- Monarchy of Norway
-
This article is about the history and function of the Norwegian monarchy as an institution. For the kingdom of Norway itself, see Norway.
King of Norway Monarchy 
Arms of His Majesty the King of Norway
Incumbent:
Harald VStyle: His Majesty First monarch: Harald I Formation: c. 872 Norway 
This article is part of the series:
Politics and government of
NorwayMonarchyGovernmentParliamentLocal Gov'tForeign policy
The Norwegian monarch or Sovereign is the head of state of Norway, which is a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system of government. The Norwegian monarchy can trace its line back to the reign of Harald Fairhair and the previous petty kingdoms which were united to form Norway; it has been in unions with both Sweden and Denmark for long periods.
The present sovereign is King Harald V, who has reigned since 17 January 1991. The heir apparent is his only son, Crown Prince Haakon. The Crown Prince undertakes various public ceremonial functions, as does the King's wife, Queen Sonja. The Crown Prince also acts as regent in the King's absence. There are several other members of the Royal Family, including the King's daughter, grandchildren and siblings. The Royal House is a branch of the princely family of Glücksburg, originally from Schleswig-Holstein in Germany,[1] the same royal house as the Danish and former Greek royal families.
While the Constitution of Norway grants important executive powers to the king, these are almost always exercised by the Council of State in the name of the King (King's Council, or cabinet). Formally the King appoints the government according to his own judgement, but parliamentary practice has been in place since 1884. Constitutional practice has replaced the meaning of the word King in most articles of the constitution from the king personally to the elected government. The powers vested in the Monarch are significant, but are treated only as reserve powers and as an important security part of the role of the Monarchy.
The King's functions are mainly ceremonial. He ratifies laws and royal resolutions, receives and sends envoys to foreign countries and hosts state visits. He has a more tangible influence as the symbol of national unity. The annual New Year's Eve speech is one venue where the king traditionally raises issues dealing with negative aspects in society. The King is also High Protector of the Church of Norway (the state church), Supreme Commander of the Norwegian armed forces and Grand Master of the Royal Norwegian Order of St. Olav and the Royal Norwegian Order of Merit.[2][3]
Contents
History
-
- Main article: Hereditary Kingdom of Norway
The position of King of Norway has been in continuous existence since the unification of Norway in 872. Although Norway has officially been a hereditary kingdom throughout that entire time there have been several instances of elective succession, latest in 1905 Haakon VII was elected by the people of Norway to the position of king through a plebiscite. In recent years members of the Socialist Left party have proposed the abolition of the monarchy during each new session of parliament, though without any likelihood of success.[4] This gives the Norwegian monarchy the unique status of being a popularly elected royal family and receiving regular formal confirmations of support from the Storting.
 King Harald receives Norway out of his father's hands in this illustration from the 14th century Flateyjarbók.
King Harald receives Norway out of his father's hands in this illustration from the 14th century Flateyjarbók.
Germanic kingdom
Prior to and in the early phase of the Viking Age Norway was divided into several smaller kingdoms. These are thought to follow the same tradition as other Germanic monarchies of the time; the king was usually elected by the high ranking farmers of the area and served mainly as judge during the popular assemblies, as a priest during the sacrifices and as a military leader during wars.
Harald Fairhair was the first king of Norway. The date of the first formation of a unified Norwegian kingdom is set to 872 when he defeated the last petty kings who resisted him at the Battle of Hafrsfjord, however the consolidation of his power took many years. The boundaries of Fairhair's kingdom were not identical to those of present day Norway, and upon his death the kingship was shared among his sons. Some historians put emphasis on the actual monarchial control over the country and assert that Olaf II alias Saint Olaf, who reigned from 1015 and to 1028, was the first king to control the entire country. Olaf is generally held to be the driving force behind Norway's final conversion to Christianity. Furthermore he was in 1031 revered as Rex Perpetuum Norvegiæ (Latin for Eternal King of Norway), and subsequently, the 1163 Succession Law stated that all kings after Olaf II's son, Magnus I, were not independent monarchs, but vassals holding Norway as a fief from Saint Olaf.[5]
Middle ages
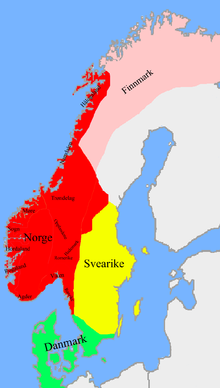 Mainland Norway during the reign of Saint Olav ca. 1020 AD. The Finnmarken ("Marches of the Sami"), most of which paid tribute to the kings of Norway, are shown in pink.
