- Flag of Norway
-
See also: List of flags of Norway
Flag of Norway
Use Civil flag and ensign 
Proportion 16:22 Adopted 13 July 1821 Design A white-fimbriated blue Nordic cross on a red field Designed by Fredrik Meltzer 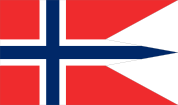
Variant flag of Norway Use State and war flag and state and naval ensign 
Proportion 16:27 The flag of Norway is red with an indigo blue Scandinavian cross outlined in white that extends to the edges of the flag; the vertical part of the cross is shifted to the hoist side in the style of the Dannebrog, the flag of Denmark.[1]
Contents
History
 The national and merchant flag of Norway (1844-1899), with the Norway and Sweden union badge, the "herring salad".
The national and merchant flag of Norway (1844-1899), with the Norway and Sweden union badge, the "herring salad".
It is difficult to establish what the earliest flag of Norway looked like. During ancient times countries did not fly flags. Kings and other rulers flew flags, especially in battle. Saint Olav used a serpent within a white mark at the Battle of Nesjar. Prior to this the raven or dragon was used. Magnus the Good used the same mark as Saint Olav. Harald Hardråde used the raven banner. This flag was flown by various Viking chieftains and other Scandinavian rulers during the ninth, tenth and eleventh centuries CE. Inge used a red lion on gold. Sverre used an eagle in gold and red. The earliest known flag which could be described as a national flag of Norway is the one used today as the Royal Standard. Eirik Magnusson used a flag described as a golden lion with axe and crown on red from 1280 and this was since regularly the flag of Norway and of the King of Norway.
The flag is based on the Coat of Arms and was originally only a flag for the ruler of Norway (as it is today). It was later also used on ships and on fortresses until it was gradually phased out during the 17th and 18th centuries. Its earliest certain depiction is on the seal of duchess Ingebjørg in 1318. Around 1500 it became the custom for ships to fly the flag of their home country to identify their nationality. At least as late as 1698 the lion banner was flown over Akershus Fortress. The "Norwegian lion" was placed in the colours of all the Norwegian regiments in 1641. In 1748 a decree stated that the Dannebrog should be the only legal merchant flag.
From about the 16th century until 1814 Norway used the same flag as Denmark, as it was in union with that country. In 1814 independent Norway adopted the Danish flag with the Norwegian lion in the canton or the upper square at the hoist. This flag was in use until 1821. Later in 1814 Norway was united with Sweden and in 1815 a common flag for both states was introduced, the Swedish flag with a white cross on a red background in the canton. This design was used for government flags and for merchant ships beyond Cape Finisterre. A distinctive Norwegian flag was designed in 1821 by Fredrik Meltzer, a member of the parliament (Storting). It was adopted by both chambers of the Storting on 11 May and 16 May, respectively. However, the king refused to sign the flag law, but approved the design for civilian use by royal order in council on 13 July 1821. The design is the same as in the present flag. But as the constitution of 1814 explicitly stated that the war flag was to be a union flag, the common flag (Swedish with a canton signifying Norway) was used by the armies and navies of both states until 1844.
Until 1838 the Norwegian flag was only used in Northern waters, as Norway had no treaty with the Barbary pirates of North Africa and had to fly the Swedish or union flag for protection. In 1844 a union badge combining Norwegian and Swedish colors was placed at the hoist of both countries' flags. The badge was popularly called Sildesalaten ("the herring salad") from its resemblance to a herring salad. Initially, the union flag was popular in Norway, since it clearly denoted the equal status of the two united states. As the union with Sweden became less popular, the Norwegian parliament abolished the union badge from the national (merchant) and state flags in 1898. Although the law was not approved by the King, it became effective since it had been passed by three consecutive Stortings. The "pure" flag was first flown in 1899, but the union badge had to be kept in the war flag. At the dissolution of the union in 1905, it was removed from the navy flag as well. Sweden kept it in all flags until 1905.
Laws regarding the flag
The Norwegian flag law of 1898 [2] specifies the appearance of the merchant and state flags and their use by merchant ships, customs and post vessels. The flag regulations of 1927 [3] further describe the use of the state flag on state property and on national holidays.
