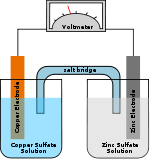
Metal–air electrochemical cell
- Metal–air electrochemical cell
-
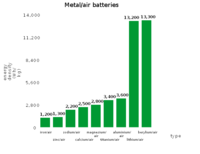
The types of metal–air batteries have different capacities
A metal–air electrochemical cell is an electrochemical cell of which the anode is a made from pure metal and the cathode connects to an inexhaustible supply of air.[1][2]
Types
- Iron–air electrochemical cell
- Zinc–air electrochemical cell
- Sodium–air electrochemical cell
- Magnesium–air electrochemical cell
- Titanium–air electrochemical cell
- Aluminium–air electrochemical cell
- Lithium–air electrochemical cell
- Berylium–air electrochemical cell
Properties of metal–air batteries
Of the various metal–air battery chemical couples (Table 1), the Li–air battery is the most attractive since the cell discharge reaction between Li and oxygen to yield Li2O, according to 4Li + O2 → 2Li2O, has an open-circuit voltage of 2.91 V and a theoretical specific energy of 5210 Wh/kg. In practice, oxygen is not stored in the battery, and the theoretical specific energy excluding oxygen is 11140 Wh/kg (40.1 MJ/kg). Compare this to the figure of 44 MJ/kg for gasoline (see petrol energy content).
| Metal–air battery |
Calculated open-circuit voltage, V |
Theoretical specific energy, Wh/kg
(including oxygen) |
Theoretical specific energy, Wh/kg
(excluding oxygen) |
| Li–O2 |
2.91 |
5210 |
11140 |
| Na–O2 |
1.94 |
1677 |
2260 |
| Ca–O2 |
3.12 |
2990 |
4180 |
| Mg–O2 |
2.93 |
2789 |
6462 |
| Zn–O2 |
1.65 |
1090 |
1350 |
Advantages
- The possibility of having a large energy density is only design limited.[citation needed]
- Some metal air electrochemical cells as lithium have a very high energy density.[citation needed]
References
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Metal hydride fuel cell — Metal hydride fuel cells are a subclass of alkaline fuel cells that are currently in the research and development phase. A notable feature is their ability to chemically bond and store hydrogen within the cell. This feature is shared with direct… … Wikipedia
Zinc–air battery — specific energy 470 (practical),1370 (theoretical) Wh/kg[1][2] (1.692, 4.932 MJ/kg) energy density 1480 9780 Wh/L[c … Wikipedia
electrochemical reaction — ▪ chemistry Introduction any process either caused or accompanied by the passage of an electric current and involving in most cases the transfer of electrons between two substances one a solid and the other a liquid. Under ordinary… … Universalium
Metal — This article is about metallic materials. For other uses, see Metal (disambiguation). Some metal pieces Metals Alkali metals … Wikipedia
Electrochemical gas sensor — Electrochemical gas sensors are gas detectors that measure the volume of a target gas by oxidizing or reducing the target gas at an electrode and measuring the resulting current. ConstructionThe sensors contain two or three electrodes,… … Wikipedia
Glossary of fuel cell terms — The Glossary of fuel cell terms lists the definitions of many terms used within the fuel cell industry. The terms in this glossary may be used by fuel cell industry associations, in education material and fuel cell codes and standards to name but … Wikipedia
Fuel cell — For other uses, see Fuel cell (disambiguation). Demonstration model of a direct methanol fuel cell. The actual fuel cell stack is the layered cube shape in the center of the image A fuel cell is a device that converts the chemical energy from a… … Wikipedia
Microbial fuel cell — A microbial electrolysis cell A microbial fuel cell (MFC) or biological fuel cell is a bio electrochemical system that drives a current by mimicking bacterial interactions found in nature. Mediator less MFCs are a more recent development; due to… … Wikipedia
Proton exchange membrane fuel cell — Diagram of a PEM fuel cell Proton exchange membrane fuel cells, also known as polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) fuel cells (PEMFC), are a type of fuel cell being developed for transport applications as well as for stationary fuel cell… … Wikipedia
Direct-ethanol fuel cell — Direct ethanol fuel cells or DEFCs are a subcategory of Proton exchange fuel cells where the fuel, ethanol, is fed directly to the fuel cell. Contents 1 Advantages 2 Reaction 3 Issues 4 … Wikipedia