- Type 56 assault rifle
-
Type 56 Assault Rifle 
Type 56 (top) and AKS-47Type Assault rifle Place of origin  People's Republic of China
People's Republic of ChinaService history In service 1956–present Used by See Users Wars Vietnam War
Laotian Civil War
Cambodian Civil War
Cambodian-Vietnamese War
Sino-Vietnamese War
Sri Lankan Civil War
Soviet war in Afghanistan
Iran–Iraq War
Croatian War of Independence
Bosnian War
Kosovo Conflict
Cambodian–Thai border stand-off
War on Terror and numerous othersProduction history Designed 1947 Manufacturer Norinco, Bangladesh Ordnance Factory (License-made) Produced 1956 to present Number built 10-15 Million Variants Type 56 Assault Rifle, Type 56-1 Assault Rifle, Type 56-2 Assault Rifle, QBZ-56C Assault Rifle, Type 56S, Type 84S rifle Specifications Weight Type 56: 4.03 kg (8.88 lb)
Type 56-1: 3.70 kg (8.16 lb)
Type 56-2: 3.9 kg (8.60 lb)
QBZ-56C: 2.85 kg (6.28 lb)Length Type 56: 874 mm (34.4 in)
Type 56-1/56-2: 874 mm (34.4 in) w/ stock extended, 654 mm (25.7 in) w/ stock folded.
QBZ-56C: 764 mm (30.1 in) w/ stock extended, 557 mm (21.9 in) w/ stock folded.Barrel length Type 56, Type 56-I, Type 56-II: 414 mm (16.3 in)
QBZ-56C: 280 mm (11.0 in)Cartridge 7.62×39mm M43 Action Gas-operated, rotating bolt Rate of fire 600 round/min [1] Muzzle velocity Type 56, Type 56-I, Type 56-II: 735 m/s (2,411 ft/s)
QBZ-56C: 665 m/s (2182 ft/s)Effective range 100–800m sight adjustments Feed system 20 or 30 round box magazine Sights Adjustable iron sights - For the Chinese SKS variant of the same designation, see SKS
The Type 56 assault rifle is a Chinese copy of the Kalashnikov AK-47 assault rifle,[1] which has been manufactured since 1956. It was produced by State Factory 66 from 1956-73, then by Norinco from 1973 onwards.
Contents
Service history
A pair of Type 56-2 rifles and a Type 69 RPG.
The Type 56 is likely the most widely proliferated AK-47 type rifle in the world having shown up on battlefields in Asia, Africa, Eastern Europe, South America, etc. While exact production figures are not known, it is commonly estimated that as many as 10-15 million Type 56 rifles have been produced since the 1950s which means they may account for nearly one-fifth of the world's AK production.
Chinese support for the Democratic Republic of Vietnam before the mid-1960s meant that the Type 56 was frequently encountered by American soldiers during the Vietnam War, in the hands of either Vietcong guerrillas or PAVN soldiers. In fact, the Type 56 was discovered in enemy hands far more often than Russian-made AK-47s or AKMs. When relations between China and the North Vietnam government declined in the 1970s and the Sino-Vietnamese War began, the Vietnamese government still had large numbers of Type 56 rifles in its arsenals while the People's Liberation Army still used the Type 56 as its standard weapon. Thus, Chinese and Vietnamese forces fought each other using the same Chinese-made Type 56 rifles.
During the Soviet war in Afghanistan in the 1980s, many Chinese Type 56 assault rifles were given to Afghan Mujahideen guerrillas to fight Soviet forces in Afghanistan by the Chinese, the Pakistanis, and the Americans who obtained them from third party arms dealers. Use of the Type 56 in Afghanistan also continued well into the 1990s and the early 21st century as the standard rifle of the Taliban when Taliban forces seized control of Kabul in 1996 (majority of the Chinese small arms used by the Taliban were provided by Pakistan). The Taliban's use of the Type 56 was a stark contrast to the weapons of the Afghan Northern Alliance, which were exclusively Russian-made small arms like the AKM and the AK-74. Since the overthrow of the Taliban by US-led Coalition forces in late 2001, the Chinese Type 56 assault rifle is used by the Afghan National Army with many Type 56 rifles being used alongside the Russian AKM and AK-74 rifles.
The Chinese Type 56 assault rifle saw considerable action in the hands of Iranian forces during the Iran–Iraq War of the 1980s with Iran purchasing large quantities of weapons from China for their war against Iraq. During the war, Iraq purchased a small quantity of Type 56 assault rifles from China despite Iraq being a major recipient of Soviet weapons and assistance during the Iran–Iraq War. Consequently, the Iran–Iraq War became another conflict in which both sides used the Type 56, much like the Sino-Vietnamese War.
