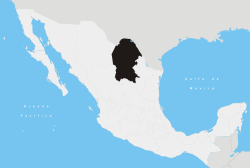
- Coahuila
-
Coahuila
Estado Libre y Soberano
de Coahuila de Zaragoza— State — 
Flag
SealAnthem: Himno Coahuilense State of Coahuila within Mexico Coordinates: 27°18′08″N 102°02′41″W / 27.30222°N 102.04472°WCoordinates: 27°18′08″N 102°02′41″W / 27.30222°N 102.04472°W Country Mexico Capital Saltillo Largest City Torreon Municipalities 38 Admission May 7, 1824[1] Order 16th[a] Government – Governor Jorge Torres López 
– Senators[2] Guillermo Anaya 
Ernesto Saro B.
Jesús María Ramón
– Deputies[3] Area[4] – Total 151,563 km2 (58,518.8 sq mi) Ranked 3rd Highest elevation[5] 3,710 m (12,172 ft) Population (2010)[6] – Total 2,748,391 – Rank 16th – Density 18.1/km2 (47/sq mi) – Density rank 26th Demonym Coahuilense Time zone CST (UTC-6) – Summer (DST) CDT (UTC-5) Postal code 25 - 27 Area code ISO 3166 code MX-COA HDI  0.850 High Ranked 9th
0.850 High Ranked 9thGDP US$ 21,556,311.01 mil[b] Website Official Web Site ^ a. Joined to the federation under the name of Coahuila y Texas also recognized as Coahuila y Tejas.
^ b. The state's GDP was 275,920,781 million of pesos in 2008,[7] amount corresponding to 21,556,311.01 millon of dollars, being a dollar worth 12.80 pesos (value of June 3, 2010).[8]Coahuila, formally Coahuila de Zaragoza (Spanish pronunciation: [koaˈwila ðe saɾaˈɣosa]), officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Coahuila de Zaragoza (English: Free and Sovereign State of Coahuila de Zaragoza) is one of the 31 states which, with the Federal District, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. The state is located in Northeastern Mexico.
Coahuila borders the Mexican states of Nuevo León to the east, Zacatecas and San Luis Potosí to the south, and Durango and Chihuahua to the west. To the north, Coahuila accounts for a 512 kilometres (318 mi) stretch of the U.S. - Mexico border, adjacent to the United States state of Texas along the course of the Rio Grande (Río Bravo del Norte). With an area of 151,563 square kilometres (58,519 sq mi), it is the nation's third-largest state. It comprises 38 municipalities (municipios). In 2010, Coahuila's population is 2,655,187 inhabitants.
The capital of Coahuila is Saltillo, and its largest city is Torreón. Coahuila also includes the cities of Monclova (a former state capital), Piedras Negras, and Ciudad Acuña.
Contents
Etymology
From the Nahuatl Kuahuilan also Cuahuilan (Place of the Trees). The researcher Vito Alessio Robles gave the final translation to the word Coahuila.
History
The Spanish explored the north of Mexico some decades after their victory in the capital of the Aztecs. Such exploration was delayed because the northern climate was harsher and there was no gold. The first Spanish settlement in the region, now called Coahuila, was at Minas de la Trinidad in 1577. Saltillo was settled in 1586 to form part of the province of New Spain, Nueva Vizcaya of the vice-royalty. Later it became one of first provinces of Nueva Extremadura to be explored by Europeans.
"Coahuila and Texas" was one of the constituent states of the newly independent United Mexican States under its 1824 Constitution, and included Texas, Coahuila, and Nuevo León. Later in the same year Nuevo León was detached, but Texas remained a part of the state until 1835, when it seceded to form the Republic of Texas. Monclova was the capital of the state from 1833 to 1835.
In 1840 Coahuila briefly became a member of the short lived Republic of the Rio Grande.
On February 19, 1856, Santiago Vidaurri annexed Coahuila to his state, Nuevo León, but it regained its separate status in 1868.