Mainland Norway during the reign of Saint Olav ca. 1020 AD. The Finnmarken ("Marches of the Sami"), most of which paid tribute to the kings of Norway, are shown in pink.
In the twelfth and thirteenth centuries the Norwegian kingdom was at its geographical and cultural peak. The kingdom included Norway (including the now Swedish provinces of Jemtland, Herjedalen, Særna, Idre and Båhuslen), Iceland, the Faroe Islands, Greenland, Shetland, Orkney and other smaller areas in the present day United Kingdom. The king had diplomatic relations with most of the European kingdoms and formed alliances with Scotland and Castile, among others. Large castles such as Haakon's Hall and cathedrals, the foremost being Nidaros Cathedral, were built.
In the tradition of the Germanic monarchy the king had to be elected by a representative assembly of noblemen. Men eligible for election had to be of royal blood; the eldest son of the previous king was not automatically chosen. During the civil war era the unclear succession laws and the practice of power-sharing between several kings simultaneously gave personal conflicts the potential to become full-blown wars. Over the centuries kings consolidated their power and eventually a strict succession law made Norway a principally hereditary kingdom. In practice the king was elected by the Riksråd in a similar way to Denmark. He adhered to a håndfæstning and governed in the council of Norwegian noblemen according to existing laws.
After the death of Haakon VI of Norway in 1380, his son Olav IV of Norway succeeded to both the thrones of Norway and Denmark and was also elected King of Sweden. After his death at the age of 17 his mother Margrethe united the three Scandinavian kingdoms in personal union under one crown, in the Kalmar Union. Olav's death extinguished the Norwegian male royal line; he was also the last Norwegian king to be born on Norwegian soil for the next 567 years.[5]
The Black Death of 1349–51 was a contributing factor to the decline of the Norwegian monarchy as the noble families and population in general were gravely affected. But the most devastating factor for the nobility and the monarchy in Norway was the steep decline in income from their holdings. Many farms were deserted and rents and taxes suffered. This left the Norwegian monarchy weakened in terms of manpower, noble support, defence ability and economic power.[5]
Surviving the unions
The Kalmar Union was made possible not only by the complex events in the royal dynasties of Scandinavia but was also, among other things, a direct reaction to the expansive and aggressive policies of the Hanseatic League.[5]
On 6 June 1523 Sweden left the union permanently, leaving Norway in an unequal union with a Danish king already embarked on centralising the government of the Union.
In the following centuries the Norwegian monarchy was characterised by a king mostly residing abroad. This weakened the monarchial governing structures of Norway; the Riksråd, for example, was gradually undermined as the Norwegian nobles were not able to enjoy the King's confidence to the same extent as their Danish counterparts. The King was also less able to govern according to Norwegian needs as the distance meant he and his advisors had less knowledge of the conditions in Norway.[6]
Norway was one of few countries where the archdiocese was coterminous with the national territory. The church was therefore an important factor in trying to maintain the separate Norwegian monarchy. In the 16th century the power struggle between the Norwegian nobles and the king culminated at the same time as the reformation. This prompted a set of events in which the struggle against the Danish dominance in Norway was coupled with the struggle against the reformation. When both failed the effects were harsh. The Norwegian Catholic bishops were replaced with Danes and the Norwegian church was subdued and made wholly Danish. The Norwegian Riksråd was abolished in 1536 and more and more foreign men were appointed to important positions in Norway.[6]
The Danish nobles pushed the king to reduce Norway to a Danish province in order for them to gain more control in the election of future kings. However, the hereditary nature of the Norwegian monarchy meant that the King had to maintain the basic principle of Norway being a separate and extant kingdom. If the Danish nobles were to elect as king someone other than the next in line to the throne the Union would be dissolved. This gave the king the upper hand in the negotiations for the håndfesting. Potential heirs to Norway were present both in the royal dynasties of Sweden and Schleswig-Holstein, so if the King of Denmark did not assert his position as King of Norway they would.[6]
During this time the Danish kings were more preoccupied with securing the traditionally Danish fringe territories and therefore paid little attention to and made few attempts at maintaining the Norwegian interests. As a result Jemtland, Herjedalen, Båhuslen, Shetland and Orkney were lost to Sweden and Scotland. In addition all contact with Greenland ceased.