Since the end of the Cold War, the Type 56 has been used in many conflicts across the world by the military forces of various nations. During the Croatian War of Independence and the Yugoslav Wars, the Type 56 was used by the armed forces of Croatia alongside other small arms and weapons the Croatians possessed. During the late 1990s, the Kosovo Liberation Army in Kosovo were also major users of the Type 56, with the vast majority of the weapons originating from Albania, which received Chinese support during the Cold War.In the United States and the United Kingdom, the Type 56 and its derivatives are frequently used in the filming of movies and television shows, standing in for Russian-made AK-47s due to the rarity of genuine AK-47 rifles, with some even being visually modified to resemble other AK-series rifles. As with all firearms used in cinematography, these weapons are adapted to fire blank ammunition. Versions of this weapon that have the full-auto firing ability deleted (referred to as "sporter" rifles) are also available for civilian ownership in most parts of the United States. Recently, a batch of Type 56s were given to Malta.
In recent times, the Type 56 has been used by the Janjaweed in the Darfur region of Sudan with pictures and news footage showing members of the Janjaweed carrying Type 56 rifles (most of them provided by the Sudanese government); the same weapon is listed in the "Products" pages of the Military Industry Corporation of Sudan website as the MAZ rifle, hinting that Sudan may be manufacturing the rifle locally although this is not confirmed by other sources. The Type 56 has also been seen regularly in the hands of militants from the Izz ad-Din al-Qassam Brigades, the armed wing of Hamas in the Palestinian territories; these weapons are most likely provided by Iran, which is both a known supporter of Hamas and a major consumer of Chinese weaponry.
In the mid-1980s, Sri Lanka started to replace their old British L1A1 Self-Loading Rifles (SLR) and HK G3s with the Type 56. Currently, they use the fixed stock, under-folding stock and side-folding stock variants.
The Type 81,Type 95 and the Type 03 replaced Type 56 in PLA service but the Type 56 remains in production by Norinco for export customers.
Differences from and similarities to the AK-47 and AKM
 Type 56-1 (left), Type 84S (center), and Type 56 (right). Note that the Type 56 rifles in this image have been fitted with the distinctive slant compensator of the AKM, a feature not found on the original Type 56
Type 56-1 (left), Type 84S (center), and Type 56 (right). Note that the Type 56 rifles in this image have been fitted with the distinctive slant compensator of the AKM, a feature not found on the original Type 56
Originally, the Type 56 was a direct copy of the AK-47, and featured a milled receiver, but starting in the mid-1960s, the guns were manufactured with stamped receivers much like the Soviet AKM. Visually, most versions of the Type 56 are distinguished from the AK-47 and AKM by the fully enclosed hooded front sight (all other AK pattern rifles, including those made in Russia, have a partially open front sight). Many versions also feature a folding bayonet attached to the barrel just aft of the muzzle. There are three different types of bayonets made for Type 56 rifles.
- The Type 56 has a 1.5mm stamped receiver (like the RPK, although it lacks the reinforced trunnion of the RPK) versus the 1mm stamping of the AKM.
- The barrel on the Type 56 is similar to the AK-47 and heavier than that of the AKM.
- The front sights are fully enclosed, compared to the AKM and AK-47 which are partially opened.
- Has the double hook disconnector of the AK-47 rather than the single hook disconnector of the AKM.
- Has a smooth dust cover like the AK-47 and unlike the ribbed dust cover of the AKM.
- May have a folding spike bayonet (nicknamed the "pig sticker") as opposed to the detachable knife bayonets of the AK-47 and AKM. There are three different types of spike bayonets made for Type 56 rifles. Type 56 assault rifles are the only AK-pattern assault rifles that use spike bayonets.
- Military issued versions of the Type 56 lack the threaded muzzle found on the AK-47 and AKM. So they cannot use an AKM compensator or blanking firing device. Commercial versions of the Type 56 may or may not have a threaded muzzle.
- Has a blued finish like the AK-47 and unlike the AKM, which has a black oxide finish or a parkerized finish.
- Like the AK-47, sights will only adjust to 800 metres, whereas AKM sights adjust to 1000 metres.
- Most Type 56s lack the AKM scope mount plate on the left side of the receiver.
- Lacks the hammer release delay device of the AKM. The thicker receiver improves overall rigidity, making a higher rate of fire acceptable.
- The gas relief ports are located on the gas tube like the AK-47, unlike the AKM which had the gas relief ports relocated forward to the gas block.
