- Chobanids
-
Chobanids
سلسله امرای چوپانی← 
1335–1357  →
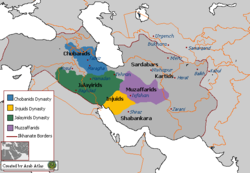
→Division of Ilkhanate territory Capital Tabriz Religion Twelver Shia Islam Government Monarchy History - Established 1335 - Disestablished 1357 The Chobanids or the Chupanids (Persian: سلسله امرای چوپانی), were descendants of a Mongol family of the Suldus clan that came to prominence in 14th century Persia.[1] At first serving under the Ilkhans, they took de facto control of the territory after the fall of the Ilkhanate. The Chobanids made Azerbaijan their stronghold, while the Jalayirids took control in Baghdad.[2]
Contents
Early Chobanids
The early Chobanids were members of the Soldus tribe. Sorgan Sira, one of the first important Chobanids, served Genghis Khan during the latter's rise to power. Later on, the Chobanids came to live under the authority of the Ilkhanate. A descendent of Sorgan Sira, Amir Tudahun, was killed in 1277 fighting against the Mamluks at the battle of Eblistan. He left a son, Malek, who in turn fathered Amir Chupan, the namesake of the Chobanids.
Amir Chupan and his Sons
During the early 14th century, Amir Chupan served under three successive Ilkhans, beginning with Ghazan Mahmud. A military commander of note, Chupan quickly gained a degree of influence over the Ilkhans and married several members of the line of Hulagu Khan. His power fueled resentment among the nobility, who conspired against him in 1319 but failed. The Ilkhan Abu Sa'id, however, also disliked Chupan's influence and successfully eliminated him from court. He fled in 1327 to Herat, where the Kartids executed him. Several of his sons fled to the Golden Horde or the Mamluks of Egypt while others were killed.
Baghdad Khatun
The Chobanids were not completely wiped out from Persia. A daughter of Chupan's, Baghdad Katun, had caught the eye of Abu Sa'id. During Chupan's lifetime, she had been married to Hasan Buzurg, the future founder of the Jalayirids, but after Chupan fled Hasan Buzurg divorced her, and she married Abu Sa'id. She quickly gained influence over the Ilkhan and exercised the wide powers given to her. She was alleged (but never proven) to have been involved in any conspiracies against the Ilkhan, but was believed by some to have caused Abu Sa'id's death in 1335. Abu Sa'id's successor Arpa Ke'un executed her.
Role During the Fall of the Ilkhnate, and Hasan-i Kuchak
Main article: Hasan KucekArpa Ke'un's position proved to be weak; when a granddaughter of Chupan, Delsad Katun, fled to Diyarbakr, it caused the governor of that region to attack and defeat the Ilkhan. During the strife that occurred in the next few years, individual members of the Chobanids sided with various factions, such as Arpa or Hasan Buzurg. The latter ended up marrying Delsad Katun, who provided for the heirs to the Jalayirid position.
While the Jalayirids were consolidating their position in Iraq, however, other Chobanid were also busy. Hasan Kucek, a grandson of Chupan, rallied much of the Chobanid family to his side and defeated the Jalayirids in 1338, paving the way for a Chobanid realm in the area around Tabriz. That same year, he elevated Sati Beg, sister of Abu Sa'id and widow of Chupan, to the Ilkhanid throne. To keep Sati Beg in check, he forced her to marry his puppet Suleiman Khan. Hasan Kucek continued to fight the Jalayirids (a fight which was further complicated by the incursions made by Togha Temur of Khurasan), but family infighting proved to be the most difficult challenge. Several members defected to the Jalayirids; in any case, Hasan Kucek was forced to deal with them up until his death in 1343.
Malek Ashraf and the Chobanid decline
A power struggle quickly emerged after Hasan Kucek's death. During the dispute, Hasan Kucek's brother Malek Asraf gained the upper hand and eliminated his uncles. By the end of 1344, Malek Asraf had gained effective control of the Chobanid lands. Like his predecessor, Malek Asraf used puppet monarchs from behind which he ruled. During his reign, the Chobanid attempted to capture Baghdad from the Jalayirids in 1347 but failed miserably. He also failed to seize Fars from the Injuids in 1350. As his reign wore on, Malek Asraf became more and more cruel, prompting widespread dissatisfaction amongst his subjects. When forces of the Golden Horde overran the Chobanid realm and captured Tabriz in 1357, few lamented the loss of power by the Chupanids. Malek Asraf was executed, and his family brought north to the Golden Horde. Malek Asraf's offspring were eventually killed off in Persia, bringing a definitive end to the Chobanids as a power.
Family tree
Chupan Hassan Timurtash Demasq Kaja Shaikh Mahmoud Bagdad Katun Hassan Kuchak Malek Ashraf Delsad Katun Modern descendents
Modern descendents of the Chobanids in Iran today share the dynastic surname Amir Chupani and are primarily found in the north, south, and Razavi Khorasan provinces, especially in the area of Mashhad.