In 1661 Frederick III introduced absolute monarchy in Denmark and Norway and introduced new laws in both countries to that effect. Up until that time the law of Magnus the law-mender given in 1274 and 1276 had been the law of Norway. Christian IV's Norwegian law was in effect a translation into Danish of that older law. 1661 also marks the point where the last remnants of representational local government were removed and had to be rebuilt. However, that process started almost immediately when local men of means started putting pressure on local governors in order to gain or regain influence on local matters.[6]
Emerging independence
During the Napoleonic Wars the King aligned Denmark–Norway with France. When Napoleon lost the war, the king was forced to cede Norway to the king of Sweden under the Treaty of Kiel in 1814. It was initially proposed that the Norwegian dependencies of Greenland, Iceland and the Faroes would remain with Norway, but that point was dropped during the negotiations so they became Danish.[7]
On hearing news of the treaty, the Prince of the Kingdom of Denmark-Norway, Christian Frederick, the resident viceroy in Norway, participated in founding a Norwegian independence movement. The independence movement was successful, partly due to clandestine support from the Danish Crown, but also because of the strong desire for independence in Norway. On April 10, a national assembly met at Eidsvoll to decide on a constitution. Norway eventually declared independence on May 17, 1814, electing Christian Frederick as King. A short war with Sweden later that year ended with the Convention of Moss. This led to the ousting of Christian Frederick, and the Norwegian Storting electing Charles XIII of Sweden as King of Norway, creating the union between Sweden and Norway.[7] In turn the king recognised the Norwegian constitution which was only changed to facilitate the union.
The end result was that the Norwegian monarchy became a constitutional monarchy. In this new union the King was much more a King of Norway than under the previous Danish system. The only area of policy not in the hands of the Norwegians was foreign policy.
Norway had been brought along into the new developments of the world as they arrived in Denmark. However, with the break the Norwegians were able to forge a more progressive political development than was the case in Denmark. Denmark introduced a constitutional monarchy 35 years after Norway. Parliamentarism was introduced in Norway 17 years before Denmark and 33 years before Sweden.[8] The union with Denmark also had its adverse effects on the monarchy, among other things it resulted in the crown of Norway experiencing a loss of territory which today amounts to 2 322 755 km².[9] Very few royal undertakings had been located to Norway and the country is thus lacking the monumental palaces of the period as can be seen in Copenhagen and other parts of Denmark.
Union with Sweden
The Treaty of Kiel stipulated that Norway was to be ceded by the king of Denmark–Norway to the king of Sweden. This was however rejected in Norway, where calls for self-determination were already mounting. A Norwegian constituent assembly was called, and a liberal constitution was adopted on 17 May 1814. A short war ensued, ending in a new agreement between the Norwegian parliament and the Swedish king.
 Jean Baptiste Bernadotte [a.k.a. King Charles XIV John], Marshal of France, King of Sweden (1818). Joseph Nicolas Jouy, after François Kinson. As Crown Prince, Jean Baptiste Bernadotte was primarily responsible for establishing the union.
Jean Baptiste Bernadotte [a.k.a. King Charles XIV John], Marshal of France, King of Sweden (1818). Joseph Nicolas Jouy, after François Kinson. As Crown Prince, Jean Baptiste Bernadotte was primarily responsible for establishing the union.
The Convention of Moss was from a Norwegian point of view a significant improvement over the terms dictated to Denmark-Norway at the treaty of Kiel. Notably, Norway was no longer to be treated as a Swedish conquest but rather as an equal party in a personal union of two independent states. Both the principle and substance of the Norwegian Constitution were preserved, with only such amendments as were required to allow for the union with Sweden. Norway retained its own parliament and separate institutions, except for the common king and foreign service.
The Norwegian Storting would propose Norwegian laws without interference from Sweden, to be approved by the common King in his capacity as King of Norway. The King would occasionally enact laws unfavourable to Sweden. As the Norwegian movement towards full independence gained momentum, the King approved the building of forts and naval vessels intended to defend Norway against a Swedish invasion.
The union was nevertheless marked by the Norwegians' constant and growing discontent with being in a union of any kind. The Storting would propose laws to reduce the king's power or to assert Norwegian independence. This would most often be vetoed by the king, but as he only had the right to veto the same law twice, it would eventually be passed. Already the constitution of 1814 specified that Norway would have a separate flag, and the present design was introduced in 1821. The flags of both kingdoms were defaced with the union mark in 1844 to denote their equal status within the union. It was discarded despite royal objections from the Norwegian flag in 1898. In 1837 local self-government in certain areas of policy was introduced in rural areas as well as towns. Parliamentarism was introduced in 1884.
It also has to be said that the Royal House of Bernadotte tried hard to be a Norwegian Royal House as well. The Royal Palace in Oslo was built during this period. There were separate coronations in Trondheim as stipulated in the Constitution. The royal princes even had a hunting lodge built in Norway in order to spend more private time there.[10] King Oscar II himself spoke and wrote Norwegian fluently.
