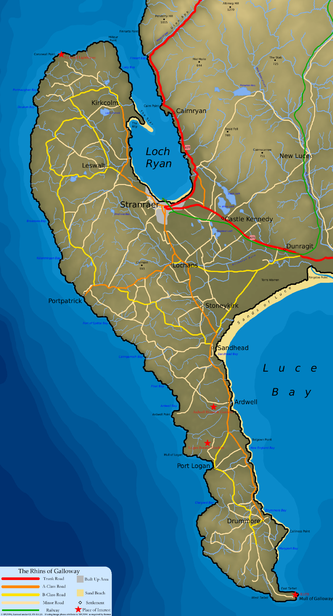
- Rhins of Galloway
-
Not to be confused with Rinns of Islay.
The Rhins of Galloway (also known as The Rhins; and can be spelt The Rhinns; Scottish Gaelic: Na Rannaibh [1]) is a hammer-head peninsula in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland. Stretching more than 25 miles (40 km) from north to south, its southern tip is the Mull of Galloway, the southernmost point of Scotland.
The principal settlements are Stranraer at the head of Loch Ryan and the small tourist village of Portpatrick on the west coast, other villages are dotted up and down the peninsula, including Kirkcolm, Leswalt, Lochans, and in the South Rhins; Stoneykirk, Sandhead, Ardwell and Drummore.
Herbert Maxwell[1] defines "Rhinns" as rionn, rinn, meaning a point or promontory.
Contents
Geography and climate
The peninsula is bounded on its west coast by the North Channel and by Loch Ryan and Luce Bay in the east. With around 50 miles (80 km) of coastline running from Stranraer in the north to Torrs Warren in the south the land is heavily influenced by the seas. The coastal landscape varies; with the western coast generally having steep rugged cliffs and occasional inlets, which contrasts with the calmer eastern coast, with its sandy beaches and softer landscape.
Sitting on the west coast of Scotland receiving the westerlies from the Atlantic the area receives a large amount of rainfall (around 1000 mm annually); this has led to the peninsula being principally used for farming, with the relatively flat land offering good dairy and beef production. Due to the seas very much 'surrounding' the land the area sees a significant effect of the North Atlantic drift, which ensures that the land is cooled in the summer and warmed in the winter, producing a stabilising effect on the temperatures. Severe frosts are therefore minimised and this allows the area to play host to numerous tropical palms and flora which otherwise could not exist this far north. Examples of these tropical plants can be seen at Logan Botanical Gardens.
 Tree Ferns at Logan Botanic Gardens adds a tropical feel to the area
Tree Ferns at Logan Botanic Gardens adds a tropical feel to the area
The natural geography of the Rhins has led directly to the use of the area for development, with the entire peninsula acting as a huge breakwater from the currents of the North Channel and to a lesser extent the Atlantic. This creates relatively calm and safe waters in Loch Ryan and Luce Bay which can be utilised. This is most easily shown with the ferries that sail to Belfast and Larne, which were originally based at Portpatrick. As the ships became larger they required larger protective harbours and the exposed Portpatrick could no longer fulfil the needs and so they moved to the shelter of Loch Ryan from where they still sail today.
The southernmost point of the Rhinns is also the southernmost point in Scotland, The Mull of Galloway. Here the land and rocky cliffs support a diverse range of animals and plants, with the mull area designated a site of special scientific interest and it has become a RSPB nature reserve. Razorbills, Guillemots and Puffins are just three of the bird species which nest on the steep cliffs.
Just north of the Mull the land narrows significantly, forming two bays (the East and West Tarbets), here in ancient times boats were brought ashore and moved across the thin strip of land by man power, with the aid of log rollers and lubrication. This large effort to cross the land bridge was all in an attempt to avoid navigation around the Mull and its dangerous currents.
The Southern Upland Way begins in the Rhins at Portpatrick and winds its way through the area on its long journey east across Scotland to its finish at Cockburnspath in the east.
 Cliffs at the Mull of Galloway
Cliffs at the Mull of Galloway
History and settlements
Having been settled from ancient times, the area has a long history, forming part of the western kingdoms that collectively ruled most of western Scotland, Ireland, the Isle of Man and Wales. The Novantae Celtic tribe was based in the Rhinns area and were known to the Romans as trading partners.
Subsistence, Crofting, lifestyles are likely to have been dominant throughout much of the peninsula's history. Farming would have been practised to satisfy the needs of the tenants and, later on, the estates. Fishing would have generally been practised on a local scale for local consumption rather than export. Due to the very sparse populations that lived in the area it was not until the Industrial Revolution that changes from a basic subsistence crofting lifestyle would be noted.
Resources in the area were traditionally used locally and increasingly exported. Salt Pans on the western coast of the peninsula were used for centuries as a local source of salt. Kelp harvesting became increasingly popular, both for local uses and also exported for use in chemical production. Sands, silts and gravels, common to all glaciated alluvial areas were frequently quarried.