The flag regulations also describe the time of day when the flag should be hoisted and lowered. From March to October the flag should be hoisted from 08.00. From November to February it should be hoisted from 09.00. The flag is lowered at sunset, although no later than 21.00, even if sunset is later than that. In the northern counties Nordland, Troms and Finnmark the flag is flown between 10.00 and 15.00 from November to February. These rules do not apply for private use of the flag, but they are generally observed by all citizens.
There also exist written rules for the proper folding of the flag, for not letting it touch the ground, and in addition the unwritten rule that it should not be worn on the body below the waist.
Legal definition

National and merchant flag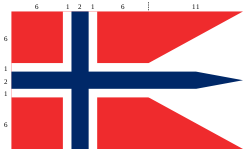
State and war flagThe proportions of the national flag are 22:16 (width to height), its colour elements having widths of 6:1:2:1:12 and heights of 6:1:2:1:6. The proportions of the state flag are 27:16, or 6:1:2:1:6:11 horizontally and 6:1:2:1:6 vertically.
The red colour shall be PMS 032 U and the blue PMS 281 U in the Pantone system. This approximates to the RGB values #EF2B2D (red) and #002868 (blue).[citation needed]
Traditions regarding the flag
Music when raising (hoisting) or lowering the flag
When raising the Norwegian flag on festive or ceremonial occasions, the hoisting will often be accompanied by a bugle call, fanfare, or the national anthem (Ja, vi elsker). For civilian use on ceremonial occasions, there are no written rules concerning this. The Norwegian armed forces have a unified bugle call for hoisting and lowering the flag, known as "flaggappell" (Attention to the flag) [4] (cf.Bugle calls of the Norwegian Army).
Code of conduct during flag hoisting and lowering
According to Norwegian Law as well as common usage, flags of other sovereign states are to be treated with the same respect as the Norwegian flag.
For civilians and non-uniformed government employees, there are no formal hand gestures (e.g. the U.S hand-over-the-heart gesture (cf. United States Flag Code) that must be performed. But it is commonly agreed that during the hoisting or lowering of the flag, civilians should conduct themselves in a respectful manner by facing the flag and standing still, straight, and quiet. Males should be bareheaded (unless there are religious, medical or climatic reasons for covering the head).
All uniformed government personnel (e.g.: Municipal traffic wardens, policemen, customs official, prison wardens, Maritime pilots, Armed Forces personnel) follow the Norwegian Armed Forces regulation during flag hoisting or lowering. The regulations stipulate that when seeing the flag being hoisted or lowered, or hearing the bugle call, all activity should if possible be stopped, and personnel should execute the foot drill manoeuvre of "Halt and front face" (stopping up and turning one's body to face the flagpole).
If a person is not in formation and is wearing a uniform hat, cap or beret, he or she must render a salute. A person in formation or not wearing a prescribed uniform hat, should stand at attention for the duration of the bugle signal, or if in sight of the hoisting or lowering, until the flag is either at the top of the pole, at half mast, or until 2/3 of the flag is in the hands of the flag party.
Rolling up the flag
Unlike the Anglo-American traditions of folding a flag (the triangular shape of the US flag or the square shape of the Union Jack), the Norwegian tradition is to roll the flag into a cylindrical shape and tie it up after lowering it.
The first step of this procedure is to fold the flag lengthwise so that its two long sides meet. Each half will then be folded 180 degrees, concealing the longitudinal white and blue stripes. Finally the folded full length flag, its height 1/4 of the hoist, will be rolled up into a red cylinder.
If the flag is fitted with a line, this is wrapped around the flag and tied with a simple slip knot. The use of a simple slip knot allows one person alone to hoist the flag unaided.
Occupation flag
When on international missions, Norwegian armed forces may keep a flag (national or merchant flag) raised during the night and illuminated by a spotlight, to affirm their presence and to boost morale.
This tradition stems from WW2, when a small-sized flag was hoisted (usually above the CO quarters) in the numerous camps of Norwegian forces in the UK, USA, Sweden and Canada, to symbolize that fight against the enemy would go on day and night until final victory.
