- Rosette Nebula
-
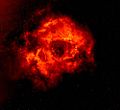
Rosette Nebula 
The Rosette Nebula (H-Alpha)Observation data: J2000.0 epoch Type Emission Right ascension 06h 33m 45s[1] Declination +04° 59′ 54″[1] Distance 5,200 ly (1,600 pc)[2] Apparent magnitude (V) 9.0 Apparent dimensions (V) 1.3 ° Constellation Monoceros Physical characteristics Radius 65 ly Absolute magnitude (V) - Notable features Multipart nebula Other designations SH 2-275,[1] CTB 21,[1] Caldwell 49 See also: Diffuse nebula, Lists of nebulae The Rosette Nebula (also known as Caldwell 49) is a large, circular H II region located near one end of a giant molecular cloud in the Monoceros region of the Milky Way Galaxy. The open cluster NGC 2244 (Caldwell 50) is closely associated with the nebulosity, the stars of the cluster having been formed from the nebula's matter.
The complex has the following NGC designations:
- NGC 2237 – Part of the nebulous region (Also used to denote whole nebula)
- NGC 2238 – Part of the nebulous region
- NGC 2239 – Part of the nebulous region (Discovered by John Herschel)
- NGC 2244 – The open cluster within the nebula (Discovered by John Flamsteed in 1690)
- NGC 2246 – Part of the nebulous region
The cluster and nebula lie at a distance of some 5,200 light-years from Earth (although estimates of the distance vary considerably, down to 4,900 light-years.[3]) and measure roughly 130 light years in diameter. The radiation from the young stars excite the atoms in the nebula, causing them to emit radiation themselves producing the emission nebula we see. The mass of the nebula is estimated to be around 10,000 solar masses.
It is believed that stellar winds from a group of O and B stars are exerting pressure on interstellar clouds to cause compression, followed by star formation in the nebula. This star formation is currently still ongoing.
A survey of the nebula with the Chandra X-ray Observatory in 2001 has revealed the presence of very hot, young stars at the core of the Rosette Nebula. These stars have heated the surrounding gas to a temperature in the order of 6 million kelvins causing them to emit copious amounts of X-rays.
Contents
Observing the Rosette Nebula
The cluster of stars is visible in binoculars and quite well seen in small telescopes while the nebula itself is more difficult to spot visually and requires a telescope with a low magnification. A dark site is a must to see it. Photographically the Rosette Nebula is easier to record and it is the only way to record the red color which is not seen visually.
Other images
References
- ^ a b c d "SIMBAD Astronomical Database". Results for NGC 2237. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/Simbad. Retrieved 2006-10-23.
- ^ Phelps, Randy L.; Ybarra, Jason E. (2005). "A Parsec-Scale Outflow in the Rosette Molecular Cloud?". The Astrophysical Journal 627 (2): 845–849. Bibcode 2005ApJ...627..845P. doi:10.1086/430431.
- ^ 'Cambridge Deep Sky Companions - The Caldwell Objects' , S.J. O'Meara & P. Moore, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0521827965 (2002)
External links
- Rosette Nebula (SEDS)
- Chandra Observatory study of the Rosette Nebula
- NOAO; "Fitful Young Star Sputters to Maturity in the Rosette Nebula"
- NightSkyInfo.com – Rosette Nebula
- Astronomy Picture of the Day
- Dust Sculptures in the Rosette Nebula – 2007 June 6
- Dust Sculptures in the Rosette Nebula – 2009 December 2
- Field of Rosette – 2010 February 14
- Slooh Videocast on Rosette Nebula
- Rosette Nebula from the Netherlands
- Deep image of the Rosette Nebula
- Rosette Nebula on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images