See also
- List of Shi'a Muslims dynasties
References
- ^ Ta'rīkh-i Shaikh Uwais: History of Shaikh Uwais - by Abū Bakr al-Quṭbī Aharī, Abu Bakr al Qutbi al-Ahri, Johannes Baptist van Loon
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica
External links and references
- Charles Melville and Abbas Zaryab [1]
 Iran topics
Iran topicsHistory Pre-IslamicPrehistory · Proto-Elamite civilization BCE 3200– BCE 2800 · Elamite dynasties BCE 2800– BCE 550 · Bactria-Margiana Complex BCE 2200– BCE 1700 · Kingdom of Mannai BCE 10th– BCE 7th cent. · Median Empire BCE 728– BCE 550 · Achaemenid Empire BCE 550– BCE 330 · Seleucid Empire BCE 330– BCE 150 · Greco-Bactrian Kingdom BCE 250– BCE 125 · Parthian Empire BCE 248–CE 224 · Kushan Empire CE 30–CE 275 · Sassanid Empire CE 224–CE 651 · Hephthalite Empire CE 425–CE 557 · Kabul Shahi kingdom CE 565–CE 879
IslamicPatriarchal Caliphate 637–651 · Umayyad Caliphate 661–750 · Abbasid Caliphate 750–1258 · Tahirid dynasty 821–873 · Alavid dynasty 864–928 · Saffarid dynasty 861–1003 · Samanid dynasty 819–999 · Ziyarid dynasty 928–1043 · Buyid dynasty 934–1055 · Ghaznavid Empire 975–1187 · Ghori dynasty 1149–1212 · Seljuk Empire 1037–1194 · Khwarezmid dynasty 1077–1231 · Ilkhanate 1256–1335 · Kartids dynasty 1231–1389 · Ottoman Empire 1299–1923 · Muzaffarid dynasty 1314–1393 · Chupanid dynasty 1337–1357 · Jalayerid dynasty 1339–1432 · Timurid Empire 1370–1506 · Qara Qoyunlu Turcomans 1407–1468 · Aq Qoyunlu Turcomans 1378–1508 · Safavid Empire 1501–1722 or 1736 · Hotaki dynasty 1722–1729 · Afsharid dynasty 1736–1750 · Zand Dynasty 1750–1794 · Durrani Empire 1794–1826 · Qajar Dynasty 1794–1925
ModernSee also: Greater Iran · Ancient Iran · Iranian Cultural Continent · Indo-Iranians (languages) · Jiroft civilization · Aryans · Persian peoples · Iranian peoples · Tajiks · Kings of Persia · Military history · Years in IranPolitics
GovernmentIntellectual movements · Women's movement · Elections · Constitution · Supreme Leader · President · Judicial system · Assembly of Experts · Parliament · Guardian Council · Expediency Discernment Council · Supreme National Security Council · City and Village Councils · Human rights (LGBT) · Officials · Provincial governors · Reformists · Principlists · United Nations Security Council Resolution 1747 · Ambassadors · Foreign relations · Ministry of Intelligence · Terrorism · Military (Army · Air Force · Navy) · Censorship · Nuclear program · Allegations of state terrorism · Iranian Green Revolution Anglo-Iranian Oil Company · Operation Ajax · White Revolution · Iranian Revolution · Embassy siege · Iran-Iraq war · Iran Air Flight 655 · 1987 massacre of Iranian pilgrims · Chicago's Persian heritage crisis · History of the Islamic Republic of Iran · Iranian Presidential Election, 2009 · Persian Constitutional Revolution ·Demographics Iranian citizens (abroad) · Religion · Muslims · Bahá'ís · Christians · Armenians · Jews · Ethnic minorities · Religious minorities · Zoroastrians (persecution) · WomenLanguages Geography Cities (list) · Iranian Azerbaijan · Iranian Balochistan · Iranian Kurdistan · Iranian Plateau · Islands · Mountains · Provinces · Earthquakes · WildlifeEconomy Economic history of Iran · Agriculture · Fruit · Industry · Water and sanitation · Health care · Central bank · Companies (automobile manufacturers - Banks) · Research centers · Brain drain · Iran Electronics Industries (IEI) · Military equipment · IDRO · National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC) · Iran Aviation Industries Organization (IAIO) · Space · Milad Tower and complex · Military exports · Rial · Tehran Stock Exchange · Electronic banking · Intellectual property · International Oil Bourse · Bonyad · Asalouyeh industrial corridor · Kish Island Free Trade Zone · Chabahar Free Trade-Industrial Zone · Labor and tax laws · Economic Cooperation Organization (ECO) · Mining · Construction · Privatization · Foreign Direct Investment · Supreme Audit Court · Communications · Telecommunication Company of Iran (TCI) · Transport · Railways · Metro · Airlines · Iran Shipping Lines · Energy · Petroleum industry · Nuclear program · Tourism · Environmental issues · Economic Reform Plan · Middle East economy · List of major economic laws in Iran · Iran and WTO · Economic history of IranSociety
CultureIranian nationality · Iranology · Education (Higher · Science · Scientists and scholars · Universities) · Philosophy · List of Iranians · Literature · Media (News agencies (student) · newspapers) · Architecture (architects) · Achaemenid architecture · Art (modern/contemporary) · Persian gardens · Cinema · Cuisine · Public holidays · National symbols · Opium consumption · Music (Ey Iran · Heavy metal · Persian traditional music · Folk · Pop · Rap and hip-hop · Rock and alternative) · Blogs · Mythology · Folklore · Islam · Islamization · Scouting · Sport (Football)Other topics Calendar · Crown jewels · Anti-Iranianism · Persian names · Tehrangeles · International rankings of Iran · Sorood-e Shahanshahi IranCategories:- Former monarchies
- Former countries in the Middle East
- Former empires
- States and territories established in 1335
- States and territories disestablished in 1357
- History of Iran
- 1357 disestablishments
- Chobanids
- Muslim dynasties
- History of Islam
- Shi'a Muslim dynasties
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.