- NEAR Shoemaker
-
This article is about the robotic space probe named NEAR Shoemaker. For the type of asteroid, see Near-Earth asteroid. For the public alarm system tested by the U.S. government in the 1950s and 1960s, see National Emergency Alarm Repeater.

Artist's conception of the NEAR Shoemaker spacecraftFlyby of 253 Mathilde Satellite of 433 Eros Orbital insertion date 2000-02-14 at 433 Eros[1] Orbits 230 orbits of 433 Eros[1] Launch date 20:43:27 UTC
1996-02-17Launch vehicle Booster: Delta 7925-8
Upper Stage: Star 48Launch site Cape Canaveral Air Force Station[1] Orbital decay Never - landed on 433 Eros 2001-02-12[1] COSPAR ID 1996-008A Homepage http://near.jhuapl.edu/ Mass Launch: ~800 kg
On orbit dry: 487 kgPower Instruments: 81 w
Total: 1800 wThe Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous - Shoemaker (NEAR Shoemaker), renamed after its 1996 launch in honor of planetary scientist Eugene M. Shoemaker, was a robotic space probe designed by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory for NASA to study the near-Earth asteroid Eros from close orbit over a period of a year. The mission succeeded in closing in with the asteroid and orbited several times around it, finally terminating by touching down on the asteroid on 12 February 2001.
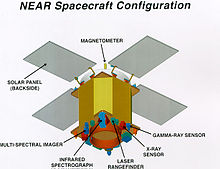
The primary scientific objective of NEAR was to return data on the bulk properties, composition, mineralogy, morphology, internal mass distribution and magnetic field of Eros. Secondary objectives include studies of regolith properties, interactions with the solar wind, possible current activity as indicated by dust or gas, and the asteroid spin state. This data will be used to help understand the characteristics of asteroids in general, their relationship to meteorites and comets, and the conditions in the early solar system. To accomplish these goals, the spacecraft was equipped with an X-ray/gamma ray spectrometer, a near-infrared imaging spectrograph, a multi-spectral camera fitted with a CCD imaging detector, a laser rangefinder, and a magnetometer. A radio science experiment was also performed using the NEAR tracking system to estimate the gravity field of the asteroid. The total mass of the instruments was 56 kg, and they required 81 W power.
Contents
Mission profile
- Launch date/time: 1996-02-17 at 20:43:27 UTC
- On-orbit dry mass: 487 kg
- Nominal power output: 1800 W
Summary
The primary goal of the mission was to study the near Earth asteroid 433 Eros from orbit for approximately one year. Eros is an S-type asteroid approximately 13 × 13 × 33 km in size, the second largest near-Earth asteroid. Initially the orbit was circular with a radius of 200 km. The radius of the orbit was brought down in stages to a 50 × 50 km orbit on 30 April 2000 and decreased to 35 × 35 km on July 14, 2000. The orbit was raised over succeeding months to a 200 × 200 km orbit and then slowly decreased and altered to a 35 × 35 km retrograde orbit on December 13, 2000. The mission ended with a touchdown in the "saddle" region of Eros on February 12, 2001.
Some scientists claim that the ultimate goal of the mission was to link Eros, an asteroidal body, to meteorites recovered on Earth. With sufficient data on chemical composition, a causal link could be established between Eros and other S-type asteroids, and those meteorites believed to be pieces of S-type asteroids (perhaps Eros itself). Once this connection is established, meteorite material can be studied with large, complex, and evolving equipment, and the results extrapolated to bodies in space. NEAR-Shoemaker did not prove or disprove this link to the satisfaction of scientists. However, it is undeniable that NEAR data advanced the field of asteroidal studies tremendously.
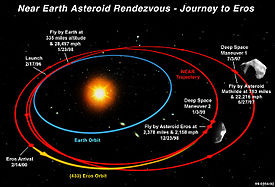
The journey to Eros
After launch on a Delta 7925-8 (a Delta II launch vehicle with nine strap-on solid-rocket boosters and a Star 48 (PAM-D) third stage) and exit from Earth orbit, NEAR entered the first part of its cruise phase. NEAR spent most of the cruise phase in a minimal activity "hibernation" state, which ended a few days before the flyby of the 61 km diameter asteroid 253 Mathilde.
