- Olecranon bursitis
-
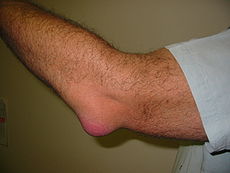
Olecranon bursitis Classification and external resources ICD-10 M70.2 ICD-9 726.33 Olecranon bursitis (informally known as "student's elbow" or "baker's elbow") is a condition characterised by pain, swelling and inflammation of the olecranon bursa located in the elbow.
This bursa is located over the extensor aspect of the extreme proximal end of the ulna. In common with other bursae, it is in the normal state invisible and impalpable, and contains only a very small amount of fluid, but fulfills the function of all bursae in facilitating movement at a joint (in this case the elbow) by enabling anatomical structures to glide more easily over each other. Also in common with other bursae, it can become inflamed, producing a condition called bursitis. This is sometimes known as a "swellbow" or "water on the elbow."
Causes
Bursitis normally develops as a result either of a single injury to the elbow, or perhaps more commonly due to repeated minor injuries, such as may be caused by repeatedly leaning on the point of the elbow on a hard surface. The chance of developing bursitis is higher if one's job or hobby involves a repetitive movement, for example, tennis, golf and even repetitive computer work involving leaning on your elbow are common causes of bursitis of the elbow. The possibility of developing the condition is more common as one gets older.[1]
As a reaction to injury, the lining of the bursa becomes inflamed. It then secretes a much greater than normal amount of fluid into the closed cavity of the bursa, from where it has nowhere to go. The bursa therefore inflates, producing a swelling over the proximal end of the ulna which is usually inflamed and tender.
Treatment
As with most forms of bursitis the ideal treatment consists of rest and avoiding further injury to the area. Medical intervention will often include one or more combinations of the following: oral or topical anti-inflammatory medications such as NSAIDs, aspirating the excess with a syringe, or injecting into the bursa a hydrocortisone type medication which is aimed at relieving the inflammation and preventing further accumulation of fluid. If the bursa is infected then antibiotics may be required.
It is important to try to identify the cause of one's bursitis as early as possible. This is because long-term (chronic) bursitis is likely to eventuate into the formation of scar which may lead to more regular flare ups and possibly further complications in later years.
The first approach in treating olecranon bursitis should be removing mechanical stress from the affected area, such as avoiding leaning on the elbow. You should identify if a repetitive activity is the cause and if so, cease this activity until your bursitis has completely healed.
Olecranon bursitis that does not heal from rest alone or which is causing pain or discomfort may then need medical intervention such as oral or topical NSAIDs or corticosteroid injections. It is also quite common for a doctor to drain the bursitis with a syringe (aspiration), although this may still result in the fluid returning.
If the fluid continues to return after multiple drainings or the bursa is constantly causing pain to the patient, surgery[2] to remove the bursa is an option. The minor operation removes the bursa from the elbow and is left to regrow but at a normal size over a period of ten to fourteen days. It is usually done under general anaesthetic and has very minimal risks.
References
Soft tissue disorders / Rheumatism / Connective tissue arthropathy (M65–M79, 725–728) Capsular joint Synovitis/Tenosynovitis (Calcific tendinitis, Stenosing tenosynovitis, Trigger finger, DeQuervain's syndrome) · Transient synovitis · Ganglion cystvillonodular synovitis (Giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath)BursopathyBursitis (Olecranon, Prepatellar, Trochanteric, Subacromial) · Synovial cyst (Baker's cyst) · Calcific bursitisNoncapsular joint upper limb (Adhesive capsulitis of shoulder, Impingement syndrome Rotator cuff tear, Golfer's elbow, Tennis elbow)lower limb (Iliotibial band syndrome, Patellar tendinitis, Achilles tendinitis, Calcaneal spur, Metatarsalgia) · Bone spurNonjoint M: JNT
anat(h/c, u, t, l)/phys
noco(arth/defr/back/soft)/cong, sysi/epon, injr
proc, drug(M01C, M4)
Categories:- Soft tissue disorders
- Bursae
- Medicine stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.