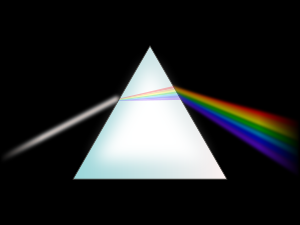
- Photonics
-
The science of photonics[1] includes the generation, emission, transmission, modulation, signal processing, switching, amplification, detection and sensing of light. The term photonics thereby emphasizes that photons are neither particles nor waves — they are different in that they have both particle and wave nature. It covers all technical applications of light over the whole spectrum from ultraviolet over the visible to the near-, mid- and far-infrared. Most applications, however, are in the range of the visible and near infrared light. The term photonics developed as an outgrowth of the first practical semiconductor light emitters invented in the early 1960s and optical fibers developed in the 1970s.
Contents
History of photonics
The word 'photonics' is derived from the Greek word "photos" meaning light; it appeared in the late 1960s to describe a research field whose goal was to use light to perform functions, that traditionally fell within the typical domain of electronics, such as telecommunications, information processing, etc.
Photonics as a field began with the invention of the laser in 1960. Other developments followed: including the laser diode in the 1970s, optical fibers for transmitting information, and the Erbium-doped fiber amplifier. These inventions formed the basis for the telecommunications revolution of the late 20th century and provided the infrastructure for the Internet.
Though coined earlier, the term photonics came into common use in the 1980s as fiber-optic data transmission was adopted by telecommunications network operators. At that time, the term was used widely at Bell Laboratories. Its use was confirmed when the IEEE Lasers and Electro-Optics Society established an archival journal named Photonics Technology Letters at the end of the 1980s.
During the period leading up to the dot-com crash circa 2001, photonics as a field focused largely on telecommunications. However, photonics covers a huge range of science and technology applications, including: laser manufacturing, biological and chemical sensing, medical diagnostics and therapy, display technology, and optical computing.
Various non-telecom photonics applications exhibit strong growth, particularly since the dot-com crash, partly because many companies have been looking for new application areas. Further growth of photonics is likely if current silicon photonics developments are successful.
Relationship to other fields
Classical optics
Photonics is closely related to optics. However optics preceded the discovery that light is quantized (when Albert Einstein explained the photoelectric effect in 1905). Optics tools include the refracting lens, the reflecting mirror, and various optical components known prior to 1900. Key tenets of classical optics, such as Huygens Principle, Maxwell's Equations, and wave equations, do not depend on quantum properties of light.
Modern optics
Photonics is related to quantum optics, optomechanics, electro-optics, optoelectronics and quantum electronics. However each area has slightly different connotations by scientific and government communities and in the marketplace. Quantum optics often connotes fundamental research, whereas photonics is used to connote applied research and development.
The term photonics more specifically connotes:
- The particle properties of light,
- The potential of creating signal processing device technologies using photons,
- The practical application of optics, and
- An analogy to electronics.
The term optoelectronics connotes devices or circuits that comprise both electrical and optical functions, i.e., a thin-film semiconductor device. The term electro-optics came into earlier use and specifically encompasses nonlinear electrical-optical interactions applied, e.g., as bulk crystal modulators such as the Pockels cell, but also includes advanced imaging sensors typically used for surveillance by civilian or government organizations.
Emerging fields
Photonics also relates to the emerging science of quantum information in those cases where it employs photonic methods. Other emerging fields include opto-atomics, in which devices integrate both photonic and atomic devices for applications such as precision timekeeping, navigation, and metrology; polaritonics, which differs from photonics in that the fundamental information carrier is a polariton, which is a mixture of photons and phonons, and operates in the range of frequencies from 300 gigahertz to approximately 10 terahertz.
Applications
 Aphrodita aculeata, a sea mouse,[2] showing colorful spines, a remarkable example of photonic engineering by a living organism
Aphrodita aculeata, a sea mouse,[2] showing colorful spines, a remarkable example of photonic engineering by a living organism
Applications of photonics are ubiquitous. Included are all areas from everyday life to the most advanced science, e.g. light detection, telecommunications, information processing, lighting, metrology, spectroscopy, holography, medicine (surgery, vision correction, endoscopy, health monitoring), military technology, laser material processing, visual art, biophotonics, agriculture, and robotics.
Just as applications of electronics have expanded dramatically since the first transistor was invented in 1948, the unique applications of photonics continue to emerge. Economically important applications for semiconductor photonic devices include optical data recording, fiber optic telecommunications, laser printing (based on xerography), displays, and optical pumping of high-power lasers. The potential applications of photonics are virtually unlimited and include chemical synthesis, medical diagnostics, on-chip data communication, laser defense, and fusion energy, to name several interesting additional examples.
