- DVB-SH
-
List of digital television broadcast standards DVB standards (Europe) DVB-S (satellite) DVB-T (terrestrial) DVB-C (cable) DVB-H (handheld) - DVB-SH (satellite)
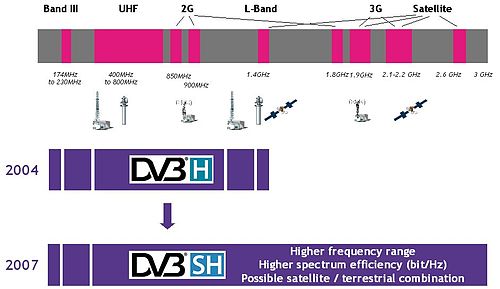
ATSC standards (North America/Korea) ATSC (terrestrial/cable) ATSC-M/H (mobile/handheld) ISDB standards (Japan/Latin America) ISDB-S (satellite) ISDB-T (terrestrial) ISDB-C (cable) SBTVD/ISDB-Tb (Brazil) DTMB standards (China) DTMB-T/H (terrestrial/handheld) CMMB (handheld) DMB standards (Korean handheld) T-DMB (terrestrial) S-DMB (satellite) MediaFLO Codecs Video Audio Frequency bands VHF UHF SHF DVB-SH, Digital Video Broadcasting - Satellite services to Handhelds, is a physical layer standard for delivering IP based media content and data to handheld terminals such as mobile phones or PDAs, based on a hybrid satellite/terrestrial downlink and for example a GPRS uplink. The DVB Project published the DVB-SH standard in February 2007.[1]
The DVB-SH system was designed for frequencies below 3 GHz, supporting UHF band, L Band or S-band. It complements and improves the existing DVB-H physical layer standard. Like its sister specification (DVB-H), it is based on DVB IP Datacast (IPDC) delivery, electronic service guides and service purchase and protection standards.
DVB-SH specifies two operational modes:
- SH-A: specifies the use of COFDM modulation on both satellite and terrestrial links with the possibility of running both links in SFN mode.
- SH-B: uses Time-Division Multiplexing (TDM) on the satellite link and COFDM on the terrestrial link.
Contents
Comparison with DVB-H
The DVB-SH incorporates a number of enhancements when compared to DVB-H:
- More alternative coding rates are available
- The omission of the 64QAM modulation scheme
- The inclusion of support for 1.7 MHz bandwidth and 1k FFT
- FEC using Turbo coding
- Improved time interleaving
- Support for antenna diversity in terminals
Recently, results from BMCO forum[citation needed] (Alcatel April 2008) shows a radio improvement of at least 5.5 dB on signal requirements between DVB-H and DVB-SH in the UHF frequencies. The improvements to signal requirements translates to better in-building penetration, better in-car coverage and extension of outdoor coverage. DVB-SH chipsets are being developed now by DiBcom and NXP Semiconductors, and are expected to be available in beginning of 2008. Initial specifications show that the chipsets supports both UHF and S-Band and are compatible with DVB-H.
DiBcom has announced a DVB-SH chip with availability in 2008 Q3. Dibcom DVB-SH 2008 Q3. The chip "has dual RF tuners supporting VHF, UHF, L-Band and S-Band frequencies".
Project organization
French Agence de l'innovation industrielle is now financing this effort through TVMSL, a project led by Alcatel-Lucent that plans to develop a DVB-SH standard suitable for hybrid satellite and terrestrial transmission. Other partners involved in TVMSL are Sagem Wireless, Alenia, RFS, Philips, DiBcom, TeamCast, UDcast, CNRS, INRIA, CEA-LETI.[2]
Satellites
ICO, one of the biggest satellite operator in the United States, recently announced a nationwide deployment of an hybrid satellite/terrestrial network in DVB-SH with Alcatel-Lucent[3] and Expway.[4] ICO G1 satellite carrying DVB-SH technology on board was launched on April 14, 2008. It is the world's first DVB-SH satellite in orbit.
