- Melting point apparatus
-
A melting point apparatus is a scientific instrument used to determine the melting point of a substance. Some types of melting point apparatuses include the Thiele tube, Fisher-Johns apparatus, Gallenkamp (Electronic) melting point apparatus and automatic melting point apparatus.
Contents
Design
While the outward designs of apparati can vary greatly most apparati use a sample loaded into a sealed capillary (melting point capillary) that is then placed in the apparatus. The sample is then heated, either by a heating block or an oil bath, and as the temperature increases the sample is observed to determine when the phase change from solid to liquid occurs. The operator or the machine records the temperature range starting with the initial phase change temperature and ending with the completed phase change temperature. The temperature range that is determined can then be averaged to gain the melting point of the sample being examined.
Apparati usually have a control panel that allows the starting and final temperatures, as well as the temperature gradient (in units per minute) to be programmed. Some machines have several channels which permit more than one sample to be tested at a time. The control panel might have buttons which allow the start and end of the melting point range to be recorded.
Apparati
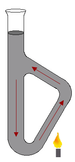
Thiele tube
A Thiele tube is a glass instrument that is filled with oil that is heated by using an open flame. The sample is placed in the opening in a capillary tube alongside a mercury thermometer and allowed to be heated by the oil as it circulates through the Thiele tube. By using different oils different temperature ranges can be reached and used to determine melting points. The Thiele tube may also be used to determine boiling points, by substituting a solid sample for a liquid one.
References
External links
FisherSci: Fisher-Johns melting point apparatus
Analytical chemistry Instrumentation Atomic absorption spectrometer · Flame emission spectrometer · Gas chromatograph · High performance liquid chromatograph · Infrared Spectrometer · Mass spectrometer · Melting point apparatus · Microscope · Spectrometer · SpectrophotometerTechniques Sampling Coning and quartering · Dilution · Dissolution · Filtration · Masking · Pulverization · Sample preparation · Separation process · Sub-samplingProminent publications The Analyst · Analytica Chimica Acta · Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry · Analytical Chemistry · Analytical BiochemistryChemistry Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.