- Consumer equipment: barcode scanner, printer, CD/DVD/Blu-ray devices, remote control devices
- Telecommunications: optical fiber communications, optical down converter to microwave
- Medicine: correction of poor eyesight, laser surgery, surgical endoscopy, tattoo removal
- Industrial manufacturing: the use of lasers for welding, drilling, cutting, and various methods of surface modification
- Construction: laser leveling, laser rangefinding, smart structures
- Aviation: photonic gyroscopes lacking mobile parts
- Military: IR sensors, command and control, navigation, search and rescue, mine laying and detection
- Entertainment: laser shows, beam effects, holographic art
- Information processing
- Metrology: time and frequency measurements, rangefinding
- Photonic computing: clock distribution and communication between computers, printed circuit boards, or within optoelectronic integrated circuits; in the future: quantum computing
Overview of photonics research
The science of photonics includes investigation of the emission, transmission, amplification, detection, and modulation of light.
Light sources
Light sources used in photonics are usually more sophisticated than light bulbs. Photonics commonly uses semiconductor light sources like light-emitting diodes (LEDs), superluminescent diodes, and lasers. Other light sources include fluorescent lamps, cathode ray tubes (CRTs), and plasma screens. Note that while CRTs, plasma screens, and organic light-emitting diode displays generate their own light, liquid crystal displays (LCDs) like TFT screens require a backlight of either cold cathode fluorescent lamps or, more often today, LEDs.
Characteristic for research on semiconductor light sources is the frequent use of III-V semiconductors instead of the classical semiconductors like silicon and germanium. This is due to the special properties of III-V semiconductors that allow for the implementation of light emitting devices. Examples for material systems used are gallium arsenide (GaAs) and aluminium gallium arsenide (AlGaAs) or other compound semiconductors. They are also used in conjunction with silicon to produce hybrid silicon lasers.
Transmission media
Light can be transmitted through any transparent medium. Glass fiber or plastic optical fiber can be used to guide the light along a desired path. In optical communications optical fibers allow for transmission distances of more than 100 km without amplification depending on the bit rate and modulation format used for transmission. A very advanced research topic within photonics is the investigation and fabrication of special structures and "materials" with engineered optical properties. These include photonic crystals, photonic crystal fibers and metamaterials.
Amplifiers
Optical amplifiers are used to amplify an optical signal. Optical amplifiers used in optical communications are erbium-doped fiber amplifiers, semiconductor optical amplifiers, Raman amplifiers and optical parametric amplifiers. A very advanced research topic on optical amplifiers is the research on quantum dot semiconductor optical amplifiers.
Detection
Photodetectors detect light. Photodetectors range from very fast photodiodes for communications applications over medium speed charge coupled devices (CCDs) for digital cameras to very slow solar cells that are used for energy harvesting from sunlight. There are also many other photodetectors based on thermal, chemical, quantum, photoelectric and other effects.
Modulation
Modulation of a light source is used to encode information on a light source. Modulation can be achieved by the light source directly. One of the easiest examples is to use a flashlight to send Morse code. Another method is to take the light from a light source and modulate it in an external optical modulator.
An additional topic covered by modulation research is the modulation format. On-off keying has been the commonly used modulation format in optical communications. In the last years more advanced modulation formats like phase-shift keying or even orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing have been investigated to counteract effects like dispersion that degrade the quality of the transmitted signal.
Photonic systems
Photonics also includes research on photonic systems. This term is often used for optical communication systems. This area of research focuses on the implementation of photonic systems like high speed photonic networks. This also includes research on optical regenerators, which improve optical signal quality.
See also
- Related topics
- Biophotonics
- Holography
- Microphotonics
- Nano-optics
- Optics
- Optronics
- Photonic crystal
- Photonic crystal fiber
- Photonics mast
- Quantum optics
- Solar cell
- Photonic computer
- Industry consortia
- European Photonics Industry Consortium
- Photonics21 - a voluntary association of industrial enterprises and other stakeholders in the field of photonics in Europe.
References
External links
International optical societies
- EOS - European Optical Society
- EPIC - The European Photonics Industry Consortium
- OSA - Optical Society of America
- IEEE Photonics Society
- SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering
National and regional societies and associations
- OP-TEC - National Science Foundation's National Center for Optics and Photonics Education
- Photonics Cluster Netherlands - The Internet Portal of the Dutch Photonics Society
- CPIA - Colorado Photonics Industry Association
Periodicals
- Photonics Spectra
- Laser Focus World
- Electro Optics
- Optics & Photonics Focus
- Optics & Laser Europe
- Nature Photonics
- Photonics news
- Industrial Laser Solutions
- Photonics Online
Research networks
- EURO-FOS - Europe's Research Network on Photonic Systems
- ePIXnet - European Network of Excellence on Photonic Integrated Components and Circuits
- BONE - Building the Future Optical Network in Europe
Further reading
Tools biophoton · Optical DPSK demodulator · delay line interferometer · erbium-doped waveguide amplifier · laser · optical interleaver · optical hybrid · photonic integrated circuit · Photonic crystals · Photonic-crystal fiber · slot-waveguide · Subwavelength-diameter optical fibre · superprism · Time-stretch analog-to-digital converter · Wireless energy transfer · extraordinary optical transmissionConcepts Applications See also
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.