Dishonoured flag
Military regulations stipulate that a Norwegian flag shall never touch the ground, since this is disrespectful towards the flag and may signify surrender.
If this strictly observed rule is broken, the commanding officer of the military unit must decide if the flag is dishonoured. If he decides that this is the case, he must order the flag to be cut into separate pieces (separating the red, white and blue colours) and the pieces to be burned on the parade ground before the next flag hoist.
Symbolism
Fredrik Meltzer submitted his proposal just in time to be exhibited in parliament on 4 May 1821 together with a large number of other proposals. It was approved by both chambers during the following two weeks. Meltzer himself provided no written explanation of his choice of design and colours. However, his intentions may be inferred from an earlier letter of 30 April with his comments regarding the proposal from the flag committee. That design was divided quarterly red and white. Meltzer objected to the colours because they were too similar to those of the Danish flag. He added that it would be equally unseemly to choose the colours of any of "those states with which we have been or are connected". Instead, he recommended a tricolor of red, white and blue, "three colours that now denote freedom, such as we have seen in the French flag of freedom, and still see in that of the Dutch and Americans, and in the Union of the English".[5]
His eventual choice a few days later of a Nordic cross was clearly based on the tradition established by the other Nordic countries, Denmark and Sweden. This cross represents Christianity.[6][7] The red and blue colours also explicitly referred to the same two countries, former and present union partners. It was clearly understood by all who took part in the flag discussions locally, in the press or in parliament what those colours denoted. A predominantly red flag had many adherents among those who were attached to the union with Denmark or to its flag, which for centuries had also been that of Norway. Others, who saw Denmark as an oppressor, favoured the blue colour associated with the new Swedish dynasty.[8] Consequently, most of the other flag proposals on the agenda had either red or blue as the predominant colour, depending on the political preferences of the proposers.[9]
Norwegian flag days
- 1 January - New Year's Day
- 21 January - Princess Ingrid Alexandra's birthday
- 6 February - The Sami National Day. (An official flag day both for the Sami people and for the whole of Norway.)

- 21 February - King Harald V's birthday
- Easter Day
- 1 May - Labour Day
- 8 May - Liberation Day 1945
- 17 May - Constitution Day 1814 (National Day)

- Whitsunday
- 7 June - Union Dissolution Day 1905
- 4 July - Queen Sonja's birthday
- 20 July - Crown Prince Haakon Magnus's birthday
- 29 July - Olsok. (Olav's Mass. In memory of King Olav Haraldsson (the Holy), who died in the battle of Stiklestad 29 July 1030.)
- 19 August - Crown Princess Mette-Marit's birthday
- Second Monday of September every 4 years - General election
- 25 December - Christmas Day
Chronology
-
Likely flag of the Old Kingdom of Norway, with the traditional «Norwegian Lion» motif. Confirmed usage from 1318 to ca. 18th century, probably[vague]much older[citation needed]. -
Likely flag of the Kalmar Union 1397-1523 (unconfirmed).
It is important to note that the use of flags on land (other than in battle) is fairly new.
See also
- Nordic Cross Flag
- List of flags of Norway
- Coat of arms of Norway
- Union badge of Norway and Sweden
- Royal Standard of Norway
- Holidays in Norway
- Norwegian Constitution Day
- National anthem of Norway
- Flag of Denmark
- Flag of Orkney
- Flag of Sweden
- Flag of Sami
Notes
- ^ Andrew Evans. Iceland. Bradt. http://books.google.com/books?id=9_GfdBAASUQC&pg=PA27&dq=iceland+flag+christianity&hl=en&ei=3YNGTbOfNML98AaumrzkDQ&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=1&ved=0CEQQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q=iceland%20flag%20christianity&f=false. Retrieved 2007-12-31. "Legend states that a red cloth with the white cross simply fell from the sky in the middle of the 13-century Battle of Valdemar, after which the Danes were victorious. As a badge of divine right, Denmark flew its cross in the other Scandinavian countries it ruled and as each nation gained independence, they incorporated the Christian symbol."