On June 27, 1997 the spacecraft flew within 1200 km of Mathilde at 12:56 UT at 9.93 km/s, returning imaging and other instrument data. The flyby produced over 500 images which covered 60% of Mathilde's surface,[2] as well as gravitational data allowing calculations of Mathilde's dimensions and mass.[3]
On July 3, 1997 NEAR executed the first major deep space maneuver, a two-part burn of the main 450 N thruster. This decreased the velocity by 279 m/s and lowered perihelion from 0.99 AU to 0.95 AU. The Earth gravity assist swingby occurred on January 23, 1998 at 7:23 UT. The closest approach was 540 km, altering the orbital inclination from 0.5 to 10.2 degrees, and the aphelion distance from 2.17 to 1.77 AU, nearly matching those of Eros. Instrumentation was active at this time.
Failure of first attempt at orbital insertion
The first of four scheduled rendezvous burns was attempted on December 20, 1998 at 22:00 UT. The burn sequence was initiated but immediately aborted. The spacecraft subsequently entered safe mode and began tumbling. The spacecraft's thrusters were fired thousands of times during the anomaly which expended 29 kg of propellant reducing the program's propellant margin to zero. This anomaly almost resulted in the complete loss of the spacecraft due to the loss of solar orientation and subsequent battery drain. Contact between the spacecraft and mission control was not re-established for over 24 hours. The full root cause has not been determined but software programming errors and operational errors contributed to the severity of the anomaly.[4]
The original mission plan called for the four burns to be followed by an orbit insertion burn on January 10, 1999, but the abort of the first burn and loss of communication made this impossible. A new plan was put into effect in which NEAR flew by Eros on December 23, 1998 at 18:41:23 UT at a speed of 965 m/s and a distance of 3827 km from the center of mass of Eros. Images of Eros were taken by the camera, data were collected by the near IR spectrograph, and radio tracking was performed during the flyby. A rendezvous maneuver was performed on January 3, 1999 involving a thruster burn to match NEAR's orbital speed to that of Eros. A hydrazine thruster burn took place on January 20 to fine-tune the trajectory. On August 12 a two-minute thruster burn slowed the spacecraft velocity relative to Eros to 300 km/h.
Orbital insertion
Orbital insertion around Eros occurred on 14 February 2000 at 15:33 UT (10:33 AM EST) after NEAR completed a 13 month heliocentric orbit which closely matched the orbit of Eros. A rendezvous maneuver was completed on February 3 at 17:00 UT, slowing the spacecraft from 19.3 to 8.1 m/s relative to Eros. Another maneuver took place on February 8 increasing the relative velocity slightly to 9.9 m/s. Searches for satellites of Eros took place on January 28, and 4 and 9 February, none were found. The scans were for scientific purposes and to mitigate any chances of collision with a satellite. NEAR went into a 321 x 366 km orbit around Eros on February 14. The orbit was slowly decreased to a 35 km circular polar orbit by July 14. NEAR remained in this orbit for 10 days and then was backed out in stages to a 100 km circular orbit by September 5, 2000. Maneuvers in mid-October led to a flyby of Eros within 5.3 km of the surface at 07:00 UT on 26 October.
Orbits and landing
 Eros asteroid from approximately 250 meters altitude (area in image is roughly 12 meters across [1]). This image was taken during NEAR's descent to the surface of the asteroid.
Eros asteroid from approximately 250 meters altitude (area in image is roughly 12 meters across [1]). This image was taken during NEAR's descent to the surface of the asteroid.
Following the flyby NEAR moved to a 200 km circular orbit and shifted the orbit from prograde near-polar to a retrograde near-equatorial orbit. By December 13, 2000 the orbit was shifted back to a circular 35 km low orbit. Starting on January 24, 2001 the spacecraft began a series of close passes (5 to 6 km) to the surface and on January 28 passed 2 to 3 km from the asteroid. The spacecraft then made a slow controlled descent to the surface of Eros ending with a touchdown just to the south of the saddle-shaped feature Himeros on February 12, 2001 at approximately 20:01 UT (3:01 p.m. EST). To the surprise of the controllers, the spacecraft was undamaged and operational after the landing at an estimated speed of 1.5 to 1.8 meters per second (thus becoming the first spacecraft to soft-land on an asteroid). After receiving an extension of antenna time on the Deep Space Network, the spacecraft's gamma-ray spectrometer was reprogrammed to collect data on Eros' composition from a vantage point about four inches from the surface where it was ten times more sensitive than when it was used in orbit.[5]
At 7 p.m. EST on February 28, 2001 the last data signals were received from NEAR Shoemaker before it was shut down. A final attempt to communicate with the spacecraft on December 10, 2002 was unsuccessful. This was likely due to the extreme -279 °F (-173 °C, 100 K) conditions the probe experienced while on Eros.[6]
Spacecraft and subsystems
The spacecraft has the shape of an octagonal prism, approximately 1.7 m on a side, with four fixed gallium arsenide solar panels in a windmill arrangement, a fixed 1.5 m X-band high-gain radio antenna with a magnetometer mounted on the antenna feed, and an X-ray solar monitor on one end (the forward deck), with the other instruments fixed on the opposite end (the aft deck). Most electronics were mounted on the inside of the decks. The propulsion module was contained in the interior.
