- Mill Creek chert
-
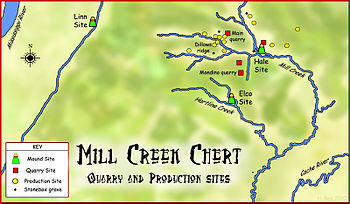
Mill Creek chert is a type of chert found in Southern Illinois and heavily exploited by members of the Mississippian culture (800 to 1600 CE).[1] Artifacts made from this material are found in archeological sites throughout the American Midwest and Southeast. It is named for a village and stream near the quarrys, Mill Creek, Illinois and Mill Creek, a tributary of the Cache River.[2] The chert was used extensively for the production of utilitarian tools such as hoes and spades, and for polished ceremonial objects such as bifaces, spatulate celts and maces.
Contents
History
 Diorama at Cahokia of flintknapper at work on hoes and bifaces
Diorama at Cahokia of flintknapper at work on hoes and bifaces
Chert is a siliceous (silica) stone, a variety of quartz similar to flint but more brittle. It naturally occurs as large, flat, elliptically shaped nodules in creek beds, and sometimes as hill-top residuum. The nodules were formed as part of the Ullin limestone formation during the Mississippian geologic period (roughly 359 to 318 million years ago). Mill Creek Chert is a tough, coarse-grained chert, usually brown or gray in color, and occurs as large tabular shaped nodules, a shape used by members of the Mississippian culture for the manufacture of broad bifaces such as hoes, spades, and ceremonial maces and spuds.[1][3] At the turn of the twentieth century archaeologists began realizing that in the hilly lands of Southern Illinois was the location for the quarrying and production centers, one of the greatest in prehistoric North America for this type of stone.[2] The sites were located near Mill Creek, Illinois, a village in Union County, located between Jonesboro and Cairo on the Alexander County line.[3] From this collection of sites, known colloquially as the "Indian Diggings", Native Americans quarried, worked into tools and blanks, and exported this stone to the wider Mississippian world. The chert found here was one of the major exported raw materials of the Mississippian culture and its distribution and procurement was one of the largest mining and production efforts organized during the Mississippian period.[2] The raw material was dug up in the quarries and then transported to small hamlets for production in hoes, spades and blanks. Archaeologists believe they were then transported to and traded at regional mound centers such as the Hale Site, a palisaded village with a platform mound and a burial mound. From these local sites they were then transported and traded at sites even further afield. These materials were some of the most widely exchanged items during this period,[2] with especially large amounts transported to the American Bottom region. Examples are numerous at Cahokia, where it was especially prized for hoes and spades,[1] but finds have been made in locations as distant as Spiro and Moundville.
Types of use
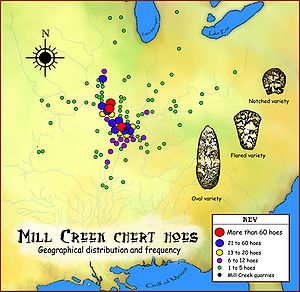
The most common tools made from Mill Creek chert were digging implements. The physical properties of the stone, its ability to absorb repeated use without breaking as often as other stone, made it especially suitable for these types of tools.[1] The Mississippian cultures heavy dependence on maize agriculture and their monumental architecture (platform mounds, moats and embankments) made such tools especially valuable. Three main varieties of Mississippian culture hoes have been found, differentiated by their shape, oval, flared and notched. The oval and flared varieties were hafted to L-shaped wooden handles, such as the one wielded by the Birger figurine. The notched version was probably hafted as a spade. Another advantageous property of the Mill Creek chert was the large size of the nodules, which meant that the corresponding tools could be large. Some hoes were up to 60 centimetres (24 in) in length.[4]
The other main use for the chert was large ceremonial bifaces, spatulate celts and stone maces. These were ritual objects which often display a high degree of craftmanship. Unlike the hoes and other utilitarian tools, the ritual objects were often ground and polished to a high degree of finish.[4] Many Southeastern Ceremonial Complex artworks depict figures wielding these ceremonial items, especially the sword shaped ceremonial bifaces and maces. As with the hoes, these artifacts could also be quite large, with some of the swordlike bifaces being up to 50 centimetres (20 in) in length. These ritual objects have been found throughout the American Bottom, the Lilbourn Site in New Madrid County, Missouri[5] and as far away as Spiro and Gahagan Mounds,[6] Caddoan Mississippian culture sites in Oklahoma and Louisiana. Although the objects are modelled after actual weapons, such as war clubs, archaeologists believe they were too delicate to function as actual weapons and instead functioned as status symbols.[4]
Gallery of Mill Creek chert artifacts
-
Hoe from the Parkin Site
-
Hoes from the Nodena Site
-
Mississippian culture stone mace from Spiro
-
Stone figurine wielding a hoe hafted to an L-shaped handle
-
SECC design from an engraved shell found at Spiro
-
SECC design from an repousse copper plate found at Moundville
-
SECC design from an engraved shell found at Castalian Springs
See also
- Visual arts by indigenous peoples of the Americas
- List of Mississippian sites
References
- ^ a b c d "Illinois Agriculture-Technology-Hand tools-Native American Tools". http://www.museum.state.il.us/exhibits/agriculture/htmls/technology/hand_tools/tech_hand_na.html. Retrieved 2010-07-12.
