- Deposition (phase transition)
-
Deposition is a process in which gas transforms into solid (also known as desublimation). The reverse of deposition is sublimation.
One example of deposition is the process by which, in sub-freezing air, water vapor changes directly to ice without first becoming a liquid. This is how snow forms in clouds, as well as frost and hoar frost on the ground.
Another example of physical deposition is the artificial process of lamaw physical vapor deposition, used to deposit thin films of various materials onto various surfaces.
Deposition releases energy and is an exothermic phase change.
References
- Jacobson, Mark Z., Fundamentals of Atmospheric Modeling, Cambridge University Press, 2nd ed., 2005, p. 525 ISBN 978-0521839709
- Moore, John W., et. al., Principles of Chemistry: The Molecular Science, Brooks Cole, 2009, p. 387 ISBN 978-0495390794
- Whitten, Kenneth W., et. al., Chemistry, Brooks-Cole, 9th ed., 2009, p. 7 ISBN 978-0495391630
States of matter 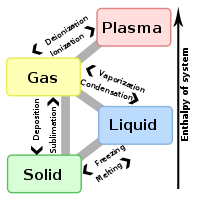
Low energy High energy Other states Colloid · Glass · Liquid crystal · Magnetically ordered (Antiferromagnet, Ferrimagnet, Ferromagnet) · String-net liquid · SuperglassTransitions Boiling · Boiling point · Critical line · Critical point · Crystallization · Deposition · Evaporation · Flash evaporation · Freezing · Lambda point · Melting · Melting point · Regelation · Saturated fluid · Sublimation · Supercooling · Triple pointQuantities Enthalpy of fusion · Enthalpy of sublimation · Enthalpy of vaporization · Latent heat · Latent internal energy · Trouton's constant · Trouton's ratio · VolatilityConcepts Binodal · Compressed fluid · Cooling curve · Equation of state · Leidenfrost effect · Mpemba effect · Order and disorder (physics) · Spinodal · Superconductivity · Superheated vapor · Superheating · Thermo-dielectric effectCategories:- Physics stubs
- Phase changes
- Physics
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

