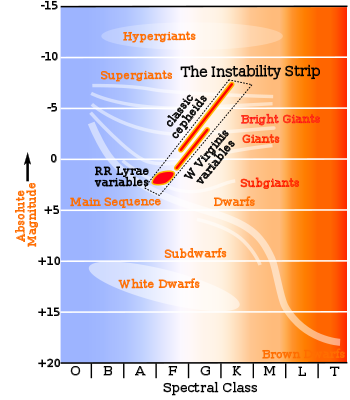
- Instability strip
-
The Instability strip is a nearly vertical region in the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram which is occupied by pulsating variable stars (including RR Lyrae variable, Cepheid variable, W Virginis variable, ZZ Ceti variable, RV Tauri variable, Delta Scuti variable, SX Phoenicis variable and rapidly oscillating Ap stars).[1]
The instability strip intersects the main sequence in the region of A and F stars (1–2 solar mass) and extends upwards almost vertically (slightly inclined to the right) to the highest luminosities. The lower part of instability strip appears as the Hertzsprung gap on the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram.
Pulsations
Stars in the instability strip pulsate due to He III (doubly ionized helium). In normal A-F-G stars He is neutral in the stellar photosphere. Deeper below the photosphere, at about 25,000–30,000K, begins the He II layer (first He ionization). Second ionization (He III) starts at about 35,000–50,000K.
When the star contracts, the density and temperature of the He II layer increase. He II starts to transform to He III (second ionization). Opacity increases and the energy flux from the interior of the star is effectively absorbed. The temperature of the layer increases and it starts to expand. After expansion, density and temperature decrease and He III begins to recombine into He II. The outer layers contract and the cycle starts from the beginning.
The phase shift between a star's radial velocity pulsations and brightness variability depends on the distance of He II zone from the stellar surface in the stellar atmosphere.
References
- ^ "Cepheid instability strip". A Dictionary of Astronomy. encyclopedia.com. http://www.encyclopedia.com/doc/1O80-Cepheidinstabilitystrip.html. Retrieved 2010-03-28.
Categories:- Hertzsprung-Russell classifications
- Stellar evolution
- Astronomy stubs
- Variable star stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.