal dynamics of Omega Centauri have been analyzed using measurements of the radial velocities of 469 stars.[13] The cluster is strongly rotating, with a peak rotational velocity of 7.9 km s-1. The mass distribution inferred from the kinematics is slightly more extended than, though not strongly inconsistent with, the luminosity distribution.
Central black hole?
A 2008 study presented evidence for an intermediate-mass black hole at the center of Omega Centauri, based on observations made by the Hubble Space Telescope and Gemini Observatory on Cerro Pachon in Chile.[14] Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys showed that stars are bunching up near the center of Omega Centauri, as evidenced by the gradual increase in starlight near the center. Using instruments at the Gemini Observatory to measure the speed of stars swirling in the cluster's core, E. Noyola and colleagues found that stars closer to the core are moving faster than stars farther away. This measurement was interpreted to mean that unseen matter at the core is interacting gravitationally with nearby stars. By comparing these results with standard models, the astronomers concluded that the most likely cause was the gravitational pull of a dense, massive object such as a black hole. They calculated the object's mass at 4.0 x 104 solar masses.[14]
However, more recent work has challenged these conclusions, in particular disputing the proposed location of the cluster center.[15] [16] Calculations using a revised location for the center found that the velocity of core stars does not vary with distance, as would be expected if an intermediate-mass black hole were present. The same studies also found that starlight does not increase toward the center but instead remains relatively constant. The authors noted that their results do not entirely rule out the black hole proposed by Noyola and colleagues, but they do not confirm it, and they limit its maximum mass to 1.2 x 104 solar masses.
Disrupted dwarf galaxy
It has been speculated that Omega Centauri may be the core of a dwarf galaxy which was disrupted and absorbed by our Milky Way galaxy.[17] Omega Centauri's chemistry and motion in the galaxy is also consistent with this picture. Like Mayall II, Omega Centauri has a range of metallicities and stellar ages which hints that it did not all form at once (as globular clusters are thought to form) and may in fact be the remainder of the core of a smaller galaxy long since incorporated into the Milky Way.[18]
See also
- Sagittarius Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy
- Canis Major Dwarf Galaxy
- Globular Cluster M54
- Mayall II
External links
- StarDate: Omega Centauri Fact Sheet
- Hubblesite - Peering into the core of a globular cluster
- Omega Centauri: Former Core of a Dwarf Galaxy?
- Omega Centauri: Proud Cluster or Sad Remnant?
- Omega Centauri at ESA/Hubble
- Omega Centauri on Wikisky.org
- Omega Centauri, Galactic Globular Clusters Database page
- Omega Centauri on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images
References
- ^ a b c d "SIMBAD Astronomical Database". Results for NGC 5139. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/Simbad. Retrieved 2006-11-16.
- ^ a b van de Ven, G.; van den Bosch, R. C. E.; Verolme, E. K.; de Zeeuw, P. T. (January II 2006). "The dynamical distance and intrinsic structure of the globular cluster ω Centauri". Astronomy and Astrophysics 445 (2): 513–543. arXiv:astro-ph/0509228. Bibcode 2006A&A...445..513V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20053061. "best-fit dynamical distance D=4.8±0.3 kpc ... consistent with the canonical value 5.0±0.2 kpc obtained by photometric methods"
- ^ Omega Centauri - Britannica Online Encyclopedia
- ^ Globular cluster NGC 5139
- ^ distance × sin( diameter_angle / 2 ), using distance of 5kpc and angle 36.3', = 86 ± 6 ly. radius
- ^ "Peering into the Core of a Globular Cluster"[1]
- ^ http://www.france-info.com/spip.php?article124990&theme=81&sous_theme=166
- ^ Black Hole found in enigmatic Omega Centauri
- ^ http://www.maa.clell.de/Messier/E/Xtra/NGC/n5139.html
- ^ Eva Noyola; Karl Gebhardt; Marcel Bergmann (2008). "Gemini and Hubble Space Telescope Evidence for an Intermediate Mass Black Hole in omega Centauri". The Astrophysical Journal 676 (2): 1008. arXiv:0801.2782. Bibcode 2008ApJ...676.1008N. doi:10.1086/529002.
- ^ "Black hole found in Omega Centauri". ESA. 2008-04-02. http://www.esa.int/esaSC/SEMPGM5QGEF_index_0.html. Retrieved 2009-11-06.
- ^ http://www.newscientist.com/article/mg20427334.100-backward-star-aint-from-round-here.html
- ^ Merritt, David; Meylan, Georges; Mayor, Michel (September 1997). "The stellar dynamics of Omega Centauri". The Astrophysical Journal 114: 1074–1086. arXiv:astro-ph/9612184. Bibcode 1997AJ....114.1074M. doi:10.1086/118538.
- ^ a b Noyola, E. and Gebhardt, K. and Bergmann, M. (apr 2008). "Gemini and Hubble Space Telescope Evidence for an Intermediate-Mass Black Hole in ω Centauri". The Astrophysical Journal 676 (2): 1008–1015. arXiv:0801.2782. Bibcode 2008ApJ...676.1008N. doi:10.1086/529002.
- ^ Anderson, J. and van der Marel, R. P. (feb 2010). "New Limits on an Intermediate-Mass Black Hole in Omega Centauri. I. Hubble Space Telescope Photometry and Proper Motions". The Astrophysical Journal 710 (2): 1032–1062. arXiv:0905.0627. Bibcode 2010ApJ...710.1032A. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/710/2/1032.
- ^ van der Marel, R. P. and Anderson, J. (feb 2010). "New Limits on an Intermediate-Mass Black Hole in Omega Centauri. II. Dynamical Models". The Astrophysical Journal 710 (2): 1063–1088. arXiv:0905.0638. Bibcode 2010ApJ...710.1063V. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/710/2/1063.
- ^ "Astronomers Find Suspected Medium-Size Black Hole in Omega Centauri" (Press release). 2008-04-02. http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/2008/14/full/. Retrieved 2009-11-06.
- ^ Hughes, 1999, "G1 in M31 - Giant Age and Metallicity Effects in Omega Centauri I: Stromgren Photometry"
The Caldwell catalogue List C1 · C2 · C3 · C4 · C5 · C6 · C7 · C8 · C9 · C10 · C11 · C12 · C13 · C14 · C15 · C16 · C17 · C18 · C19 · C20 · C21 · C22 · C23 · C24 · C25 · C26 · C27 · C28 · C29 · C30 · C31 · C32 · C33 · C34 · C35 · C36 · C37 · C38 · C39 · C40 · C41 · C42 · C43 · C44 · C45 · C46 · C47 · C48 · C49 · C50 · C51 · C52 · C53 · C54 · C55 · C56 · C57 · C58 · C59 · C60 · C61 · C62 · C63 · C64 · C65 · C66 · C67 · C68 · C69 · C70 · C71 · C72 · C73 · C74 · C75 · C76 · C77 · C78 · C79 · C80 · C81 · C82 · C83 · C84 · C85 · C86 · C87 · C88 · C89 · C90 · C91 · C92 · C93 · C94 · C95 · C96 · C97 · C98 · C99 · C100 · C101 · C102 · C103 · C104 · C105 · C106 · C107 · C108 · C109See also Stars of Centaurus Bayer Flamsteed Categories:- Globular clusters
- Centaurus constellation
- Dwarf galaxies
- Bayer objects
- NGC objects
- Caldwell objects
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.