Full independence
In 1905 a series of disputes between parliament and the King culminated with the matter of separate Norwegian consuls to foreign countries. Norway had grown into one of the world's leading shipping nations while Sweden retained control of both the diplomatic and consulate corps. The Swedes had little insight in the matters Norwegian ships and businessmen needed assistance with abroad and consulates were not even established in several important shipping cities. The demand for separate Norwegian consuls was seen as very important by the Norwegian parliament and society. The Storting proposed a law establishing a separate Norwegian consulate corps. King Oscar II refused to ratify the law and subsequently the Norwegian cabinet resigned. The king was not able to form any other government that had the support of parliament and as such it was deemed on 7 June that he had failed to function as King of Norway.[7][11]
The Norwegian people gave their consent in a plebiscite held on 13 August which resulted in an overwhelming 368,208 votes (99.95%) in favor of dissolution of the Union, against 184 (0.05%) opposed, with 85 percent of Norwegian men voting. No women voted, as universal suffrage was not granted until 1913, however Norwegian feminists collected more than 200,000 signatures in favor of dissolution.[7][11]
On November 12 and November 13, in the second constitutional plebiscite in three months, Norwegian voters decided by a nearly 79 percent majority (259,563 to 69,264) to keep the monarchy instead of establishing a republic.[11]
During the summer a Norwegian delegation had already approached the 33-year-old Prince Carl of Denmark, the second son of the Crown Prince Frederick of Denmark. The Norwegian parliament had considered other candidates but ultimately chose Prince Carl, partly because he already had a son to continue the line of succession, but more significantly because Carl was married to Maud of Wales, the daughter of King Edward VII. By bringing in a king with British royal ties, it was hoped that Norway could court Britain's support.[11]
Prince Carl impressed the delegation in many ways, not the least because of his sensitivity to the liberal and democratic movements that had led to Norway's independence. Though the Norwegian constitution stipulated that the Storting could choose a new king if the throne were vacant, Carl was aware that many Norwegians — including leading politicians and high-ranking military officers — favored a republican form of government. Attempts to persuade the prince to accept the throne on the basis of Parliament's choice failed; Carl insisted that he would accept the crown only if the Norwegian people expressed their will for monarchy by referendum and if the parliament then elected him king.
Following the November plebiscite affirming Norwegians' desire for a monarchy, the parliament by an overwhelming majority offered Carl a clear mandate to the Norwegian throne on November 18. The prince accepted the same evening, choosing the name Haakon, a traditional name used by Norwegian kings. The last king with that name was Haakon VI, who died in the year 1380.
The new king therefore became Haakon VII, King of Norway. His two-year-old son Alexander, the heir apparent, was renamed Olav and became Crown Prince Olav. The new royal family arrived in the capital Kristiania (later Oslo) on November 25. Haakon VII was sworn in as king of Norway on November 27.[11]
A new monarchy
The early years of the new Norwegian monarchy were marked by a shortage of funds. The Norwegian state was poor and funds were needed elsewhere than in the upkeep of a large court. In that sense it was a stroke of good fortune that Prince Carl had set as a condition for accepting the throne that he would not be forced to keep a large court. However, the royal travels and the upkeep of the royal residences, after the initial refurbishment in 1905, were to some extent neglected. One example of the negative financial situation is that Prince Carl had been promised a Royal Yacht when he accepted the throne, but this was not fulfilled until 1947.[12]
One important incident in the early years of the new monarchy was in 1928 when the King appointed the first Labour government. The Norwegian Labour Party was at that time quite radical and even had the abolition of monarchy as part of their programme. It was the custom for the King to rely on the advice of previous Prime Minister in deciding who to give the assignment as new Prime Minister. In this case the previous conservative Prime Minister was opposed to giving power to the radicals and advised the appointment of someone else. But the King adhered to the established practice of parliamentarism and decided to appoint Christopher Hornsrud the first Labour Prime Minister. The Labour party later dropped the abolition of monarchy from their programme.
During the German occupation of World War II the King was an important symbol of national unity and resistance. His steadfast opposition to the German demands of surrender was important for the fighting spirit of the Norwegian population. The constitutional powers granted to the King in the Norwegian monarchial system made his position very important and enabled the government in exile to continue its work with the utmost legitimacy.
