- Dallas Phase
-
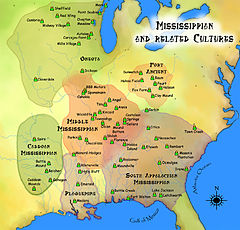
Dallas Phase (c. 1300–1600 CE) is an archaeological phase, within the Mississippian III period, in the South Appalachian Geologic province.[1][2]
Contents
Geography
Dallas peoples moved into southwest Virginia from northeastern Tennessee in the early 13th century.[3] Dallas phase settlements ranged from Holston River to Cobb Island, and up the Nolichucky River and Little Pigeon Creek in Tennessee and along the Clinch River in Virginia.[4]
Characteristics
The Dallas Phase settlements typically have one to three mounds; however, some (40Un11 and 40An44) have no mounds at all.[4] Their society was hierarchical and is characterized by distinctions between nobles and commoners in burial practices. Elites were buried in mounds, unlike the remaining population.[5] Artifacts included shell gorgets, ear pins, and beads.[6]
Dallas peoples built "large log houses."[7] Their towns had central plazas, surrounded by winter and summer homes.[8]
Ceramics
Further information: Mississippian culture potteryDallas Ware pottery was tempered with mussel shells and featured lugs, incised decoration, notched fillets, and strap handles.[9] Two distinct styles were Dallas Plain and Dallas Cordmarked.[10]
Sites
Dallas Phase sites include the following:
- Fain's Island (40JE1), Jefferson County, Tennessee
- Cox Site (40AN19), Anderson County, Tennessee
- David Davis Site (40HA301), Hamilton County, Tennessee[11]
- Hixon Site (40HA3), Hamilton County, Tennessee
- DeArmond Site (40RE12),[12] Roane County, Tennessee
- Toqua (40MR6),[13] Monroe County, Tennessee
- Bussell Island (40LD17), Loudon County, Tennessee
- Henderson Site (40SV4), Sevier County, Tennessee
- McMahan Indian Mounds (40SV1),[14] Sevier County, Tennessee
- Chiaha, Jefferson County, Tennessee
Overhill Cherokee sites, such as Citico (40Mr7), Hiwassee Old Town (40Pk3), and Chilhowee (40Bt7) have Dallas Phase artifacts;[15] however, the Dallas Phase is associated with ancestral Muscogee Creek peoples.[16]
Dates
In the same region, the Hiwassee Island Phase ran from 1000–1250 CE, followed by Early Dallas from 1250–1450 CE. Late Dallas ranged from 1450–1650 CE, which was followed by the Overhill Cherokee and Mouse Creek Phases.[2]
See also
Notes
- ^ Sullivan and Prezzano 201
- ^ a b Sullivan and Prezzano 281
- ^ Sullivan and Prezzano 220
- ^ a b Sullivan and Prezzano 208
- ^ Peregrine 49
- ^ Harle 79
- ^ Sullivan and Prezzano 203
- ^ Harle 81
- ^ Sullivan and Prezzano 204
- ^ Sullivan and Prezzano 218
- ^ Harle 7
- ^ Harle 47
- ^ Peregrine 86
- ^ Harle 59
- ^ Sullivan and Prezzano 285
- ^ Harle 50
References
- Harle, Michaelyn S. "Biological Affinities and the Construction of Cultural Identity for the Proposed Coosa Chiefdom." University of Tennessee. Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange. 2010.
- Peregrine, Peter Neal. Archaeology of the Mississippian Culture: A Research Guide. Taylor and Francis, 1996. ISBN 0-8153-0336-X.
- Sullivan, Lynne P. and Susan C. Prezzano, eds. Archaeology of the Appalachian Highlands. Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press, 2001. ISBN 1-57233-142-9.
 Pre-Columbian North America
Pre-Columbian North AmericaArchaeological cultures North American pre-Columbian chronology – Adena – Alachua – Ancient Pueblo (Anasazi) – Baytown – Belle Glade – Buttermilk Creek Complex – Caborn-Welborn – Calf Creek – Caloosahatchee – Clovis – Coles Creek – Deptford – Folsom – Fort Ancient – Fort Walton – Fremont – Glades – Glacial Kame – Hopewell (List of Hopewell sites) – Hohokam – Leon-Jefferson – Mississippian (List of Mississippian sites) – Mogollon – Monongahela – Old Cordilleran – Oneota – Paleo-Arctic – Paleo-Indians – Patayan – Plano – Plaquemine – Poverty Point – Prehistoric Southwest – Red Ocher – Santa Rosa-Swift Creek – St. Johns – Steed-Kisker – Tchefuncte – Tocobaga – Troyville
Archaeological sites Angel Mounds – Bandelier National Monument – The Bluff Point Stoneworks – Cahokia – Chaco Canyon – Casa Grande – Coso Rock Art District – Eaker – Effigy Mounds National Monument – Etowah Indian Mounds – Eva – Folsom Site – Fort Ancient – Fort Center – Gila Cliff Dwellings National Monument – Holly Bluff Site – Hopewell Culture National Historical Park – Kincaid Mounds – Kolomoki – Manitou Cliff Dwellings – Marksville – Meadowcroft Rockshelter – Mesa Verde – Moorehead Circle – Moundville – Mummy Cave – Nodena Site – Ocmulgee National Monument – Old Stone Fort – Parkin Park – Pinson Mounds – Portsmouth Earthworks – Poverty Point – Pueblo Bonito – Rock Eagle – Rock Hawk – Salmon Ruins – Serpent Mound – Spiro Mounds – SunWatch – Taos Pueblo – Toltec Mounds – Town Creek Indian Mound – WintervilleMiscellaneous Ballgame – Black drink – Buhl woman – Calumet – Chunkey – Clovis point – Container Revolution – Eastern Agricultural Complex – Eden point – Effigy mound – Falcon dancer – Folsom point – Green Corn Ceremony – Horned Serpent – Kennewick man – Kiva – Metallurgy – Mi'kmaq hieroglyphic writing – Medicine wheel – Mound builders – N.A.G.P.R.A. – Norse colonization of the Americas – Piasa – Pueblo dwellings – Southeastern Ceremonial Complex – Three Sisters agriculture – Thunderbird – Underwater panther
Categories:- South Appalachian Mississippian culture
- Muscogee
- Pre-state history of Tennessee
- Native American history of Virginia
- Pre-state history of Virginia
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.