The craft was three-axis stabilized and used a single bipropellant (hydrazine / nitrogen tetroxide) 450 newton (N) main thruster, and four 21 N and seven 3.5 N hydrazine thrusters for propulsion, for a total delta-V potential of 1450 m/s. Attitude control was achieved using the hydrazine thrusters and four reaction wheels. The propulsion system carried 209 kg of hydrazine and 109 kg of NTO oxidizer in two oxidizer and three fuel tanks.
Power was provided by four 1.8 by 1.2 meter gallium arsenide solar panels which could produce 400 watts at 2.2 AU (329,000,000 km), NEAR's maximum distance from the Sun, and 1800 W at one AU (150,000,000 km). Power was stored in a nine ampere-hour, 22-cell rechargeable super nickel-cadmium battery.
Spacecraft guidance was achieved through the use of a sensor suite of five digital solar attitude detectors, an inertial measurement unit, (IMU) and a star tracker camera pointed opposite the instrument pointing direction. The IMU contained hemispherical resonator gyroscopes and accelerometers. Four reaction wheels (arranged so that any three can provide complete three-axis control) were used for normal attitude control. The thrusters were used to dump angular momentum from the reaction wheels, as well as for rapid slew and propulsive maneuvers. Attitude control was to 0.1 degree, line-of-sight pointing stability is within 50 microradians over one second, and post-processing attitude knowledge is to 50 microradians.
The command and data handling subsystem was composed of two redundant command and telemetry processors and solid state recorders, a power switching unit, and an interface to two redundant 1553 standard data buses for communications with other subsystems. The solid state recorders are constructed from 16 Mbit IBM Luna-C DRAMs. One recorder has 1.1 gigabits of storage, the other has 0.67 gigabits.
The NEAR mission was the first launch of NASA's Discovery Program, a series of small-scale spacecraft designed to proceed from development to flight in under three years for a cost of less than $150 million. The construction, launch, and 30 day cost for this mission is estimated at $122 million. The final total mission cost was $224 million which consisted of $124.9 million for spacecraft development, $44.6 million for launch support and tracking, and $54.6 million for mission operations and data analysis.[1]
References
- ^ a b c d e "NEAR: FAQ". Applied Physics Lab. http://near.jhuapl.edu/intro/faq.html.
- ^ Williams, David R. (December 18, 2001). "NEAR Flyby of Asteroid 253 Mathilde". NASA. http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/planetary/mission/near/near_mathilde.html. Retrieved 2006-08-10.
- ^ D. K. Yeomans et al (1997). "Estimating the mass of asteroid 253 Mathilde from tracking data during the NEAR flyby". Science 278 (5346): 2106–9. Bibcode 1997Sci...278.2106Y. doi:10.1126/science.278.5346.2106. PMID 9405343. http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/278/5346/2106. Retrieved 2007-08-29.
- ^ "The NEAR Rendezvous Burn Anomaly of December 1998". Final Report of the NEAR Anomaly Review Board. November 1999. http://klabs.org/richcontent/Reports/Failure_Reports/NEAR_Rendezvous_Burn.pdf. Retrieved 2009-08-18.
- ^ Worth, Helen (2001-02-28). "The End of an Asteroidal Adventure: NEAR Shoemaker Phones Home for the Last Time". Applied Physics Lab. http://near.jhuapl.edu/news/flash/01feb28.html.
- ^ "NEAR Shoemaker's Silent Treatment". Applied Physics Laboratory. 2001-02-23. http://near.jhuapl.edu/news/flash/02dec12_1.html.
- Text adapted from public domain NASA webpage.
- Trombka JI, Squyres SW, Bruckner J, Boynton WV, Reedy RC, McCoy TJ, Gorenstein P, Evans LG, Arnold JR, Starr RD, Nittler LR, Murphy ME, Mikheeva I, McNutt RL, McClanahan TP, McCartney E, Goldsten JO, Gold RE, Floyd SR, Clark PE, Burbine TH, Bhangoo JS, Bailey SH, Petaev M (2000). "The elemental composition of asteroid 433 Eros: Results of the NEAR-Shoemaker x-ray spectrometer". Science 289 (5487): 2101–2105. Bibcode 2000Sci...289.2101T. doi:10.1126/science.289.5487.2101. PMID 11000107.
