- Graduated cylinder
-
A graduated cylinder, measuring cylinder or graduate is a piece of laboratory equipment used to accurately measure the volume of a liquid. Water displacement can be used to find out the volume of a solid. Graduated cylinders are generally more accurate and precise for this purpose than flasks and beakers. Often, the largest graduated cylinders are made of polypropylene for its excellent chemical resistance or polymethylpentene for its transparency, making them lighter and less fragile than glass. Polypropylene is easy to repeatedly autoclave; however, autoclaving in excess of about 130 °C (266 °F) (depending on the chemical formulation: typical commercial grade polypropylene melts in excess of 160 °C (320 °F)),can warp or damage polypropylene graduated cylinders, affecting accuracy.
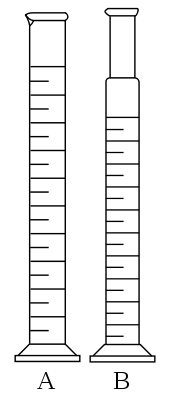
A traditional cylinder (A in the image) is usually narrow and high (so as to increase the accuracy of volume measurement) and has a plastic or glass stem and a "spout" for easy pouring from the measured liquid. Certain types of cylinders (B in the picture) have ground glass joints instead of a "spout", so that they can be closed with a stopper or connect directly with other elements of a manifold; they are also known as mixing cylinders.[1] With this kind of cylinder, the metered liquid does not pour directly, but is often removed using cannula. A graduated cylinder is meant to be read with the surface of the liquid at eye level, where the center of the meniscus shows the measurement line. Typically the accuracy of the graduated cylinder is +/-0.05 mL. The measuring cylinder is normally and most commonly used in laboratories.
types
- V = 3inch3type;
- V = 15inch3type;
- V = 30inch3type
,as volume, v
Gallery
[[sv:Mätgla
Categories:- Laboratory glassware
- Volumetric instruments
- Chemistry stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.