Eutelsat W2A satellite carrying a Solaris Mobile (an Eutelsat and SES Astra joint venture) DVB-SH S band payload was launched on 3 April 2009. It will cover Western Europe.[5][6][7] S-band payload was scheduled to enter into service in May 2009 but this not occurred due to an anomaly currently being investigated.[8] On 1 July 2009, Solaris Mobile filed the insurance claim. The technical findings indicate that the company should be able to offer some, but not all of the services it was planning to offer.[9]
Inmarsat's S band satellite programme, called EuropaSat, will deliver mobile multimedia broadcast, mobile two-way broadband telecommunications and next-generation MSS services across all 27 member states of the European Union and as far east as Moscow and Ankara by means of a hybrid satellite/terrestrial network. It will be built by Thales Alenia Space and launched in early 2011 launched by ILS.[10]
Trials
DVB-H/SH trials are now underway in many cities and countries: Ireland,[11] United Kingdom,[12] Malaysia, Singapore,[13] Helsinki, Berlin, Cambridge, Pittsburgh, Paris, Tehran, Madrid, Sydney,[14] South Africa, Taiwan,[15] The Hague, Brussels, Bern, Vienna, New Zealand,[16] Philippines, Copenhagen, Budapest, Erlangen,[17] Sri Lanka, Roeselare, and india.[18]
DVB-SH in S-band is seen as an alternative in Europe. Recent field trials and studies showed better performance in radio than DVB-H standard that would lead to much cheaper costs for network deployments.[citation needed]
In France again, SFR and Alcatel-Lucent teamed up to deploy a DVB-SH trial. The results confirmed the theorical assumptions on the superiority of the DVB-SH to DVB-H, being the natural evolution of this legacy one.[19]
In Italy, 3 Italia, RAI and Alcatel-Lucent joined forces for the first DVB-SH trial in Italy.[20]
In US, Dish Network and Alcatel-Lucent joined forces for the first DVB-SH trial in US.[21][citation needed]
See also
- Electronic program guide
- E-VSB ATSC standard
- Handheld projector
- IP over DVB
- DVB over IP
- MediaFLO
- Mobile DTV Alliance industry association
- Mobile TV a term for the entire category
- Multimedia Broadcast Multicast Service (MBMS)
- OFDM system comparison table
- Spectral efficiency comparison table
- WiMAX
References
- ^ dvb.org: DVB approves DVB-SH specification
- ^ Alcatel Unlimited mobile TV [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9]
- ^ ICO Global Communications - ICO and Alcatel-Lucent Finalize Agreement for Mobile Interactive Media Services
- ^ Expway’s FastESG Solution Selected by ICO Global Communications for Mobile TV Services
- ^ [10]
- ^ Solaris Mobile
- ^ [11]
- ^ [12]
- ^ [13], [14]
- ^ [15], [16], [17]
- ^ DTG News: O2 and Arqiva launch DVB-H trial in Ireland
- ^ DTG News: UK's first DVB-H mobile TV trial goes live
- ^ Charged.mobi
- ^ Dba.org.au
- ^ mobile-ent.biz
- ^ Ihaka, James (14 April 2007). "Peek at where-ever when-ever cell TV". The New Zealand Herald. http://www.nzherald.co.nz/section/story.cfm?c_id=5&objectid=10434227. Retrieved 29 September 2011.
- ^ DVB-H Versuchssender Erlangen
- ^ [18]
- ^ SFR and Alcatel-Lucent tests in the field validate the fundamental assumptions for the deployment of a DVB-SH Mobile TV terrestrial network
- ^ [19]
- ^ DISH Network Corporation and Alcatel-Lucent to Perform Joint DVB-SH Test in the U.S
External links
- DVB-SH standardization history, performance evaluation, research papers on DVB-SH system, DVB-SH trials and other scientific contributions
- DVB Project
- DVB-H.org
- DVB-SH: Mobile digital TV in S-Band (EBU Technical Review article)
- Alcatel April 2008
- April 2008 in Italian
- Solaris Mobile
- Eutelsat
- ICO
- AT&T CruiseCast
Analog and digital audio broadcasting TerrestrialRadio modulation Frequency allocations Digital systems SatelliteFrequency allocations Digital systems Commercial radio providers Subcarrier signalsRelated topicsTechnical (Audio): Audio processing · Audio data compression
Technical (AM Stereo formats): Belar · C-QUAM · Harris · Magnavox · Kahn-Hazeltine
Technical (Emission): Digital radio · Error correction · Multipath propagation · SW Relay Station · AM radio · AM broadcasting · Extended AM broadcast band · FM radio · FM broadcasting · FM broadcast band · Cable radio
Cultural: History of radio · International broadcasting
Comparison of radio systemsCategories:- DVB
- Broadcast engineering
- Mobile telephone broadcasting
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.