- ^ a b c d Charles R. Cobb (2000). From Quarry to Cornfield-The Political Economy of Mississippian Hoe Production. University of Alabama Press. pp. 15–18. ISBN 0-8173-1050-9.
- ^ a b "Mill Creek chert, Millstone Bluff, Kincaid Mounds:900 to 1550 AD". http://www.southernmostillinoishistory.net/mississippian.htm. Retrieved 2010-07-12.
- ^ a b c Charles R. Cobb (2000). From Quarry to Cornfield-The Political Economy of Mississippian Hoe Production. University of Alabama Press. pp. 48–50. ISBN 0-8173-1050-9.
- ^ "Central States Archaeological Societies-Selected Pictures from the 2004 October Journal". http://www.csasi.org/2004_october_journal/2004_selected_pictures_from_the_october_journal.htm. Retrieved 2010-07-17.
- ^ "Early Caddo, A.D. 800-1200". http://www.texasbeyondhistory.net/tejas/ancestors/early.html. Retrieved 2010-07-17.
External links
Coordinates: 37°20′37.75″N 89°16′12.36″W / 37.3438194°N 89.2701°W
- Mill Creek Chert Spade found in St. Frances Co, MO
- Mill Creek Chert found in Moundville, Alabama
- Mill Creek chert ceremonial mace from Lilbourn Site in New Madrid County, Missouri
 Pre-Columbian North America
Pre-Columbian North AmericaArchaeological cultures North American pre-Columbian chronology – Adena – Alachua – Ancient Pueblo (Anasazi) – Baytown – Belle Glade – Buttermilk Creek Complex – Caborn-Welborn – Calf Creek – Caloosahatchee – Clovis – Coles Creek – Deptford – Folsom – Fort Ancient – Fort Walton – Fremont – Glades – Glacial Kame – Hopewell (List of Hopewell sites) – Hohokam – Leon-Jefferson – Mississippian (List of Mississippian sites) – Mogollon – Monongahela – Old Cordilleran – Oneota – Paleo-Arctic – Paleo-Indians – Patayan – Plano – Plaquemine – Poverty Point – Prehistoric Southwest – Red Ocher – Santa Rosa-Swift Creek – St. Johns – Steed-Kisker – Tchefuncte – Tocobaga – Troyville
Archaeological sites Angel Mounds – Bandelier National Monument – The Bluff Point Stoneworks – Cahokia – Chaco Canyon – Casa Grande – Coso Rock Art District – Eaker – Effigy Mounds National Monument – Etowah Indian Mounds – Eva – Folsom Site – Fort Ancient – Fort Center – Gila Cliff Dwellings National Monument – Holly Bluff Site – Hopewell Culture National Historical Park – Kincaid Mounds – Kolomoki – Manitou Cliff Dwellings – Marksville – Meadowcroft Rockshelter – Mesa Verde – Moorehead Circle – Moundville – Mummy Cave – Nodena Site – Ocmulgee National Monument – Old Stone Fort – Parkin Park – Pinson Mounds – Portsmouth Earthworks – Poverty Point – Pueblo Bonito – Rock Eagle – Rock Hawk – Salmon Ruins – Serpent Mound – Spiro Mounds – SunWatch – Taos Pueblo – Toltec Mounds – Town Creek Indian Mound – WintervilleMiscellaneous Ballgame – Black drink – Buhl woman – Calumet – Chunkey – Clovis point – Container Revolution – Eastern Agricultural Complex – Eden point – Effigy mound – Falcon dancer – Folsom point – Green Corn Ceremony – Horned Serpent – Kennewick man – Kiva – Metallurgy – Mi'kmaq hieroglyphic writing – Medicine wheel – Mound builders – N.A.G.P.R.A. – Norse colonization of the Americas – Piasa – Pueblo dwellings – Southeastern Ceremonial Complex – Three Sisters agriculture – Thunderbird – Underwater panther
Related: Genetic history · Indigenous Portal of North America · Pre-Columbian era Categories:- Mississippian culture
- Native American art
- American Indian relics
- Lithics
- Chert
-
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.