During the Mexican Revolution, Francisco Villa attacked the city of Torreón.
On April 4, 2004, the border city of Piedras Negras was flooded. More than 30 people died and more than 4000 lost their homes.
In 2007, Coahuila became the first state in Mexico to offer civil unions (Pacto Civil de Solidaridad) to same-sex couples.[9]
Geography
The Sierra Madre Oriental runs northwest to southeast through the State, and the higher elevations are home to the Sierra Madre Oriental pine-oak forests.
East of the range, the land slopes gently toward the Rio Grande, and is drained by several rivers, including the Salado and its tributary the Sabinas. The Tamaulipan mezquital, a dry shrubland ecoregion, occupies the eastern portion of the State, and extends across the Rio Grande into southern Texas.
The portion of the State west of the Sierra Madre Oriental lies on the Mexican Plateau, and is part of the Chihuahuan Desert. The Bolsón de Mapimí is a large endorheic basin which covers much of the western portion of the State and extends into adjacent portions of Chihuahua, Durango, and Zacatecas. The Nazas River, which flows east from Durango, and the Aguanaval River, which flows north from Zacatecas, empty into lakes in the Bolsón. Torreón, the most populous city in the State, lies on the Nazas in the irrigated Laguna Region, the (Comarca Lagunera), which straddles the border of Coahuila and Durango.
Coahuila contains two biosphere reserves. Maderas del Carmen lies on the northern border of the State, and includes sections of the Chihuahuan desert and sky islands of pine-oak forest in the Sierra del Carmen. The springs, lakes, and wetlands of Cuatro Ciénegas lie west of Monclova on the west slope of the Sierra Madre.
Coahuila is largely arid or semi-arid, but the rivers of the State support extensive irrigated agriculture, particularly cotton. The Parras district in the southern part of the State produces wines and brandies. The pine-oak forests of the Sierra Madre produce timber.
- Images showing two large wildfires in the state on April 9, 2011
Demographics
The last population census run across Mexico in the year 2005, reports Coahuila de Zaragoza as having roughly 2,500,000 inhabitants, which, considering its size, means that the state has a very low density, in fact as low as only 15 persons per square kilometer.
Coahuila's population is mainly made up of people of Criollo (European) extraction along with mestizos. Less than 7,500 natives reside in Coahuila, or merely 0.3% of the total population. The rest of the population is composed of American, Canadian, and Japanese communities.
The rest of the demographic particulars in the state are very similar to national averages, such as a high life expectancy (reaching 75 years of age) and a Catholic majority.
Education
Institutions of higher learning in Coahuila, Mexico include:
- Instituto Tecnológico de Saltillo
- Universidad Autónoma Agraria Antonio Narro (UAAAN)
- Universidad Autónoma de Coahuila
Economy
About 95% of Mexico's coal reserves are found in Coahuila, which is the country's top mining state. Saltillo also has a growing automobile industry, hosting General Motors and Chrysler assembly plants.
As of 2005, Coahuila's economy represents 3.5% of Mexico's total gross domestic product or 22,874 million USD.[10] Coahuila's economy has a strong focus on export oriented manufacturing (i.e. maquiladora / INMEX). As of 2005, 221,273 people are employed in the manufacturing sector.[11] Foreign direct investment in Coahuila was 143.1 million USD for 2005. The average wage for an employee in Coahuila is approximately 190 pesos per day.[citation needed] On the other hand Coahuila is the Mexican state with the highest level of public debt in the nation.