After the war the Norwegian royal house succeeded in maintaining a balance between regality and approachability. King Olav V was deemed the people's king and the spontaneous show of mourning from the population upon his death in 1991 demonstrated the high standing he had among the Norwegian people. Even republicans were among the masses lighting candles in front of the Palace.[13]
In later years the marriages of the then Crown Prince Harald in 1968 and of Crown Prince Haakon in 2001 sparked considerable controversy, but the lasting effect on the popularity of the monarchy has been minimal. Although decreased from its level of above 90 percent after the war, support for the monarchy seems to remain stable around and mostly above the 70 percent mark.[14]
Constitutional rights and privileges
Although the 1814 constitution grants important executive powers to the king, these are almost always exercised by the Council of State in the name of the King (King's Council, or cabinet). Constitutional practice has replaced the meaning of the word King in most articles from the king personally to the elected government. The reserve powers vested in the Monarch by the constitution are significant and an important security part of the role of the Monarchy, and were last used during World War II.
Immunity
Article 5 states: The King's person is sacred; he cannot be censured or accused. The responsibility rests with his Council.[15]
This article applies to the king personally. The king has legal sovereign immunity.
Article 37 states: The Royal Princes and Princesses shall not personally be answerable to anyone other than the King, or whomever he decrees to sit in judgment on them.[15]
This means that the Princes and Princesses also have immunity on the discretion of the king. He could decide to let them be judged by the regular courts or he could decide to judge them himself. This has never been tested in practice.
Council of State
The Council of State consists of a Prime Minister and his council, all formally appointed by the King. The Council of State is the Government of Norway. Parliamentarism has been in place since 1884 and entails that the cabinet must not have the parliament against it, and that the appointment by the King is a formality. In practice, the monarch will ask the leader of a parliamentary block that has a majority in the Storting to form a government. The King relies on the advice of the previous prime minister and the President of the Storting in this question. The last time the King appointed a new prime minister contrary to the advice of the previous was in 1928 when he appointed the first Labour government.
Article 12 states: The King himself chooses a Council from among Norwegian citizens who are entitled to vote. [...] The King apportions the business among the Members of the Council of State, as he deems appropriate.
Article 30 states: [...] Everyone who has a seat in the Council of State has the duty frankly to express his opinion, to which the King is bound to listen. But it rests with the King to make a decision according to his own judgment. [...][15]
Veto of laws
The King has to sign all laws in order for them to become valid. He can veto any law. However, if three separate Stortings approves the law it becomes valid even without the King's consent. The King has not vetoed any law in modern times. The last law enacted without the King's consent was the law regarding a pure national flag in 1898.
Article 78 states: If the King assents to the Bill, he appends his signature, whereby it becomes law.[15]
If he does not assent to it, he returns it to the Odelsting with a statement that he does not for the time being find it expedient to sanction it. In that case the Bill must not again be submitted to the King by the Storting then assembled. [...][15]
Church of Norway
The Church of Norway, also known as the Evangelical Lutheran Church of Norway, is the state church of Norway, to which 86% of Norwegians are members. The Church of Norway professes the Lutheran branch of Christianity, and is a member of the Porvoo Communion.
The King is the supreme governor and protector of the Church of Norway. He formally decides who is to become bishops and oversees that the church conducts its business according to "the norms prescribed" for them. In practice this authority has been delegated to the Ministry of Church Affairs.[15]
Pardoning criminals
Article 20 states: The King shall have the right in the Council of State to pardon criminals after sentence has been passed.[15]
A pardon is the forgiveness of a crime and the penalty associated with it. It may be given if new information on the crime or criminal has come to light after sentencing has begun. A pardon may entail a complete or partial withdrawal of punishment. The practical execution of this right has been delegated to the Ministry of Justice which may dismiss an application for a pardon.[16] The formal approval of a pardon has to be done by the King in Council. In 2004 a total of 51 applications for pardon were approved and 274 were denied.[17]
Appointing senior officials
Article 21 states: The King shall choose and appoint, after consultation with his Council of State, all senior civil, ecclesiastical and military officials.[15] The appointment is formally made by the king, but is in practice up to the elected government.
Dismissing the government
Article 22 states: The Prime Minister and the other Members of the Council of State, together with the State Secretaries, may be dismissed by the King without any prior court judgment, after he has heard the opinion of the Council of State on the subject.[15]
Chivalric orders
Article 23 states: The King may bestow orders upon whomever he pleases, as a reward for distinguished services[...][15]
Norway has two chivalric orders: the Royal Norwegian Order of St. Olav and the Royal Norwegian Order of Merit. In addition the King awards several other distinguished medals for a wide range of accomplishments.
War
Article 25 states: The King is Commander-in-Chief of the land and naval forces of the Realm.[15] The King is also Commander-in-Chief of the Air Force. It is not mentioned because there was no Air Force in 1814.