- Zuber MT, Smith DE, Cheng AF, Garvin JB, Aharonson O, Cole TD, Dunn PJ, Guo YP, Lemoine FG, Neumann GA, Rowlands DD, Torrence MH (2000). "The shape of 433 Eros from the NEAR-Shoemaker Laser Rangefinder". Science 289 (5487): 2097–2101. Bibcode 2000Sci...289.2097Z. doi:10.1126/science.289.5487.2097. PMID 11000106.
- Yeomans DK, Antreasian PG, Barriot JP, Chesley SR, Dunham DW, Farquhar RW, Giorgini JD, Helfrich CE, Konopliv AS, McAdams JV, Miller JK, Owen WM, Scheeres DJ, Thomas PC, Veverka J, Williams BG (2000). "Radio science results during the NEAR-Shoemaker spacecraft rendezvous with Eros". Science 289 (5487): 2085–2088. Bibcode 2000Sci...289.2085Y. doi:10.1126/science.289.5487.2085. PMID 11000104.
External links
- NEAR Shoemaker Profile by NASA's Solar System Exploration
- NSSDC Master Catalog: Spacecraft - NEAR Shoemaker
- NASA JPL: NEAR Shoemaker, Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous
- Official NEAR Mission Site (Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory)
Spaceflight missions to asteroids Flybys Orbiters Landers Planned Hayabusa 2 (lander) · OSIRIS-REx (lander)Proposed Don Quijote · MarcoPolo-R · SIMONECancelled AGORA · MAOSEP · VESTA · CRAF · Marco PoloItalics indicate active missions. ← 1995 · Orbital launches in 1996 · 1997 → STS-72 (SPARTAN-206) | PAS-3R · MEASAT-1 | Koreasat 2 | Kosmos 2327 | Gorizont #43L | Palapa C1 | N-Star B | Intelsat 708 | NEAR Shoemaker | Kosmos 2328 · Kosmos 2329 · Kosmos 2330 · Gonets-D1 #1 · Gonets-D1 #2 · Gonets-D1 #3 | Gran' #44L | Soyuz TM-23 | STS-75 (TSS-1R) | Polar | REX II | Intelsat 707 | Kosmos 2331 | IRS-P3 | STS-76 | USA-117 | Inmarsat-3 F1 | Astra 1F | MSAT-1 | Priroda | MSX | Kosmos 2332 | USA-118 | BeppoSAX | Progress M-31 | USA-119 · USA-120 · USA-121 · USA-122 · USA-123 · USA-124 | Kometa #18 | Palapa C2 · Amos-1 | MSTI-3 | STS-77 (SPARTAN-207 · IAE · PAMS-STU) | Galaxy 9 | Gorizont #44L | Cluster F1 · Cluster F2 · Cluster F3 · Cluster F4 | Intelsat 709 | STS-78 | Kobal't | TOMS-EP | USA-125 | Apstar 1A | Arabsat 2A · Turksat 1C | USA-126 | USA-127 | Progress M-32 | Télécom 2D · Italsat 2 | Molniya 1-79 | Midori · Fuji 2 | Soyuz TM-24 | Chinasat-7 | FAST | Interbol 2 · Maigon 5 · Victor | Kosmos 2333 | Kosmos 2334 · UNAMSAT-2 | Inmarsat-3 F2 | GE-1 | EchoStar II | USA-128 | STS-79 | Ekspress-6 | FSW-17 | Molniya 3-62 | HETE · SAC-B | Mars Global Surveyor | Arabsat 2B · MEASAT-2 | Mars 96 | STS-80 (WSF · ORFEUS-SPAS) | Progress M-33 | Hot Bird 2 | Mars Pathfinder (Sojourner) | Kosmos 2335 | Inmarsat-3 F3 | Kosmos 2336 | USA-129 | Bion #11Payloads are separated by bullets ( · ), launches by pipes ( | ). Manned flights are indicated in bold text. Uncatalogued launch failures are listed in italics. Payloads deployed from other spacecraft are denoted in brackets. Categories:- NASA probes
- Discovery program
- 1996 in spaceflight
- Spacecraft launched by Delta II rockets
- Comet/Asteroid missions
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.