- Colorimeter (chemistry)
-
For other uses, see Colorimeter.
Not to be confused with a calorimeter.
A colorimeter is a device used in colorimetry. In scientific fields the word generally refers to the device that measures the absorbance of particular wavelengths of light by a specific solution[1]. This device is most commonly used to determine the concentration of a known solute in a given solution by the application of the Beer-Lambert law, which states that the concentration of a solute is proportional to the absorbance.
Contents
Construction
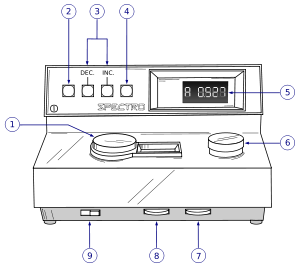
The essential parts of a colorimeter are:
- a light source (often an ordinary low-voltage filament lamp)
- an adjustable aperture
- a set of colored filters
- a cuvette to hold the working solution
- a detector (usually a photoresistor) to measure the transmitted light
- a meter to display the output from the detector
In addition, there may be:
- a voltage regulator, to protect the instrument from fluctuations in mains voltage.
- a second light path, cuvette and detector. This enables comparison between the working solution and a "blank", consisting of pure solvent, to improve accuracy.
Filters
Changeable optics filters are used in the colorimeter to select the wavelength of light which the solute absorbs the most, in order to maximize accuracy. The usual wavelength range is from 400 to 700 nanometers (nm). If it is necessary to operate in the ultraviolet range (below 400 nm) then some modifications to the colorimeter are needed. In modern colorimeters the filament lamp and filters may be replaced by several light-emitting diodes of different colors. [3]
Cuvettes
Main article: CuvetteIn a manual colorimeter the cuvettes are inserted and removed by hand. An automated colorimeter (as used in an AutoAnalyzer) is fitted with a flowcell through which solution flows continuously.
Output
The output from a colorimeter may be displayed by an analogue or digital meter and may be shown as transmittance (a linear scale from 0-100%) or as absorbance (a logarithmic scale from zero to infinity). The useful range of the absorbance scale is from 0-2 but it is desirable to keep within the range 0-1 because, above 1, the results become unreliable due to scattering of light.
In addition, the output may be sent to a chart recorder, data logger, or computer.
Notes
References
- The Nuffield Foundation 2003. March 30 2003. [1]
- "Colour." Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 2011. Web. 17 Nov. 2011. [2]
- "Colorimetry"Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 2011. Web. 17 Nov. 2011. [3]
- Orion Colorimetry Theory. The Technical Edge. [4]
See also
- Spectronic 20
- Spectrophotometer
Categories:- Physics stubs
- Color
- Optical devices
- Spectroscopy
- Laboratory equipment
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.