Article 26 states: The King has the right to call up troops, to engage in hostilities in defence of the Realm and to make peace, to conclude and denounce conventions, to send and to receive diplomatic envoys.[15]
The King is revered in the armed forces as their highest commander, but there is no doubt as to the complete control of the armed forces by the elected government. The Kings of Norway have traditionally received an extensive military training and to some extent pursued a career within the armed forces before ascending to the throne. During World War II the King took a more active role in the decision-making and while the government still had the last word the King's advice was given much weight. On one occasion during the invasion the King was given an ultimatum from the Germans demanding Norway's surrender. King Haakon VII told the government he would abdicate if they decided to accept. In 1944 Crown Prince Olav was appointed Chief of Defence based on his military leadership abilities.
Coronation
From before recorded Norwegian history the monarch would be installed by acclamation, a ceremony held on the ting where the king swore to uphold the laws of the land and the assembled chieftains swore allegiance to him. The first coronation in Norway and in all Scandinavia took place in Bergen in 1163 or 1164. For a long time both ceremonies were used in Norway. That way the king was invested with powers both from the noblemen and from the church. The coronations also symbolised that the king would hold the kingdom in fief to St. Olav the eternal king of Norway. The last acclamation took place on Akershus Castle in 1648. The last medieval coronation in Norway took place 29 July 1514. Today the king still goes through a ceremony similar to the acclamation when he takes the oath of allegiance to the Constitution in the Storting. The Norwegian Constitution of 1814 determined that any Norwegian coronations from that time onward were to take place in Nidaros Cathedral in Trondheim. This re-established the relationship to the sacred king's burial church. The constitutional article about the coronation was annulled in 1908. When king Olav V ascended the throne in 1957 he still wanted to receive the blessing of the church for his reign and the Benediction of the king was introduced. The benediction is a much simpler ceremony, but it still takes place in Nidaros Cathedral and with the Royal Regalia at the high altar. King Harald V and Sonja also received the benediction in 1991.[18]
Succession
The order of succession to the Norwegian throne has followed absolute primogeniture since 1990, as is described in article 6 in the Constitution of Norway:
- The order of succession is lineal, so that only a child born in lawful wedlock of the Queen or King, or of one who is herself or himself entitled to the succession may succeed, and so that the nearest line shall take precedence over the more remote and the elder in the line over the younger.
- An unborn child shall also be included among those entitled to the succession and shall immediately take her or his proper place in the line of succession as soon as she or he is born into the world.
- The right of succession shall not, however, belong to any person who is not born in the direct line of descent from the last reigning Queen or King or a sister or brother thereof, or is herself or himself a sister or brother thereof.
- [...]
- For those born before the year 1971, Article 6 of the Constitution as it was passed on 18 November 1905 shall, however, apply. For those born before the year 1990 it shall nevertheless be the case that a male shall take precedence over a female.[15]
Article 6 of the original constitution had specified salic (male-only) succession; so Harald's sisters Ragnhild (b. 1930) and Astrid (b. 1932) and their descendants are excluded from the line of succession. Under the male-preference primogeniture applying to those born between 1971 and 1990, Princess Märtha Louise (b. 1971) places behind her younger brother Haakon and his descendants.
If a monarch were to be without any heirs they are allowed to nominate their successor, but the decision rests with the Storting.
The specific line of succession is as follows:
- HRH Crown Prince Haakon Magnus, King Harald's son (b. 1973)
- HRH Princess Ingrid Alexandra, Crown Prince Haakon's daughter (b. 2004)
- HH Prince Sverre Magnus, The Crown Prince's son (b. 2005)
- HH Princess Märtha Louise, King Harald's daughter (b. 1971)
- Maud Angelica Behn, Princess Märtha Louise's daughter (b. 2003)
- Leah Isadora Behn, Princess Märtha Louise's second daughter (b. 2005)
- Emma Tallulah Behn, Princess Märtha Louise's third daughter (b. 2008)
As specified in the constitution the line of succession to the throne will never be very long as successors will lose their right when they no longer are a direct descendant of the last reigning monarch or of his or her siblings.
Finances
The King, Queen, Crown Prince and Crown Princess are exempt from paying any taxes and their personal finances are not revealed to the public. Other members of the royal family have lost that privilege upon marriage. It is believed that only the King has a personal fortune of a notable size.
The royal farms generate some revenue, but this is always re-invested in the farms themselves.