The Caldwell catalogue List C1 · C2 · C3 · C4 · C5 · C6 · C7 · C8 · C9 · C10 · C11 · C12 · C13 · C14 · C15 · C16 · C17 · C18 · C19 · C20 · C21 · C22 · C23 · C24 · C25 · C26 · C27 · C28 · C29 · C30 · C31 · C32 · C33 · C34 · C35 · C36 · C37 · C38 · C39 · C40 · C41 · C42 · C43 · C44 · C45 · C46 · C47 · C48 · C49 · C50 · C51 · C52 · C53 · C54 · C55 · C56 · C57 · C58 · C59 · C60 · C61 · C62 · C63 · C64 · C65 · C66 · C67 · C68 · C69 · C70 · C71 · C72 · C73 · C74 · C75 · C76 · C77 · C78 · C79 · C80 · C81 · C82 · C83 · C84 · C85 · C86 · C87 · C88 · C89 · C90 · C91 · C92 · C93 · C94 · C95 · C96 · C97 · C98 · C99 · C100 · C101 · C102 · C103 · C104 · C105 · C106 · C107 · C108 · C109See also Sharpless catalog Sh2-1 · Sh2-2 · Sh2-3 · Sh2-4 · Sh2-5 · Sh2-6 · Sh2-7 · Sh2-8 · Sh2-9 · Sh2-10 · Sh2-11 · Sh2-12 · Sh2-13 · Sh2-14 · Sh2-15 · Sh2-16 · Sh2-17 · Sh2-18 · Sh2-19 · Sh2-20 · Sh2-21 · Sh2-22 · Sh2-23 · Sh2-24 · Sh2-25 · Sh2-26 · Sh2-27 · Sh2-28 · Sh2-29 · Sh2-30 · Sh2-31 · Sh2-32 · Sh2-33 · Sh2-34 · Sh2-35 · Sh2-36 · Sh2-37 · Sh2-38 · Sh2-39 · Sh2-40 · Sh2-41 · Sh2-42 · Sh2-43 · Sh2-44 · Sh2-45 · Sh2-46 · Sh2-47 · Sh2-48 · Sh2-49 · Sh2-50 · Sh2-51 · Sh2-52 · Sh2-53 · Sh2-54 · Sh2-55 · Sh2-56 · Sh2-57 · Sh2-58 · Sh2-59 · Sh2-60 · Sh2-61 · Sh2-62 · Sh2-63 · Sh2-64 · Sh2-65 · Sh2-66 · Sh2-67 · Sh2-68 · Sh2-69 · Sh2-70 · Sh2-71 · Sh2-72 · Sh2-73 · Sh2-74 · Sh2-75 · Sh2-76 · Sh2-77 · Sh2-78 · Sh2-79 · Sh2-80 · Sh2-81 · Sh2-82 · Sh2-83 · Sh2-84 · Sh2-85 · Sh2-86 · Sh2-87 · Sh2-88 · Sh2-89 · Sh2-90 · Sh2-91 · Sh2-92 · Sh2-93 · Sh2-94 · Sh2-95 · Sh2-96 · Sh2-97 · Sh2-98 · Sh2-99 · Sh2-100 · Sh2-101 · Sh2-102 · Sh2-103 · Sh2-104 · Sh2-105 · Sh2-106 · Sh2-107 · Sh2-108 · Sh2-109 · Sh2-110 · Sh2-111 · Sh2-112 · Sh2-113 · Sh2-114 · Sh2-115 · Sh2-116 · Sh2-117 · Sh2-118 · Sh2-119 · Sh2-120 · Sh2-121 · Sh2-122 · Sh2-123 · Sh2-124 · Sh2-125 · Sh2-126 · Sh2-127 · Sh2-128 · Sh2-129 · Sh2-130 · Sh2-131 · Sh2-132 · Sh2-133 · Sh2-134 · Sh2-135 · Sh2-136 · Sh2-137 · Sh2-138 · Sh2-139 · Sh2-140 · Sh2-141 · Sh2-142 · Sh2-143 · Sh2-144 · Sh2-145 · Sh2-146 · Sh2-147 · Sh2-148 · Sh2-149 · Sh2-150 · Sh2-151 · Sh2-152 · Sh2-153 · Sh2-154 · Sh2-155 · Sh2-156 · Sh2-157 · Sh2-158 · Sh2-159 · Sh2-160 · Sh2-161 · Sh2-162 · Sh2-163 · Sh2-164 · Sh2-165 · Sh2-166 · Sh2-167 · Sh2-168 · Sh2-169 · Sh2-170 · Sh2-171 · Sh2-172 · Sh2-173 · Sh2-174 · Sh2-175 · Sh2-176 · Sh2-177 · Sh2-178 · Sh2-179 · Sh2-180 · Sh2-181 · Sh2-182 · Sh2-183 · Sh2-184 · Sh2-185 · Sh2-186 · Sh2-187 · Sh2-188 · Sh2-189 · Sh2-190 · Sh2-191 · Sh2-192 · Sh2-193 · Sh2-194 · Sh2-195 · Sh2-196 · Sh2-197 · Sh2-198 · Sh2-199 · Sh2-201 · Sh2-202 · Sh2-203 · Sh2-204 · Sh2-205 · Sh2-206 · Sh2-207 · Sh2-208 · Sh2-209 · Sh2-210 · Sh2-211 · Sh2-212 · Sh2-213 · Sh2-214 · Sh2-215 · Sh2-216 · Sh2-217 · Sh2-218 · Sh2-219 · Sh2-220 · Sh2-221 · Sh2-222 · Sh2-223 · Sh2-224 · Sh2-225 · Sh2-226 · Sh2-227 · Sh2-228 · Sh2-229 · Sh2-230 · Sh2-231 · Sh2-232 · Sh2-233 · Sh2-234 · Sh2-235 · Sh2-236 · Sh2-237 · Sh2-238 · Sh2-239 · Sh2-240 · Sh2-241 · Sh2-242 · Sh2-243 · Sh2-244 · Sh2-245 · Sh2-246 · Sh2-247 · Sh2-248 · Sh2-249 · Sh2-250 · Sh2-251 · Sh2-252 · Sh2-253 · Sh2-254 · Sh2-255 · Sh2-256 · Sh2-257 · Sh2-258 · Sh2-259 · Sh2-260 · Sh2-261 · Sh2-262 · Sh2-263 · Sh2-264 · Sh2-265 · Sh2-266 · Sh2-267 · Sh2-268 · Sh2-269 · Sh2-270 · Sh2-271 · Sh2-272 · Sh2-273 · Sh2-274 · Sh2-275 · Sh2-276 · Sh2-277 · Sh2-278 · Sh2-279 · Sh2-280 · Sh2-281 · Sh2-282 · Sh2-283 · Sh2-284 · Sh2-285 · Sh2-286 · Sh2-287 · Sh2-288 · Sh2-289 · Sh2-290 · Sh2-291 · Sh2-292 · Sh2-293 · Sh2-294 · Sh2-295 · Sh2-296 · Sh2-297 · Sh2-298 · Sh2-299 · Sh2-301 · Sh2-302 · Sh2-303 · Sh2-304 · Sh2-305 · Sh2-306 · Sh2-307 · Sh2-308 · Sh2-309 · Sh2-310 · Sh2-311 · Sh2-312 · Sh2-313
Categories:- H II regions
- NGC objects
- Monoceros constellation
- Caldwell objects
- Sharpless objects
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.