 Port Kale and Port Mora Bays, near Portpatrick
Port Kale and Port Mora Bays, near Portpatrick
As communications improved the wealth of the area improved, with the sea links to Ireland, Glasgow & Liverpool both allowing the export of local farming produce (thus encouraging farming for production rather than subsistence) and also import of materials and goods not common to the area. The importance of the area's proximity to Ireland led to significant infrastructure being developed, most notably the link to the railway network, which was laid to Portpatrick to ensure a fast passage for the mail boat to Donaghadee. As the ships which served the North Channel route increased in size it became more difficult for Portpatrick to offer a safe harbour, with the shipping routes eventually moving in 1849 to the calmer waters of Stranraer in Loch Ryan.
During the Second World War the area became an important station for anti-U-Boat activities, with flying boats operating from the Loch side of the peninsula at RAF Station Wig Bay, as well as RAF Station Stranraer. RAF Corsewall operated north of Kirkcolm and was mainly used as a training school for flying boats. The bombing range in Luce Bay was used extensively throughout the second world war, with facilities based at West Freugh and Drummore
In modern times the peninsula consists of a patchwork of farms running the full length of the land. Increasingly the area is diversifying into tourism as small scale farming becomes less economically viable. The natural beauty of the area, with its long rugged coastline and numerous small bays is ideal for attracting tourists. The relatively sparse population is also a key asset, in a time when many tourist locations are suffering over popularity. The natural beauty of the area saw the BBC deciding to film the drama Two Thousand Acres of Sky in the village of Port Logan.
Sites of interest in and around the Rhinns include:
- Corsewall Lighthouse, sitting at the northern end of the peninsula, it is now a four star hotel
- Lochnaw Castle near Leswalt which is the ancestral seat of Clan Agnew
- West Freugh RAF station near Stoneykirk which was (and to a lesser extent still is) used by the RAF as an airfield for bombing target practice out in Luce Bay
- Dunskey Castle near Portpatrick, built in the 16th century by the Adairs of Kilhilt, with now only the remains remaining
- Port Logan village, where the BBC drama Two Thousand Acres of Sky was filmed, and the nearby Logan outstation of the Royal Botanic Garden, Edinburgh.
- Ardwell House & Gardens near Ardwell, the estate house and gardens of Ardwell estates
- Kirkmadrine Stones near Sandhead, earliest Christian activity on the peninsula, with the site established in the 5th century.
- The Mull of Galloway, lighthouse and RSPB nature reserve
See also
External links
References
- ^ The Places Names of Galloway (Glasgow, 1930) p.234
Traditional provinces and districts of Scotland Major districts (former counties, provincial lordships and rural deaneries) The Aird · Annandale · Angus · Argyll · Atholl · Boyne · Buchan · Badenoch · Breadalbane · Caithness · Carrick · Clydesdale (or Strathclyde) · Cowal · Cunningham · Desnes · Eskdale · Farines · Fife · Fothriff · Galloway · Garioch · Garmoran · The Glenkens · Gowrie · Kintyre · Knapdale · Kyle · Lauderdale · Lennox · Liddesdale · Lochaber · Lorn · Lothian · Mar · Mearns · Menteith · Merse · Moray · Nithsdale · The Rhinns · Ross (Easter and Wester) · Stormont · Strathavon · Strathbogie · Strathearn · Strathgryfe · Strathnaver · Strathspey · Sutherland · Teviotdale · Tweeddale
Minor districts Applecross · Appin · Ardgour · Ardmeanach · Ardnamurchan · Assynt · Avondale · Balquhidder · Benderloch · The Black Isle · Braemar · Coigach · Cromar · Cromdale · Douglasdale · Durness · Eddrachilles · Enzie · Ettrickdale · Ewesdale · Formartine · Gairloch · Glen Albyn · Glen Almond · Glen Cassley · Glen Clova · Glen Dochart · Glenelg · Glen Esk · Glengarry · Glen Lethnot · Glen Lyon · Glen Moriston · Glen Orchy · Glen Prosen · Glenshee · Glen Spean · Glen Urquhart · Gruinard · Howe of Fife · Howe of the Mearns · Kintail · Kintyre · Knoydart · Lochalsh · Loch Broom · Locheil · The Machars · Midmar · Moidart · Morar · Morven · Muir of Ord · Rannoch Moor · Rhinns of Kells · Strathallan · Strathardle · Strathbran · Strathbraan · Strathcarron (Forth) · Strathcarron (Oykel) · Strathconon · Strathdearn · Strathdeveron · Strathdee (Deeside) · Strathdon · Strathfarrar · Strath Gartney · Strathglass · Strathisla · Strathmore · Strath of Kildonan · Strath Oykel · Strath Tay · Strathyre · Sunart · Trossachs
Insular districts
For smaller islands, usually districts in their own right, see List of Scottish islandsBorder Areas Places in the Rhins of Galloway, Scotland North to SouthKirkcolm • Cairnryan • Leswalt • Stranraer • Castle Kennedy • Lochans • Portpatrick • Stoneykirk • Sandhead • Ardwell • Port Logan • Kirkmaiden • Drummore • Mull of Galloway • ClachanmoreCategories:- Places in the Rhins
- Peninsulas of Scotland
- Dumfries and Galloway
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.