Municipalities
Coahuila is subdivided into five regions and 38 municipalities (municipios). For a full list with municipal seats, see: municipalities of Coahuila
Major communities
- Ciudad Acuña
- Ciudad Frontera
- Guerrero
- Ciudad Melchor Múzquiz
- Francisco I. Madero
- Matamoros
- Monclova
- Nueva Rosita
- Parras de la Fuente
- Piedras Negras
- Ramos Arizpe
- Sabinas
- Saltillo
- San Pedro
- Torreón
List of governors
This list is incomplete
- José María Garza Galán (1886–1893)[12]
- José María Múzquiz (1894)
- Miguel Cárdenas (1894–1909)
- Jesús de Valle (1909–1911)
- Venustiano Carranza (1911–1913)
- Gustavo Espinoza Mireles (1917–1920)
- Luis Gutiérrez Ortíz (1920–1921)
- Arnulfo González (1921–1923)
- Carlos Garza Castro (1923–1925)
- Manuel Pérez Treviño (1925–1929)
- Bruno Neira González (1929-1929)
- Nazario S. Ortiz Garza (1929–1933)
- Jesús Valdez Sánchez (1933–1937)
- Pedro Rodríguez Triana (1937–1941)
- Gabriel Cervera Riza (1941-1941)
- Benecio López Padilla (1941–1945)
- Ignacio Cepeda Dávila (1945–1947)
- Ricardo Ainslie Rivera (1947–1948)
- Paz Faz Risa (1948-1948)
- Raúl López Sánchez (1948–1951)
- Roman Cepeda Flores (1951–1957)
- Raúl Madero González (1957–1963)
- Braulio Fernández Aguirre (1963–1969)
- Eulalio Gutiérrez Treviño (1969–1975)
- Oscar Flores Tapia (1975–1981)
- Francisco José Madero González (1981-1981)
- José de las Fuentes Rodríguez (1981–1987)
- Eliseo Mendoza Berrueto (1987–1993)
- Rogelio Montemayor Seguy (1993–1999)
- Enrique Martínez y Martínez (1999–2005)
- Humberto Moreira Valdés (2005–2010) (Left)
- Jorge Torres López (2010-) (Humberto Moreira's sustitute)
- Rubén Moreira Valdés (2011-2017)
Notable people
- Venustiano Carranza - President of Mexico
- Luis Farell - Combat pilot and general
- Eulalio Gutiérrez - President of Mexico
- Joakim Soria - MLB closer
- Pablo Montero - Singer and actor
- Horacio Piña - MLB pitcher)
- Sangre Chicana - Professional wrestler
- Dr. Wagner - Profesional Wrestler
- Dr. Wagner, Jr. - Professional wrestler
- Ari Telch - Actor
- Andrea Villarreal - Feminist and revolutionary
- Rosario Ybarra - Politician and senator
- Humberto Zurita - Actor, director and producer
- Francisco Ignacio Madero - President of Mexico November 1911 - February 1913
- Reading Wood Black - Founder of Uvalde, Texas spent American Civil War years in Coahuila.
See also
- Coahuila y Tejas
- Nueva Extremadura
- Nueva Vizcaya
- States of Mexico
References
- ^ "La diputación provincial y el federalismo mexicano" (in Spanish). http://books.google.com.mx/books?id=i_GK_-6deKIC&pg=PA227&lpg=PA227&dq=22+De+Mayo+De+1824+durango&source=bl&ots=eyvDzsrMIz&sig=zYxzmtG7gTQgGV-WNDfHgqcG_kU&hl=es&ei=FtAxS9joN56ltgf-_ojFDg&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=1&ved=0CAgQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q=22%20De%20Mayo%20De%201824%20durango&f=false.
- ^ "Senadores por Coahuila LXI Legislatura". Senado de la Republica. http://www.senado.gob.mx/index.php?ver=int&mn=4&sm=4&id=8. Retrieved October 20, 2010.
- ^ "Listado de Diputados por Grupo Parlamentario del Estado de Coahuila". Camara de Diputados. http://sitl.diputados.gob.mx/LXI_leg/listado_diputados_gpnp.php?tipot=Edo&edot=7. Retrieved October 20, 2010.
- ^ "Resumen". Cuentame INEGI. http://cuentame.inegi.gob.mx/monografias/informacion/coah/default.aspx?tema=me&e=05. Retrieved October 20, 2010.
