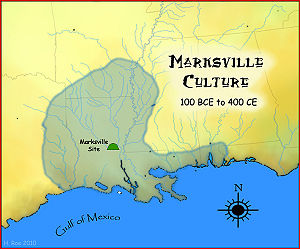
- Marksville culture
-
The Marksville culture was an archaeological culture in the lower Lower Mississippi valley, Yazoo valley, and Tensas valley areas of Louisiana, Mississippi, Missouri, Arkansas[1] and extended eastward along the Gulf Coast to the Mobile Bay area,[2] from 100 BCE to 400 CE. This culture takes its name from the Marksville Prehistoric Indian Site in Avoyelles Parish, Louisiana. Marksville Culture was contemporaneous with the Hopewell cultures of Ohio and Illinois. It evolved from the earlier Tchefuncte culture and into the Baytown and Troyville cultures[3] and later the Coles Creek and Plum Bayou cultures. It is considered ancestral to the Natchez and Taensa Peoples.[4]
Contents
Description
The Hopewell tradition was a widely dispersed set of related populations, which were connected by a common network of trade routes,[5] known as the Hopewell Exchange System. The Marksville culture was a southern manifestation of this network. Settlements were large and usually located on terraces of major streams. Evidence from excavations of burial mounds from this period suggest they were constructed for persons of high social status, and contained grave goods of imported exotic materials such as copper panpipes, earspools, bracelets and beads, rare minerals, stone platform pipes, mica figurines, marine shells, freshwater pearls, and greenstone celts.[6] The pipes had flat bases with a hole for a stem, and a bowl in the center. Animal figurines on the platform aren't unusual, with the bowl being located in the animal's back.[2] The high status leaders organized community life, and officiated at burial ceremonies, an important part of the Marksville Culture. The mounds were constructed in stages over many years, with the first stage being a flat, low platform. The ceremonies may have been held years apart and those who died between ceremonies were temporarily stored in other locations, then gathered up and buried together.[1]
Pottery
Although made from local clay, Marksville pottery was similar in design and decoration to pottery found in Illinois and Ohio. A typical vessel was three to five inches tall and three to seven inches in diameter and often decorated with geometric and effigy designs, usually stylized birds. This decorated pottery was made primarily for ceremonial uses, with other plainer utilitarian ware for daily use.[2]
Chronology
The Marksville culture was preceded by the Tchefuncte culture, and was eventually succeeded by the Troyville culture in southeastern and eastern Louisiana and western Mississippi and Baytown culturein northeastern Louisiana, northwestern Mississippi,and southeastern Arkansas.
See also
- Crooks mound
- Grand Gulf Mound
- List of Hopewell sites
References
- ^ a b "Louisiana Prehistory-Marksville, Troyville-Coles Creek, and Caddo". http://www.crt.state.la.us/archaeology/laprehis/marca.htm.
- ^ a b c "Kisatchie National Forest". http://www.fs.fed.us/r8/kisatchie/resources/heritage-pages/history.htm.
- ^ [http://www.nps.gov/seac/outline/04-woodland/index-3.htm "Southeastern Prehistory : Late Woodland Period"]. NPS.GOV. http://www.nps.gov/seac/outline/04-woodland/index-3.htm. Retrieved 2011-10-23.
- ^ "The Plaquemine Culture, A.D 1000". http://bcn.boulder.co.us/environment/cacv/cacvbrvl.htm. Retrieved 2008-09-08.
- ^ Douglas T. Price, and Gary M. Feinman (2008). Images of the Past, 5th edition. New York: McGraw-Hill. pp. 274–277. ISBN 978-0-07-340520-9.
- ^ "Southeastern Prehistory-Middle Woodland Period". http://www.nps.gov/history/seac/outline/04-woodland/index-2.htm.
External links
 Hopewellian peoples
Hopewellian peoplesWoodland period · List of Hopewell sites · Mound builder (people) · List of archaeological periods (North America) Ohio Hopewell Beam Farm · Benham Mound · Cary Village Site · Cedar-Bank Works · Dunns Pond Mound · Ellis Mounds · Ety Enclosure · Ety Habitation Site · Fort Ancient · Fortified Hill Works · Great Hopewell Road · High Banks Works · Hopeton Earthworks · Hopewell Culture National Historical Park · Indian Mound Cemetery · Keiter Mound · Marietta Earthworks · Moorehead Circle · Mound of Pipes · Nettle Lake Mound Group · Newark Earthworks · Oak Mounds · Perin Village Site · Portsmouth Earthworks · Seip Earthworks and Dill Mounds District · Shawnee Lookout · Tremper Mound and Works · Williamson Mound Archeological District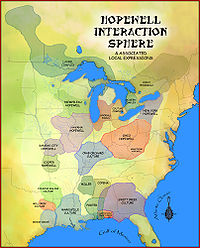
Crab Orchard culture Goodall Focus Goodall Site · Norton Mound GroupHavana Hopewell culture Kansas City Hopewell Marksville culture Miller culture Point Peninsula Complex Swift Creek culture Etowah Indian Mounds · Leake Mounds · Kolomoki Mounds Historic Park · Miner's Creek site, · Nacoochee Mound · Swift Creek mound site · Yearwood siteOther Hopewellian peoples Armstrong culture · Copena culture · Fourche Maline culture · Laurel Complex · Saugeen Complex · Old Stone Fort (Tennessee)Exotic trade items Related topics · Ancient Monuments of the Mississippi Valley · Black drink · burial mound · Calumet (pipe) · Effigy mound · Hopewell pottery · Horned Serpent · Eastern Agricultural Complex · Underwater panther Categories:- Marksville culture
- Archaeological cultures of North America
- Native American history of Louisiana
- Native American history of Mississippi
- Native American history of Missouri
- Native American history of Arkansas
- Native American archeology
- Archaeological sites in Louisiana
- Archaeological sites in Mississippi
- Classic period in the Americas
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.