- Compressed fluid
-
 A P-v diagram for liquid water. The compressed fluid region is located to the left of the blue line (the liquid-vapor phase boundary).
A P-v diagram for liquid water. The compressed fluid region is located to the left of the blue line (the liquid-vapor phase boundary).
A compressed fluid (also called a subcooled fluid or subcooled liquid) is a fluid under thermodynamic conditions that force it to be a liquid[1]. It is a liquid at a temperature lower than the saturation temperature at a given pressure. In a plot comparing absolute pressure and specific volume (commonly called a P-v diagram), of a real gas, a compressed fluid is to the left of the liquid-vapor phase boundary; that is, it will be to the left of the vapor dome.
Some of the conditions that cause a fluid to be compressed are the following:
- A specific volume lesser than the specific volume of a saturated liquid
- A fluid temperature below the saturation temperature
- A pressure exceeding the saturation pressure
- An enthalpy smaller than the enthalpy of a saturated liquid
The term "compressed liquid" emphasizes that the pressure is greater than the saturation pressure for the given temperature.
Compressed liquid properties are relatively independent of pressure. As such, it is usually acceptable to treat a compressed liquid as a saturated liquid at the given temperature.
See also
References
- ^ "Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach" by Yunus A. Çengel, Michael A. Boles, p.65, ISBN 007121688X
Turns, Stephen R. (2006). Thermal-Fluid Sciences: An Integrated Approach (1st edition ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 90–103. ISBN 0-521-85043-6.
States of matter 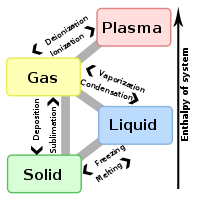
Low energy High energy Other states Colloid · Glass · Liquid crystal · Magnetically ordered (Antiferromagnet, Ferrimagnet, Ferromagnet) · String-net liquid · SuperglassTransitions Boiling · Boiling point · Critical line · Critical point · Crystallization · Deposition · Evaporation · Flash evaporation · Freezing · Lambda point · Melting · Melting point · Regelation · Saturated fluid · Sublimation · Supercooling · Triple pointQuantities Enthalpy of fusion · Enthalpy of sublimation · Enthalpy of vaporization · Latent heat · Latent internal energy · Trouton's constant · Trouton's ratio · VolatilityConcepts Binodal · Compressed fluid · Cooling curve · Equation of state · Leidenfrost effect · Mpemba effect · Order and disorder (physics) · Spinodal · Superconductivity · Superheated vapor · Superheating · Thermo-dielectric effectCategories:- Fluid mechanics
- Thermodynamics
- Physical chemistry stubs
- Fluid dynamics stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