- ^ "LOV 1898-12-10 nr 01: Lov om Norges Flag". Lovdata.no. http://www.lovdata.no/cgi-wift/ldles?doc=/all/nl-18981210-001.html. Retrieved 2010-01-14.
- ^ "FOR 1927-10-21 nr 9733: Forskrift angående bruk av statsflagget og handelsflagget". Lovdata.no. http://www.lovdata.no/for/sf/ud/xd-19271021-9733.html. Retrieved 2010-01-14.
- ^ http://www.mil.no/multimedia/archive/00012/04__Flaggappell_12475a.WMA
- ^ Stortingsarkivet: Meltzer's letter of 30 April, http://www.stortinget.no/om_stortinget/flagg/039-18210430Meltzer_01-04.pdf
- ^ Jeroen Temperman. State Religion Relationships and Human Rights Law. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers. http://books.google.com/books?id=Khag6tbsIn4C&pg=PA88&dq=flag+of+sweden+christian&hl=en&ei=S3tGTZrYAcqr8AbOqcWgDg&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=4&ved=0CFAQ6AEwAzgK#v=onepage&q=flag%20of%20sweden%20christian&f=false. Retrieved 2007-12-31. "Many predominantly Christian states show a cross, symbolising Christainity, on their national flag. Scandinavian crosses or Nordic crosses on the flags of the Nordic countries–Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden–also represent Christianity."
- ^ Carol A. Foley. The Australian Flag: Colonial Relic or Contemporary Icon. William Gaunt & Sons. http://books.google.com/books?id=WV7ag4EpHF8C&pg=PA10&dq=sweden+flag+cross+christian&hl=en&ei=ZX5GTcO3MIH58Abcq6jqAQ&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=8&ved=0CGkQ6AEwBw#v=onepage&q=sweden%20flag%20cross%20christian&f=false. Retrieved 2007-12-31. "The Christian cross, for instance, is one of the oldest and most widely used symbols in the world, and many European countries, such as the United Kingdom, Norway, Sweden, Finland, Denmark, Iceland, Greece and Switzerland, adopted and currently retain the Christian cross on their national flags."
- ^ Stortingsarkivet: printed circular letter from Kielland, 5 September 1820, http://www.stortinget.no/om_stortinget/flagg/023-18210220OEP82T_01-05.pdf
- ^ Munksgaard, Jan Henrik: "Et nytt flagg for Norge 1814-1821", In: Nordisk flaggkontakt, Vol. 40, 2005, pp.19-30.
External links
- Norway at Flags of the World
- Norwegian defense web page about the flag's history
- University of Bergen chronology
- National Archive flag history With a picture of the seal of duchess Ingebjørg.
- A commercial web site with a flag chronology
- Stortinget flag history page
- FOTW info on the Kalmar Union flag
 Norway topics
Norway topicsHistory Geography Law Politics Constitution · Counties · Elections · European Union relations · Foreign relations · Government · Monarchy · Municipalities · Political parties · Prime Minister (List) · Romantic nationalism · Sámi Parliament · ParliamentEconomy Norwegian krone · National Bank · Oslo Stock Exchange · Education · Energy · Media · Tourism · Transport · Companies · WhalingMilitary Symbols Demographics Administrative divisions · Cities · Postal codes · Languages · Religion · Immigration · Norwegians · List of NorwegiansCulture Architecture · Art · Cinema (Actors) · Music (Composers) · Cuisine · Norwegian language · Literature (Writers · Poets) · Bunad · Jul · Constitution Day · Media · Football · Rugby union · Public holidays
 Category ·
Category ·  Portal ·
Portal ·  WikiProject
WikiProjectFlags of Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- (England
- Northern Ireland
- Scotland
- Wales)
- Vatican City
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Kosovo
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- South Ossetia
- Transnistria
Dependencies
and other territories- Åland
- Faroe Islands
- Gibraltar
- Guernsey
- Jan Mayen
- Jersey
- Isle of Man
- Svalbard
Other entities - European Union
National flags and coats of arms National flags National coats of arms Categories:- National flags
- Flags of Norway
- Nordic Cross flags
- National symbols of Norway
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.









