- Open-circuit voltage
-
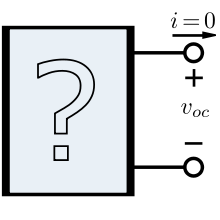 Definition of open-circuit voltage. The box is any two-terminal device, such as a battery or solar cell. The two terminals are not connected to anything (an "open circuit"), so no current can flow into or out of either terminal. The voltage voc between the terminals is the open-circuit voltage of the device.
Definition of open-circuit voltage. The box is any two-terminal device, such as a battery or solar cell. The two terminals are not connected to anything (an "open circuit"), so no current can flow into or out of either terminal. The voltage voc between the terminals is the open-circuit voltage of the device.
 Black curve: The highest possible open-circuit voltage of a solar cell in the Shockley-Queisser model under unconcentrated sunlight, as a function of the semiconductor bandgap. The red dotted line shows that this voltage is always smaller than the bandgap voltage.
Black curve: The highest possible open-circuit voltage of a solar cell in the Shockley-Queisser model under unconcentrated sunlight, as a function of the semiconductor bandgap. The red dotted line shows that this voltage is always smaller than the bandgap voltage.
Open-circuit voltage (abbreviated as OCV or VOC ) is the difference of electrical potential between two terminals of a device when there is no external load connected, i.e. the circuit is broken or open. Under these conditions there is no external electric current between the terminals, even though there may be current internally (e.g. self-discharge currents in batteries). It is sometimes given the symbol Voc.
The open-circuit voltages of batteries and solar cells are often quoted under particular conditions (state-of-charge, illumination, temperature, etc.).
See also
- short circuit current
Categories:- Electrical parameters
- Energy stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