- The Type 56 has a pressed and pinned barrel like the AKM, opposed to the AK-47 barrel which is threaded at the receiver end.
- The fixed stock of a Type 56 has a less in line stock like the AK-47, opposed to the AKM which has a straighter stock.
Type 56 variants
- Type 56 – Basic variant introduced in 1956. Copy of AK-47 with fixed wooden stock and permanently attached spike bayonet. Beginning in the mid-1960s, the guns were manufactured with stamped receivers, mimicking the improved (and cheaper) Russian AKM, while the permanently attached bayonet became optional. The weapon is still used by Chinese reserve and militia units.
- Type 56-I – Copy of the AKS-47, with an under-folding steel shoulder stock and the bayonet removed. Like the original Type 56, milled receivers were replaced by stamped receivers in the mid-1960s, which made the Type 56-1 an equivalent to the Russian AKMS.
- Type 56-II – Improved variant introduced in 1980, with a side-folding stock. Mainly export use and rare in China.
- Type 56C (QBZ-56C) – Shortened barrel version introduced in 1991 for domestic and export market. The QBZ-56C began development in 1988, shortly after it was discovered that the Type 81 assault rifle was too difficult to shorten. The QBZ-56C as it is officially designated in China, is a shortened, carbine variant of the Type 56-II. The barrel length has been reduced to 280mm and overall length of the rifle is reduced, to 557mm long with the stock folded and 764mm long with the stock extended. The QBZ-56C weighs only 2.85 kg and has an effective range of up to 300m. The QBZ-56C is used by the People's Liberation Army Navy on both surface and submersible ships and with the People's Liberation Army Special Operations Forces as a limited issue weapon, the QBZ-56C is also in limited use by PLA reserve forces and militia stationed in Tibet, as the thinner air at higher altitudes strains soldiers' ability to carry heavy objects. In order to further lighten the total weight of the weapon the bayonet lug was removed; the QBZ-56C is often carried with a twenty round box magazine, although it is capable of accepting a standard Type 56 thirty round magazine. [2]
- Type 56S or Type 56 Sporter, also known as the MAK-90 (Model of the AK)-1990 – civilian version with only semiautomatic mode.[3]
- NHM 91 - Sporterized RPK-style with a stamped receiver and 20" heavy barrel.
- Type 84S - A civilian version of the Type 56 rifle chambered for the 5.56x45mm NATO round.
KL-7.62
The Iranian state arms conglomerate Defense Industries Organization (DIO) currently manufactures a 7.62x39mm Kalashnikov-type assault rifle for the Iranian armed forces, which is designated KL-7.62.[4] The KL-7.62 is an unlicensed, reverse-engineered copy of the Type 56, which Iran purchased from the Chinese government in enormous numbers to equip its forces in the Iran–Iraq War. The original version of the KL-7.62 was indistinguishable from the Type 56, but in recent years DIO appears to have made some improvements to the Type 56 design, adding a plastic stock and hand guards (rather than wood) and a ribbed receiver cover (featured on most AKM variants, but missing from the Type 56). (See also List of military equipment manufactured in Iran)
Type 56 carbine
The "Type 56" designation was also used for Chinese version of the SKS, known as the Type 56 carbine, but the designs are entirely distinct.
Users
During the Cold War period, the Type 56 was exported to communist forces in the Third World. Many of these rifles found their way to battlefields in Africa, Southeast Asia, and the Middle East during the Cold War era and were used alongside Kalashnikov rifles from both the Soviet Union and the Warsaw Pact nations of Eastern Europe.
 Afghanistan[5]
Afghanistan[5] Albania: Uses the Type 56 and various copies of the AK-47/AKM, including domestic-built examples.[6][7]
Albania: Uses the Type 56 and various copies of the AK-47/AKM, including domestic-built examples.[6][7] Bangladesh: Built under license by Bangladesh Ordnance Factory and used by the Bangladesh Navy Special Warfare Diving And Salvage.[8]
Bangladesh: Built under license by Bangladesh Ordnance Factory and used by the Bangladesh Navy Special Warfare Diving And Salvage.[8] Benin[9]
Benin[9] Bosnia-Herzegovina[10]
Bosnia-Herzegovina[10] Cambodia[11][12]
Cambodia[11][12] Iraq[13]
Iraq[13] Laos[7]
Laos[7] Malta[7]
Malta[7] North Korea[7]
North Korea[7] Pakistan[7]
Pakistan[7] People's Republic of China[1]:The Chinese Type 56 was the standard issue assault rifle of the Chinese military from the late 1950s until the 1980s when it was replaced by the newer Type 81 assault rifle in front line units. Some Chinese Reserve, Militia and People's Armed Police units as well as border and customs security troops still use the Type 56 rifle as well as the Type 56 carbine SKS.
