- Unification of Norway
-

This article is part of a series on Scandinavia Geography Viking Age - Old Norse
- Viking
- Thing (assembly)
- Mythology
- Christianization
- Northern Arc
Political entities History of Scandinavia Other - Languages
- Scandinavism
- Nordic Council
- Monetary Union
- Defence Union
- Scandinavian Airlines
The unification of Norway into a single kingdom took place in 872 AD, during the Viking Age.
By the time of the first historical records of these events, about the 700s AD, Norway was divided into several petty kingdoms. It is also assumed that Danish rulers often held sway in the Oslofjord-area.
King Harald Fairhair is the monarch who is credited by later tradition as having unified Norway into one kingdom. According to the sagas, he ruled Norway from approximately 872 to 930. Modern historians assume that his rule was limited to the coastal areas of southern Norway.
Unification of NorwayIn 866, Harald made the first of a series of conquests over the many petty kingdoms which would compose Norway, including Värmland in Sweden, and modern day south-eastern Norway, which had sworn allegiance to the Swedish king Erik Eymundsson. In 872, after a great victory at Hafrsfjord near Stavanger, Harald found himself king over the whole country. His realm was, however, threatened by dangers from without, as large numbers of his opponents had taken refuge, not only in Iceland, then recently discovered; but also in the Orkney Islands, Shetland Islands, Hebrides Islands, Faroe Islands and the northern European mainland. However, his opponents' leaving was not entirely voluntary. Many Norwegian chieftains who were wealthy and respected posed a threat to Harald; therefore, they were subjected to much harassment from Harald, prompting them to vacate the land. At last, Harald was forced to make an expedition to the West, to clear the islands and the Scottish mainland of some Vikings who tried to hide there.
Kings of Norway until King Olav IV, who died in 1387, claimed descent from Harald Fairhair. After Harald's death, the unity of the kingdom was not preserved, and for the next century, the kingdom was variously ruled, wholly or in part, by descendants of King Harald or by earls under the suzerainty of Denmark.
The saga descriptions
The sagas tell us that Harald succeeded, on the death of his father Halfdan the Black Gudrödarson, to the sovereignty of several small, and somewhat scattered kingdoms in Vestfold, which had come into his father's hands through conquest and inheritance. His protector-regent was his mother's brother Guthorm.
The unification of Norway is, according to a tale, somewhat of a love story. The tale begins with a marriage proposal that resulted in rejection and scorn from Gyda, the daughter of Eirik, king of Hordaland. She said she refused to marry Harald "before he was king over all of Norway". Harald was therefore induced to take a vow not to cut nor comb his hair until he was sole king of Norway, and that ten years later, he was justified in trimming it; whereupon he exchanged the epithet "Shockhead" or "Tanglehair" for the one by which he is usually known. Most scholars today regard this story as a literary tale inspired by the Romance stories that were popular at the courts by the time Heimskringla was written.
The Norwegian kingdoms
These maps are mainly based on later saga sources, from the 13th century. Their historical accuracy is questionable.
-
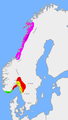
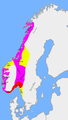
Norwegian petty kingdoms ca. 820 AD at the death of Gudrød the Hunter. The most important kingdoms were Vestfold (red), Hålogaland (purple), Alvheim (yellow) and Agder (green). -
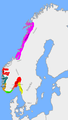
Petty kingdoms ca. 860 AD at the death of Halfdan the Black. In red is the kingdom inherited by Harald Fairhair. -
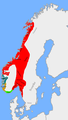
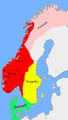
Petty kingdoms ca. 872 AD (the unified kingdom shown in red) before the defining Battle of Hafrsfjord. -
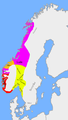
The division of the kingdom after the Battle of Svolder (1000) between Sweden (yellow), Denmark (red) and the jarl of Lade (purple).
See also
History of Europe Prehistoric Europe Classical Antiquity Classical Greece · Roman Republic · Hellenistic period · Roman Empire · Late Antiquity · Early Christianity · Crisis of the 3rd century · Fall of the Roman EmpireMiddle Ages Early Middle Ages · Migration Period · Byzantine Empire · Christianization · Kievan Rus · High Middle Ages · Holy Roman Empire · Crusades · Feudalism · Late Middle Ages · Hundred Years' War · RenaissanceEarly Modern Europe Reformation · Age of Discovery · Baroque · Thirty Years' War · Absolutism · Ottoman Empire · Portuguese Empire · Spanish Empire · Early modern France · Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth · Swedish Empire · Dutch Republic · British Empire · Habsburg Empire · Russian EmpireModern history See also History of Europe by country Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- (England
- Northern Ireland
- Scotland
- Wales)
- Vatican City
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Kosovo
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- South Ossetia
- Transnistria
Dependencies
and other territories- Åland
- Faroe Islands
- Gibraltar
- Guernsey
- Jan Mayen
- Jersey
- Isle of Man
- Svalbard
Other entities - European Union
- Sovereign Military Order of Malta
 Norway topics
Norway topicsHistory Stone Age · Bronze Age · Petty kingdoms · Viking Age · Unification · High Middle Ages · Kalmar Union · Denmark–Norway · Norway in 1814 · Sweden–Norway · End of the union · World War II · 1945–2000 · 21st centuryGeography Law Politics Constitution · Counties · Elections · European Union relations · Foreign relations · Government · Monarchy · Municipalities · Political parties · Prime Minister (List) · Romantic nationalism · Sámi Parliament · ParliamentEconomy Norwegian krone · National Bank · Oslo Stock Exchange · Education · Energy · Media · Tourism · Transport · Companies · WhalingMilitary Symbols Demographics Administrative divisions · Cities · Postal codes · Languages · Religion · Immigration · Norwegians · List of NorwegiansCulture Architecture · Art · Cinema (Actors) · Music (Composers) · Cuisine · Norwegian language · Literature (Writers · Poets) · Bunad · Jul · Constitution Day · Media · Football · Rugby union · Public holidaysCategories:- History of Norway
- Fairhair dynasty
- National unifications
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.