In the Norwegian state budget of 2010 the sum of 142.5 million Norwegian kroner was allocated to the Royal Household.[19] 16.5 million was also given to the monarchs as appanage.[20] 20.9 million was in addition allocated to rehabilitazion of royal property.[21] In 2010, the Royal Household of Norway claimed that King Haralds fortune was close to a 100 million Norwegian kroner. [22] 500 million Norwegian kroner was in the late 1990s allocated to the extensive refurbishments of the royal residences that have been taking place and are still under way. The restoration of the Royal Palace in Oslo went far beyond budget because the structural state of the palace was much worse than expected. However, the large expense was criticised in the media.[13]
Residences
The Royal Palace in Oslo is the main official residence of the monarch. It was built in the first half of the 19th century as the Norwegian residence of Norwegian and Swedish king Charles III (Carl Johan, Charles XIV of Sweden) and is used as the official residence of the present Norwegian Monarch.[23] Bygdøy Royal Estate is the official summer residence and is also situated in Oslo. Bygdøy has been under extensive restoration and has therefore not been used regularly since the accention of King Harald V.[24] Oscarshall castle is a "recreational castle" also situated in Oslo, but rarely used. There are also official residences in three other Norwegian cities:
- Gamlehaugen in Bergen
- Ledaal in Stavanger
- Stiftsgården in Trondheim
All of the official residences are partially open to the public.[25]
The King owns a royal yacht bearing the name HNoMY Norge which is manned and maintained by the Royal Norwegian Navy and used both for official and private travels in Norway and abroad.[26] The Norwegian State Railways maintains a set of royal train carriages.[27]
The crown princely couple resides at Skaugum Manor in Asker municipality outside of Oslo, while the three princesses of Norway live on estates in Oslo, Fredrikstad and Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
Both Skaugum and Bygdøy are working farms producing grain, milk and meat where the profits are re-invested in the farms themselves.[28] In 2004 the King transferred management of the farming activities on Bygdøy to the Norwegian Museum of Cultural History.[29]
The royal family also possess several other holiday homes of a private nature.[30]
Titles and styles
- Since 1991: His Majesty Harald V, Norway's King
Royal coat of arms
The Coat of arms of Norway is one of the oldest in Europe and serves both as the coat of arms of the nation and of the Royal House. This is in keeping with its origin as the coat of arms of the kings of Norway during the Middle Ages.[31]
Håkon the Old (1217-1263) used a shield with a lion. The earliest preserved reference to the colour of the arms is the King's Saga written down in 1220.[31]
In 1280 King Eirik Magnusson added the crown and silver axe to the lion.[31] The axe is the martyr axe of St. Olav, the weapon used to kill him in the battle of Stiklestad in 1030.
The specific rendering of the Norwegian arms has changed through the years, following changing heraldic fashions. In the late Middle Ages, the axe handle gradually grew longer and came to resemble a halberd. The handle was usually curved in order to fit the shape of shield preferred at the time, and also to match the shape of coins. The halberd was officially discarded and the shorter axe reintroduced by royal decree in 1844, when an authorized rendering was instituted for the first time. In 1905 the official design for royal and government arms was again changed, this time reverting to the medieval pattern, with a triangular shield and a more upright lion.[31]
The coat of arms of the royal house as well as the Royal Standard uses the lion design from 1905. The earliest preserved depiction of the Royal Standard is on the seal of Duchess Ingebjørg from 1318.[32] The rendering used as the official coat of arms of Norway is slightly different and was last approved by the king 20 May 1992.[33]
When used as the Royal coat of arms the shield features the insignias of the Royal Norwegian Order of St. Olav around it and is framed by a royal ermine robe, surmounted by the crown of Norway.
The Royal coat of arms is not used frequently. Instead, the king's monogram is extensively used, for instance in military insignia and on coins.
External links
See also
- Norwegian Royal Family
- List of Norwegian monarchs
- Royal coronations in Norway
- Politics of Norway
- Abel Prize
References
- ^ Official royal house web site Retrieved 5 November 2007
- ^ The Church of Norway on its history and status Retrieved 21 November 2006
- ^ Royal House web site on the orders and medals Retrieved 21 November 2006
- ^ Socialist Left web page on proposed republic (Norwegian) Retrieved 21 November 2006
- ^ a b c d History of Norway from the Norwegian government web site Retrieved 21 November 2006
- ^ a b c d The history of power during the Danish era (Norwegian) Retrieved 21 November 2006
- ^ a b c d History of Norway on historyworld.com Retrieved 21 November 2006
- ^ The introduction of parliamentarism is not as clear cut in Denmark and Sweden as in Norway. In Denmark the year 1901 is usually given, but the years 1905 and 1920 are also important in this respect. In Sweden parliamentarism was re-introduced in 1917.