- ^ "Relieve". Cuentame INEGI. http://cuentame.inegi.gob.mx/monografias/informacion/coah/territorio/relieve.aspx?tema=me&e=05. Retrieved October 20, 2010.
- ^ "Proyecciones de la población de México 2005-2050". Consejo Nacional de Población. http://www.conapo.gob.mx/00cifras/proyecta50/05.xls. Retrieved August 10, 2010.
- ^ "Coahuila.". 2010. http://www.inegi.org.mx/sistemas/bise/mexicocifras/default.aspx?ent=5. Retrieved October 20, 2010.
- ^ "Reporte: Jueves 3 de Junio del 2010. Cierre del peso mexicano.". www.pesomexicano.com.mx. http://www.pesomexicano.com.mx/archivo/2010/junio/03/reporte-jueves-3-de-junio-del-2010--cierre-del-peso-mexicano.htm#leermas. Retrieved August 10, 2010.
- ^ "Mexican state moves to allow same-sex unions", Advocate News, Gay.com, January 11, 2007
- ^ Industrial Costs in Mexico - A Guide for Foreign Investors 2007. Mexico City: Bancomext. 2007. p. 90.
- ^ Industrial Costs in Mexico - A Guide for Foreign Investors 2007. Mexico City: Bancomext. 2007. p. 92.
- ^ Benjamin, Thomas, and William McNellie. Other Mexicos: Essays on Regional Mexican History, 1876-1911. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press, 1984.
External links
- (Spanish) Coahuila State Government
- (English) Coahuila State Government
Saltillo (capital)Topics Architecture · Climate · Culture · Demographics · Economy · Education · Geography · Government · History · Literature · Politics · Sports · Transportation · Tourist Attractions
Municipalities
and
(municipal seats)Abasolo (Abasolo) · Acuña (Ciudad Acuña) · Allende (Allende) · Arteaga (Arteaga) · Candela (Candela) · Castaños (Castaños) · Cuatrociénegas (Cuatrociénegas de Carranza) · Escobedo (Escobedo) · Francisco I. Madero (Francisco I. Madero) · Frontera (Ciudad Frontera) · General Cepeda (General Cepeda) · Guerrero (Guerrero) · Hidalgo (Hidalgo) · Jiménez (Jiménez) · Juárez (Juárez) · Lamadrid (Lamadrid) · Matamoros (Matamoros de la Laguna) · Monclova (Monclova) · Morelos (Morelos) · Múzquiz (Santa Rosa de Múzquiz) · Nadadores (Nadadores) · Nava (Nava) · Ocampo (Ocampo) · Parras (Parras de la Fuente) · Piedras Negras (Piedras Negras) · Progreso (Progreso) · Ramos Arizpe (Ramos Arizpe) · Sabinas (Sabinas) · Sacramento (Sacramento) · Saltillo (Saltillo) · San Buenaventura (San Buenaventura) · San Juan de Sabinas (Nueva Rosita) · San Pedro de las Colonias (San Pedro de las Colonias) · Sierra Mojada (Sierra Mojada) · Torreón (Torreón) · Viesca (Viesca) · Villa Unión (Villa Unión) · Zaragoza (Zaragoza)
Northeastern Mexico Northeastern Mexico
States of Mexico States Aguascalientes · Baja California · Baja California Sur · Campeche · Chiapas · Chihuahua · Coahuila · Colima · Durango · Guanajuato · Guerrero · Hidalgo · Jalisco · México · Michoacán · Morelos · Nayarit · Nuevo León · Oaxaca · Puebla · Querétaro · Quintana Roo · San Luis Potosí · Sinaloa · Sonora · Tabasco · Tamaulipas · Tlaxcala · Veracruz · Yucatán · Zacatecas

Federal District Categories:- Coahuila
- States of Mexico
- States and territories established in 1824
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.