People's Republic of China[1]:The Chinese Type 56 was the standard issue assault rifle of the Chinese military from the late 1950s until the 1980s when it was replaced by the newer Type 81 assault rifle in front line units. Some Chinese Reserve, Militia and People's Armed Police units as well as border and customs security troops still use the Type 56 rifle as well as the Type 56 carbine SKS. Philippines: Used by the CPP-New People's Army[14]
Philippines: Used by the CPP-New People's Army[14] Sri Lanka[7]
Sri Lanka[7] Sudan: Licensed produced as known as the MAZ.[15]
Sudan: Licensed produced as known as the MAZ.[15] Vietnam: Used extensively by the Viet Cong during the Vietnam War. Replaced by the AKM.[1]
Vietnam: Used extensively by the Viet Cong during the Vietnam War. Replaced by the AKM.[1]
See also
References
- ^ a b c Miller, David (2001). The Illustrated Directory of 20th Century Guns. Salamander Books Ltd. ISBN 1-84065-245-4.
- ^ "详解中国首款QBZ56C型短突击步枪(组图)" (in Simplified Chinese). Sina.com. 2007-08-28. http://mil.news.sina.com.cn/p/2007-08-28/0849461683.html. Retrieved 2008-08-26.
- ^ Norinco
- ^ KL-7.62 photo.
- ^ defenseimagery
- ^ http://i50.photobucket.com/albums/f301/kagemushamu/SmallArms01/SmallArms01-001.jpg
- ^ a b c d e f Jones, Richard D. Jane's Infantry Weapons 2009/2010. Jane's Information Group; 35 edition (January 27, 2009). ISBN 978-0710628695.
- ^ Type 56 Submachine Gun. Retrieved on October 28, 2008.
- ^ http://www.marines.mil/unit/marforaf/_layouts/imagemeta.aspx?image=http://www.marines.mil/unit/marforaf/PublishingImages/090616-M-3107S-0461.jpg
- ^ http://noiri.blogspot.com/2006/07democrats-helped-iran-created-serb-war.html
- ^ http://www.smallarmssurvey.org/files/sas/publications/w_papers_pdf/WP/WP4_Cambodia.pdf
- ^ Unwin, Charles C.; Vanessa U., Mike R., eds (2002). 20th Century Military Uniforms (2nd ed.). Kent: Grange Books. ISBN 1840132763.
- ^ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Flickr_-_The_U.S._Army_-_Instructing_National_Police_officers.jpg
- ^ http://www.focus-philippines.de/sisoneng.htm
- ^ "MAZ". Military Industry Corporation. http://mic.sd/images/products/wepons/en/MAZbn.html. Retrieved 2009-02-08.
External links
- Sino Defence
- Modern Firearms
- 56 at IMFDB - detailing this weapon's use in Western cinema
AK-47 and derivatives Primary rifles USSR/Russia Warsaw Pact 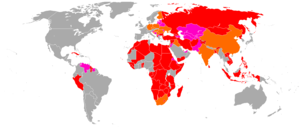
Assault rifles Classic AK-101 · AK-102 · AK-103 · AK-104 · AK-105 · AK-107/AK-108 · AMP-69 · APS-95 · AR-M1 · Kbkg wz. 1960 · Kbk wz. 1988 Tantal · Kbs wz. 1996 Beryl · NGM-81 · R4 · Truvelo Raptor · Type 56 · Wieger StG-940Bullpup Grad · Groza · K-3 · Kbk wz. 2002 BIN · Kbk wz. 2005 Jantar · Shkval · Type 86S · Vektor CR-21 · VeprFamilies Carbines Machine guns RPK · RPK-74Sniper rifles Close range Special purpose Experimental Competitors Brands Galil Zastava Valmet List of Russian weaponry Weapons and military equipment designed or licence-manufactured in IranFirearms PistolsArmour and other
land based vehiclesArtillery HM-40 · HM 41MRLS Recoilless rifles Mortars 37mm Marsh Mortaranti-aircraft guns Anti-tank missiles RPG-7 · Saegheh (rocket) · Type 69 RPG · RPG-29 · RAAD · Saeghe · Toophan · Toophan 2 · Towsan · 9K115-2 Metis-MCategories:- Assault rifles
- Cold War weapons of China
- Cold War rifles
- Infantry weapons of the Cold War
- 7.62 mm firearms
- Kalashnikov derivatives
- Weapons of the Vietnam War
- China–Soviet Union relations
- Weapons of the People's Republic of China
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.