- ^ This number is found by adding up the areas of Jämtland, Härjedalen, Bohuslän, Iceland, the Faroe Islands, Greenland, Shetland and Orkney. The entire area of Greenland was not effectively controlled by anyone at the time, however it is today under the Crown of Denmark and therefore would have been under the Crown of Norway.
- ^ Royal House web page on Prinsehytta (Norwegian) Retrieved 5 November 2007
- ^ a b c d e Royal House web page on the dissolution of the union Retrieved 5 November 2007
- ^ RNoN web page on the HNoMY Norge (Norwegian) Retrieved 21 November 2006
- ^ a b VG article on Socialist Left party leader's critique of the palace refurbishment where the republican admits to revering King Olav (Norwegian) Retrieved 21 November 2006
- ^ Aftenposten article on the Popularity of the Monarchy Retrieved 21 November 2006
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m The Constitution of Norway in English Retrieved 21 November 2006
- ^ Government web page on the procedure for pardoning criminals (Norwegian) Retrieved 21 November 2006
- ^ Private web page on criminal care in Norway (Norwegian) Retrieved 1 December 2006
- ^ Royal regalia web site Retrieved 21 November 2006
- ^ http://www.statsbudsjettet.dep.no/Statsbudsjettet-2010/Statsbudsjettet-fra-A-til-A/Kongehuset/
- ^ http://www.statsbudsjettet.dep.no/Statsbudsjettet-2010/Statsbudsjettet-fra-A-til-A/Apanasje/
- ^ http://www.statsbudsjettet.dep.no/Statsbudsjettet-2010/Statsbudsjettet-fra-A-til-A/Kongehuset/
- ^ http://e24.no/makro-og-politikk/article3603222.ece
- ^ Royal House web site with information on the history and architecture of the Royal Palace Retrieved 5 November 2007
- ^ Aftenposten article on the restoration of Bygdøy (Norwegian) Retrieved 21 November 2006
- ^ Royal House web page on the official residences Retrieved 5 November 2007
- ^ Royal House web page on the royal yacht Retrieved 5 November 2007
- ^ Dagbladet article on the new Royal Train (Norwegian) Retrieved 21 November 2006
- ^ Royal House web page on Skaugum receiving an award for good farming Retrieved 5 November 2007
- ^ Royal House web page on Bygdøy Retrieved 5 November 2007
- ^ Royal House web page on royal residences Retrieved 5 November 2007
- ^ a b c d A web page featuring the history of the coat of arms of Norway Retrieved 21 November 2006
- ^ An article from the Norwegian National Archives depicting the seal of Duchess Ingebjørg (Norwegian) Retrieved 5 November 2007
- ^ Web page on rules for the use of the coat of arms (Norwegian) Retrieved 21 November 2006
Heads of state and government of Europe Heads of state States recognised by the United NationsAlbania · Andorra · Armenia1 · Austria · Azerbaijan1 · Belarus · Belgium · Bosnia and Herzegovina · Bulgaria · Croatia · Cyprus1 · Czech Republic · Denmark · Estonia · Finland · France · Georgia1 · Germany · Greece · Hungary · Iceland · Ireland · Italy · Kazakhstan1 · Latvia · Liechtenstein · Lithuania · Luxembourg · Macedonia · Malta · Moldova · Monaco · Montenegro · Netherlands · Norway · Poland · Portugal · Romania · Russian Federation1 · San Marino · Serbia · Slovakia · Slovenia · Spain · Sweden · Switzerland · Turkey1 · Ukraine · United Kingdom · Vatican CityStates recognised by at least one United Nations memberStates not recognised by any United Nations membersHeads of government States recognised by the United NationsAlbania · Andorra · Armenia1 · Austria · Azerbaijan1 · Belarus · Belgium · Bosnia and Herzegovina · Bulgaria · Croatia · Cyprus1 · Czech Republic · Denmark · Estonia · Finland · France · Georgia1 · Germany · Greece · Hungary · Iceland · Ireland · Italy · Kazakhstan1 · Latvia · Liechtenstein · Lithuania · Luxembourg · Macedonia · Malta · Moldova · Monaco · Montenegro · Netherlands · Norway · Poland · Portugal · Romania · Russian Federation1 · San Marino · Serbia · Slovakia · Slovenia · Spain · Sweden · Switzerland · Turkey1 · Ukraine · United Kingdom · Vatican CityStates recognised by at least one United Nations memberStates not recognised by any United Nations members1 Partially or entirely in Asia, depending on the definition of the border between Europe and Asia.Categories:- Norwegian monarchy
- Government of Norway
- Current monarchies
-
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.







