- Binodal
-
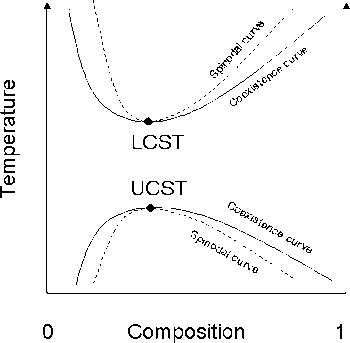
In thermodynamics, the binodal, also known as the coexistence curve or binodal curve, denotes the condition at which two distinct phases may coexist. Equivalently, it is the boundary between the set of conditions in which it is thermodynamically favorable for the system to be fully mixed and the set of conditions in which it is thermodynamically favorable for it to phase separate[1]. In general, the binodal is defined by the condition at which the chemical potential of all solution components is equal in each phase. The extremum of a binodal curve in temperature coincides with the one of the spinodal curve and is known as a critical point.
Binary systems
In binary (two component) mixtures, the binodal can be determined at a given temperature by drawing a tangent line to the free energy[1], as shown in the figure to the lower right.
References
- ^ a b IUPAC binodal curve definition http://www.iupac.org/goldbook/BT07273.pdf accessed 1/3/10
States of matter Low energy High energy Other states Colloid · Glass · Liquid crystal · Magnetically ordered (Antiferromagnet, Ferrimagnet, Ferromagnet) · String-net liquid · SuperglassTransitions Boiling · Boiling point · Critical line · Critical point · Crystallization · Deposition · Evaporation · Flash evaporation · Freezing · Lambda point · Melting · Melting point · Regelation · Saturated fluid · Sublimation · Supercooling · Triple pointQuantities Enthalpy of fusion · Enthalpy of sublimation · Enthalpy of vaporization · Latent heat · Latent internal energy · Trouton's constant · Trouton's ratio · VolatilityConcepts Binodal · Compressed fluid · Cooling curve · Equation of state · Leidenfrost effect · Mpemba effect · Order and disorder (physics) · Spinodal · Superconductivity · Superheated vapor · Superheating · Thermo-dielectric effectCategories:- Thermodynamics
- Physical chemistry stubs
- Physics stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.