- Difluoromethane
-
Difluoromethane 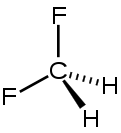
 Systematic nameDifluoromethane[1]Other namesCarbon fluoride hydride
Systematic nameDifluoromethane[1]Other namesCarbon fluoride hydride
Methylene difluoride
Freon-32
Methylene fluorideIdentifiers Abbreviations HFC-32
R-32
FC-32CAS number 75-10-5 
PubChem 6345 ChemSpider 6105 
EC number 200-839-4 UN number 3252 MeSH Difluoromethane ChEBI CHEBI:47855 
ChEMBL CHEMBL115186 
RTECS number PA8537500 Beilstein Reference 1730795 Gmelin Reference 259463 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - FCF
Properties Molecular formula CH2F2 Molar mass 52.02 g mol−1 Exact mass 52.012456474 g mol-1 Appearance Colorless gas Density 1.1 g cm-3 Melting point −136 °C, 137 K, -213 °F
Boiling point −52 °C, 221 K, -62 °F
log P -0.611 Vapor pressure 1518.92 kPa (at 21.1 °C) Hazards MSDS MSDS at Oxford University EU classification  F
FR-phrases R11 S-phrases S9, S16, S33 NFPA 704 Autoignition
temperature648 °C  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Difluoromethane, also called HFC-32 or R-32, is an organic compound of the dihalogenoalkane variety. It is based on methane, except that two of the four hydrogen atoms have been replaced by fluorine atoms. Hence the formula is CH2F2 instead of CH4 for normal methane.
Contents
Physical properties
Property Value Critical pressure (pc) 5.83 MPa Critical temperature (Tc) 78.45 °C (351 K) Compressibility factor (Z) 0.9863 Heat capacity at constant pressure (Cp) at 21 °C (70 °F) 0.043 kJ·mol−1·K−1 Heat capacity at constant volume (CV) at 21 °C (70 °F) 0.034 kJ·mol−1·K−1 Heat capacity ratio (κ) 1.253 Uses
Difluoromethane is a refrigerant that has zero ozone depletion potential. Difluoromethane in a zeotropic (50%/50%) w/w mixture with pentafluoroethane (R-125) is known as R-410A, a common replacement for various chlorofluorocarbons (aka Freon) in new refrigerant systems, especially for air-conditioning. The zeotropic mix of Difluoromethane with pentafluoroethane (R-125) and tetrafluoroethane (R-134a) is known as R-407A through R-407E depending on the composition. Likewise the azeotropic (48.2%/51.8% w/w) mixture with chlorotrifluoromethane (R13). As a refrigerant difluoromethane is classified as A2L - slightly flammable [2009 ASHRAE Handbook]. Although it has zero ozone depletion potential, it has global warming potential 675 times that of carbon dioxide, based on a 100-year time frame [May 2010 TEAP XXI/9 Task Force Report].
References
- ^ "Difluoromethane - Compound Summary". The PubChem Project. USA: National Center of Biotechnological Information. http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=6345&loc=ec_rcs.
External links
- Flammability Measurements of Difluoromethane in Air at 100°C
- Difluoromethane at Gas Encyclopaedia
- IR absorption spectra
Halomethanes Monosubstituted Disubstituted Trisubstituted 
This article about an organic halide is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.

